Archaeologists have found remnants of eight spices on a sandstone slab from an archaeological site in Vietnam, showing the early adoption of ingredients and techniques from South Asia.
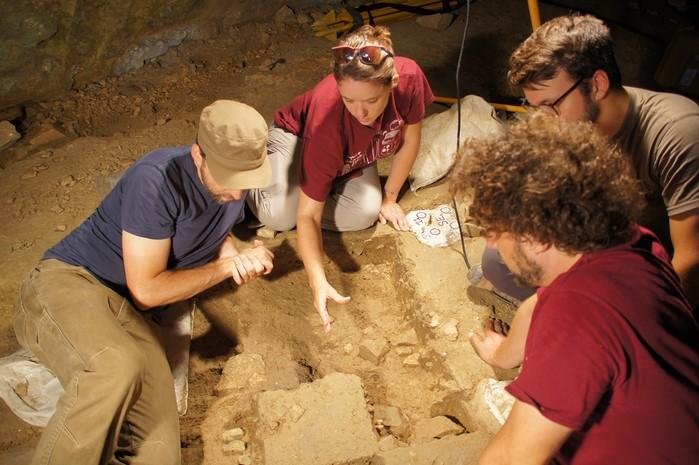
Unearthed in an ancient village in southern Vietnam, the cookware—roughly the size and shape of an anvil—was likely used to grind the spice and other ingredients familiar in today’s curries.
Dishes that are rich in flavor and aroma from combinations of spices such as earthy turmeric, warm cloves, and sharp ginger—commonly known as curries in the West—have starred in cuisines throughout South and Southeast Asia, from India to Indonesia, for centuries.
The discovery, reported today in Science Advances, marks the earliest known example of spice processing in mainland Southeast Asia.. It also suggests that millennia ago, visitors from India and Indonesia may have brought their culinary traditions to the region.
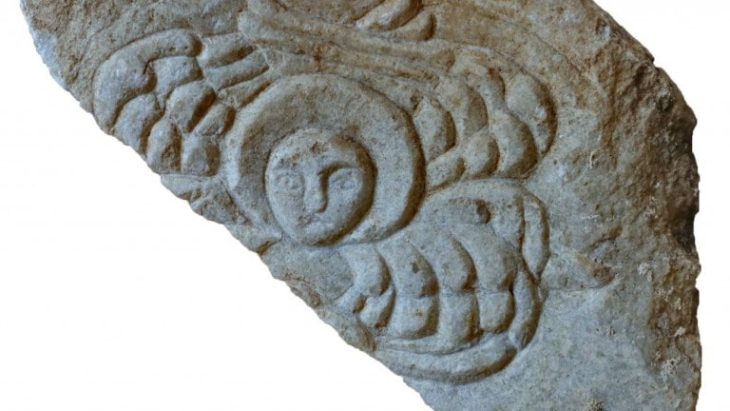
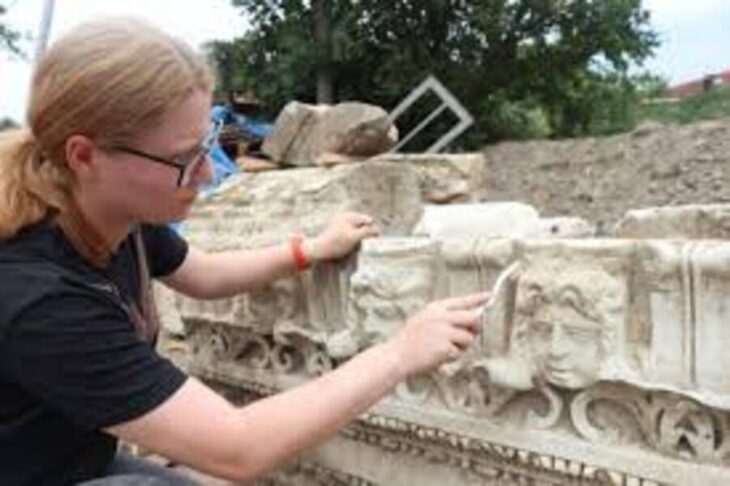
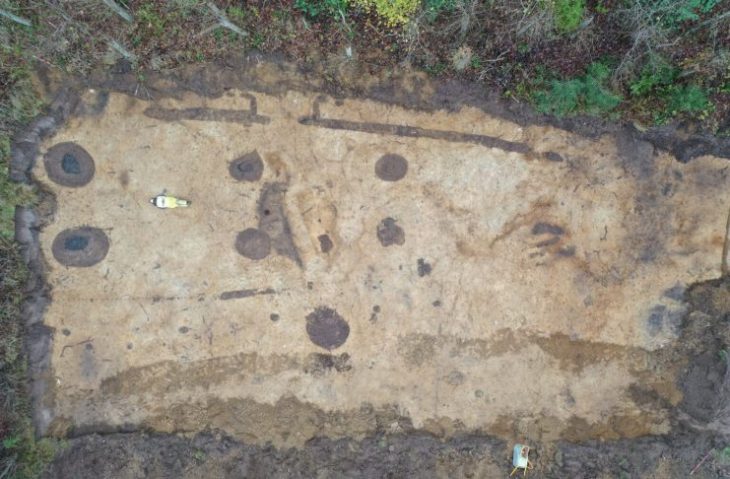
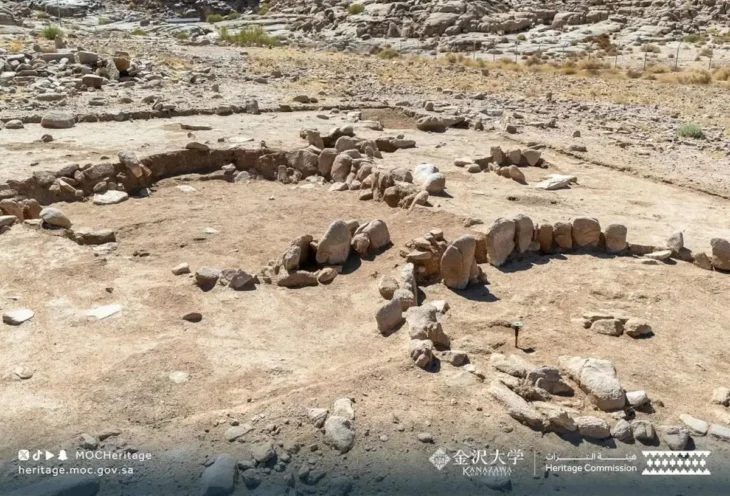
During their digs at the Oc Eo archaeological site in southern Vietnam, Hsiao-Chun Hung at the Australian National University in Canberra and her colleagues uncovered several sandstone grinding tools alongside remnants of spices.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
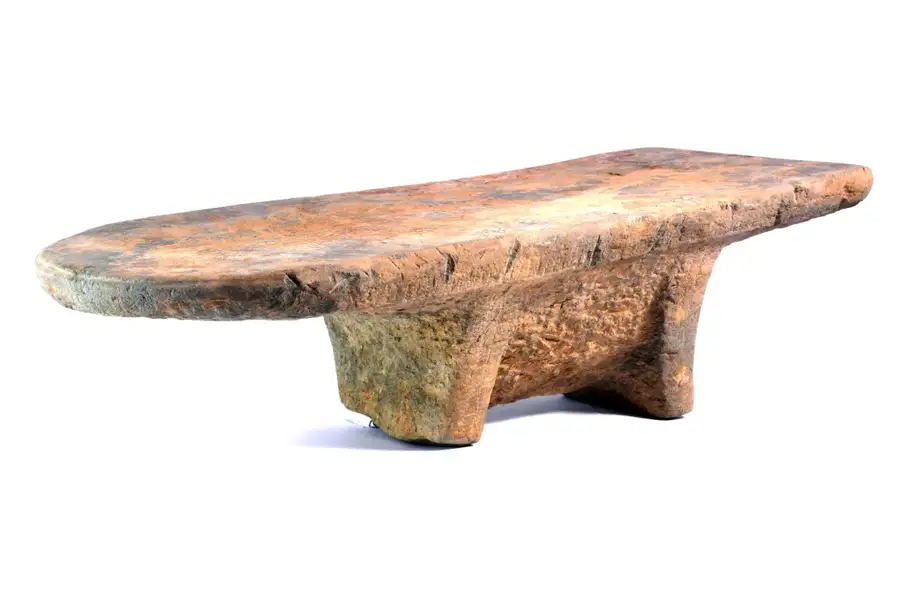

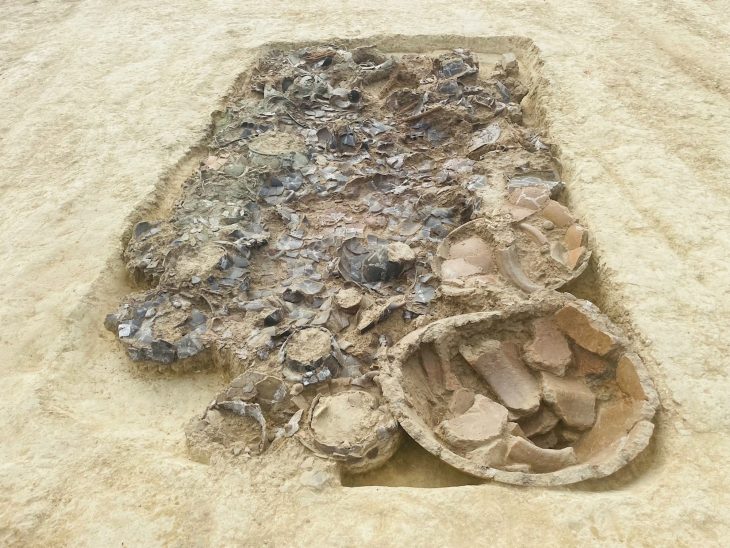
