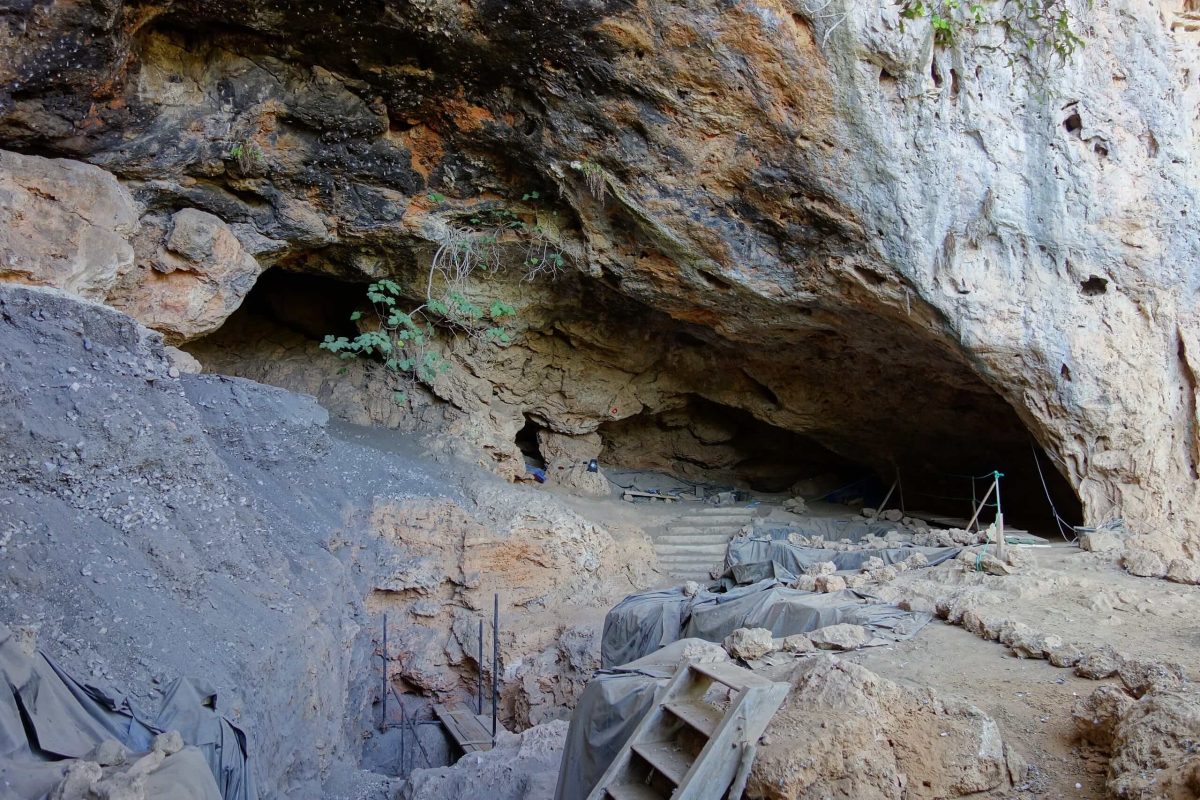
Morocco’s National Institute of Archaeology and Heritage has announced an important discovery that will enhance our understanding of ancient healing practices and shed light on humanity’s medical history. Researchers have found evidence of the use of medicinal herbs in the Grotte des Pigeons Cave in Tafoughalt, dating back 15,000 years.
