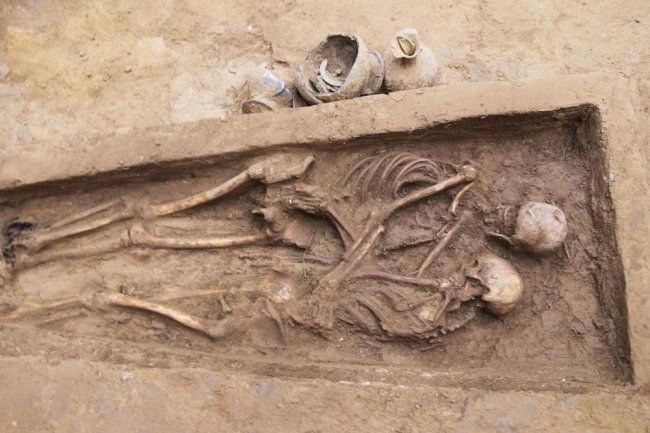
Archaeologists recently published a study of the tomb of cuddling lovers, dating to the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534), more than 1,600 years ago, according to Jilin University.
In 2020, the tomb was initially unearthed in Datong City, Shanxi Province, north China. The couple was buried in the same grave in a single casket. The man had his arms around his lover’s waist, while the female had her head on his shoulder and was cuddled against his chest. A silver ring was also discovered on her left hand’s ring finger, according to the researcher.
Further skeletal examination indicated that the male tomb owner’s right arm had an unhealed infected fracture, whereas the female’s bones looked to be healthy. This finding suggests that the two may have killed themselves.
Despite the fact that numerous graves of embracing couples from the Northern Wei Dynasty have previously been unearthed in China, the new archaeological finding of the well-preserved one is quite rare, according to the research team.
According to the researchers, such tombs assist better explain social conceptions of human life and death, as well as attitudes toward love, during that era, when the cohabitation of different ethnic groups drove the emergence and dissemination of pluralistic ethos.
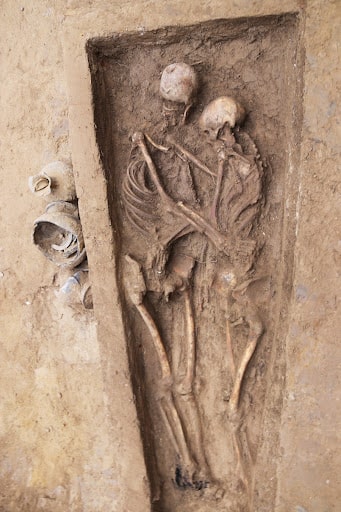
The ancient Datong region was a significant melting pot for different cultures at the period, with the trend of yearning and cherishing love blossoming. During the time of the Northern Wei Dynasty in north China, the female tomb owner’s finger ring was mostly used as a symbol of love or marriage rather than for adornment.
Tombs of embracing lovers date back over 6,000 years, including the Lovers of Valdarno in Italy and the Embracing Skeletons of Alepotrypa in Greece.
Researchers from home and abroad, including those from Datong Institute of Archaeology, Jilin University, and Xiamen University, collaborated on research and studies on the recently discovered tomb in Shanxi. This study’s findings were published in the journal International Journal of Osteoarchaeology.
Cover Photo: Photo taken on Aug. 5, 2020 shows the tomb of lovers hugging each other dating back to the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) unearthed in Datong City, north China’s Shanxi Province. (Xinhua)
