An analysis of 717 grains of starch recovered from the tools revealed the presence of eight different spices: turmeric, ginger, galangal, sand ginger, fingerroot, clove, nutmeg, and cinnamon. Many of the grains also showed signs of deformation, indicating that they had been damaged during grinding and resembled the starch granules found in modern curry powder.
Since Óc Eo was first excavated in the 1940s, it has yielded a large number of artifacts that suggest the city once lay at the crossroads of a vast trade network that spread as far as the Mediterranean Sea.
A maritime trade route that connected the Mediterranean Sea to China during the same time period as the renowned Silk Road has long been known to historians. The maritime route extended further south, connecting Southeast Asian, Iran, and modern-day Indian cultures. However, the majority of the evidence is based on written records, and the lack of physical evidence has made it difficult for researchers to verify these accounts.
“Before this study, we had only limited clues from ancient documents in India, China and Rome about the early spice trades,” says Australian National University archaeologist and study co-author Hsiao-Chun Hung. “However, this research is the first to confirm that these spices were indeed traded commodities that existed within the global maritime trading networks nearly 2,000 years ago.”
Though previous fragments discovered elsewhere predate the spices studied in the new study, the Óc Eo findings provide the first evidence that these spices were all used in Southeast Asia during this time period. The spice remains suggest that the stone mortars, pestles, and grinding slabs discovered there were most likely used for food preparation.