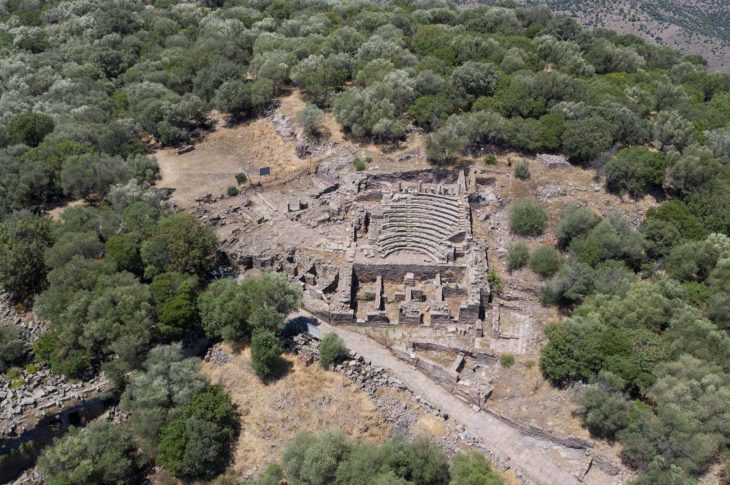
Since the cave of Taforalt, also known as the Grotte des Pigeons, discovered in 1908, there has been an ongoing series of excavations and researches at the site, which has provided archaeologists with new perspectives on the lives in prehistoric North Africa.
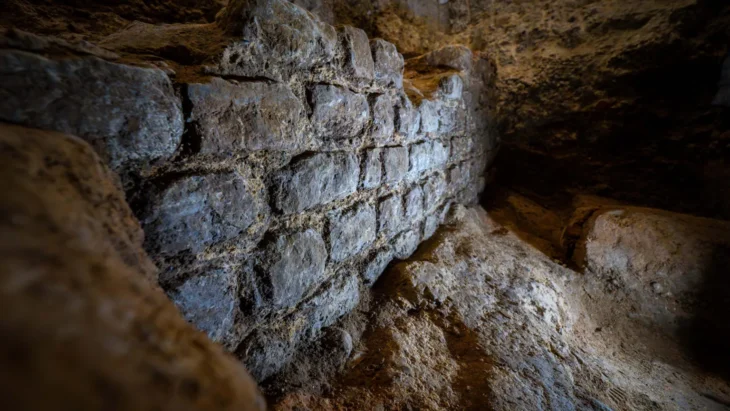
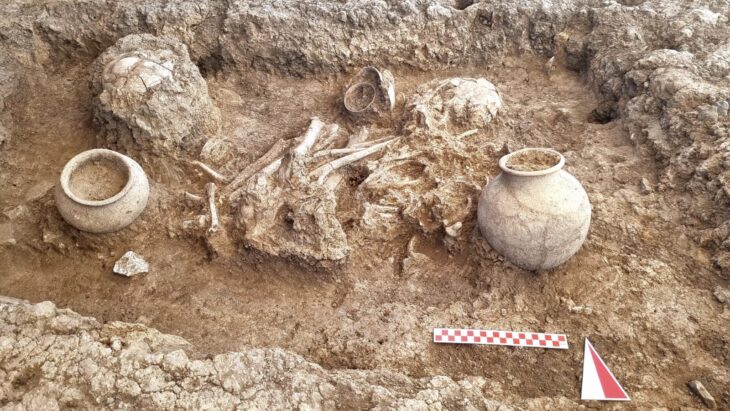
The site, which is regarded as North Africa’s oldest cemetery, was home to at least 34 Iberomaurusian skeletons from the later Stone Age (approximately 15,000 calendar years ago).
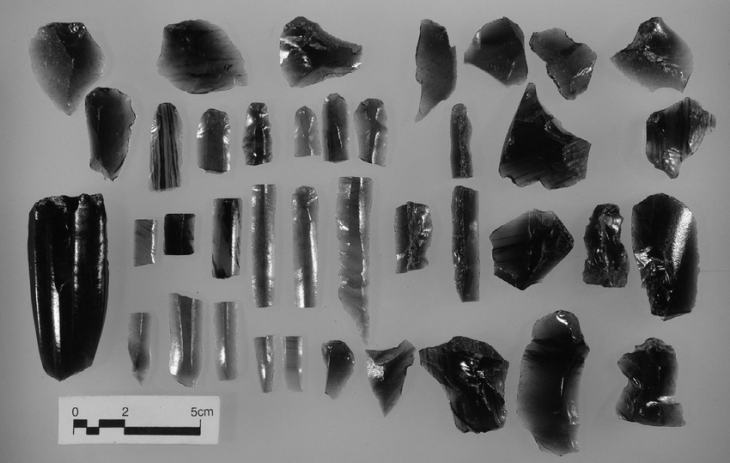
This new discovery highlights our ancestors’ inventiveness in using natural resources and deepens our understanding of ancient healing practices. The results of this important study were published in the journal Nature. The discovered herbs, particularly the “Ephedra” plant, form the cornerstone of this research.
In their study, the researchers investigated the presence and possible uses of Ephedra during the Late Pleistocene, based on the analysis of extraordinarily preserved plant macrofossils from archaeological deposits of about 15 thousand years old in a cave in northeastern Morocco.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Ephedra is a well-known medicinal plant, and the macro-remains of this plant associated with human activity discovered in this cave are the oldest ever recorded.
Ephedra plant’s fruits were found in a specific area of the cave, which was used for burial according to special funerary rituals. Direct radiocarbon dates on both Ephedra and the human remains indicate that they were contemporaneous.
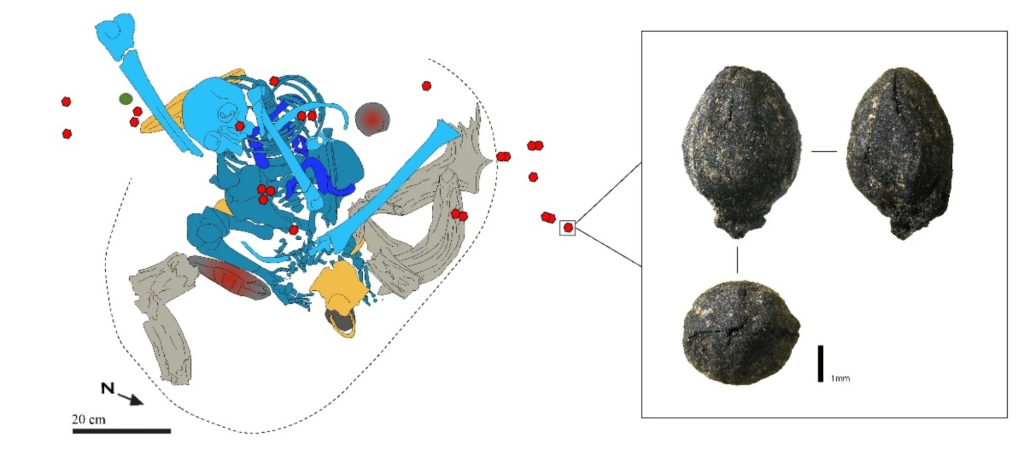
The researchers also interpreted the presence of Ephedra and its deposition at the burial site as evidence that this plant played an important role during funerary activities.
Studies indicate that human communities during that period relied on these herbs for therapeutic purposes, including treating colds and reducing bleeding.
It challenges accepted beliefs about the medical prowess of prehistoric people by proving that humans had comprehensive knowledge of how to benefit from plants 15,000 years ago.
Evidence of the oldest known surgical procedure was discovered in the same cave by earlier research, which found traces of surgery on a human skull. This suggests that the person who had the procedure survived and bore their suffering because of those herbs. Research indicates that this procedure was carried out using sophisticated methods, suggesting a high level of medical knowledge.
This discovery is more than just an archaeological find; it provides a better understanding of human abilities to use herbs for medicine, reshaping our perspectives on ancestral traditions. Understanding how these people lived in harmony with nature and developed new ways to treat diseases demonstrates humanity’s adaptability and creativity.
Source: Morales, J., Carrión Marco, Y., Cooper, J.H. et al. Late Pleistocene exploitation of Ephedra in a funerary context in Morocco. Sci Rep 14, 26443 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77785
Cover Image Credit: Grotte des Pigeons Cave. Wikipedia Commons