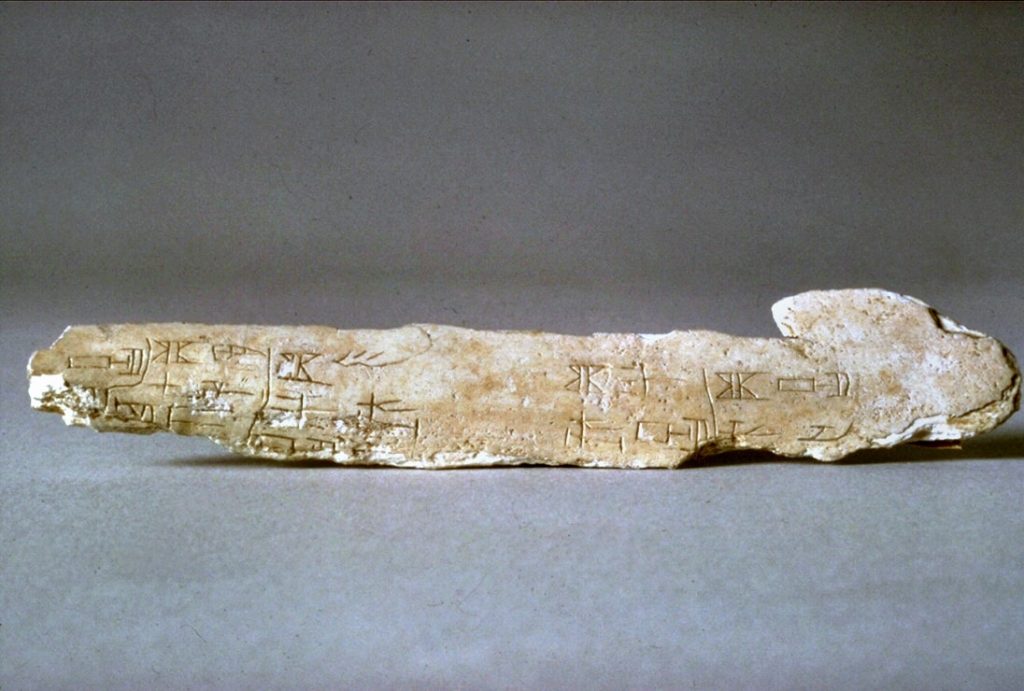
“Jiaguwen,” or the oracle bone inscriptions, are thought to be the earliest fully-developed characters as well as the source of the Chinese characters people use today.
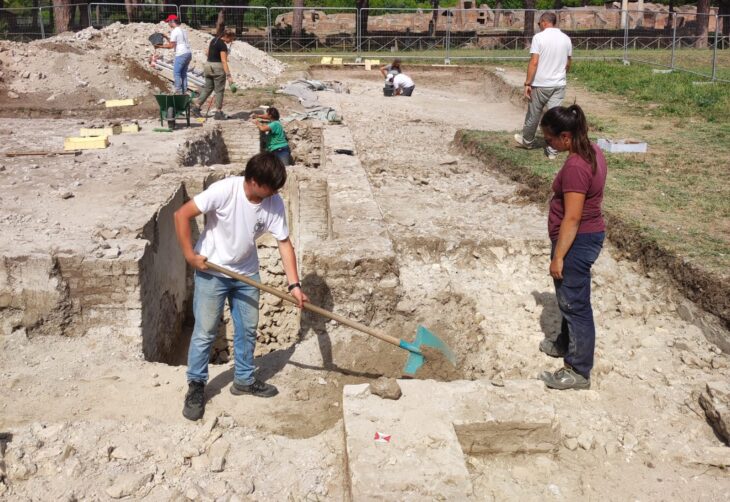
They were first discovered in 1899 at the Yin Ruins in Anyang, central China’s Henan province. They were so named because of their enigmatic “scratches” on pieces of animal bones and tortoise shells.
Dating back to China’s Shāng dynasty (1600-1046 B.C.), this ancient Chinese language was included in the UNESCO Memory of the World Register in 2017.
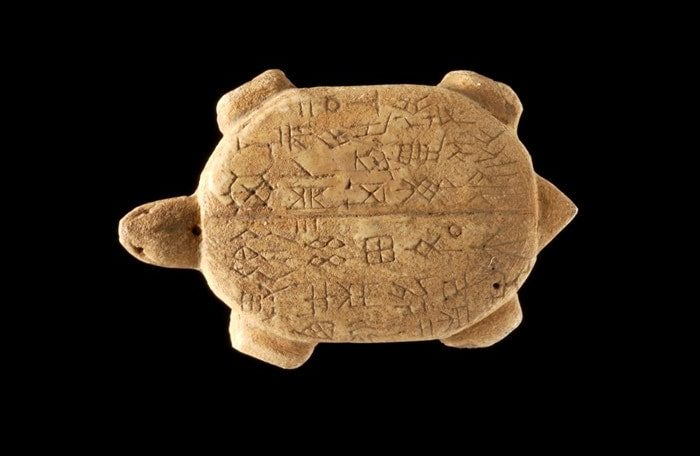
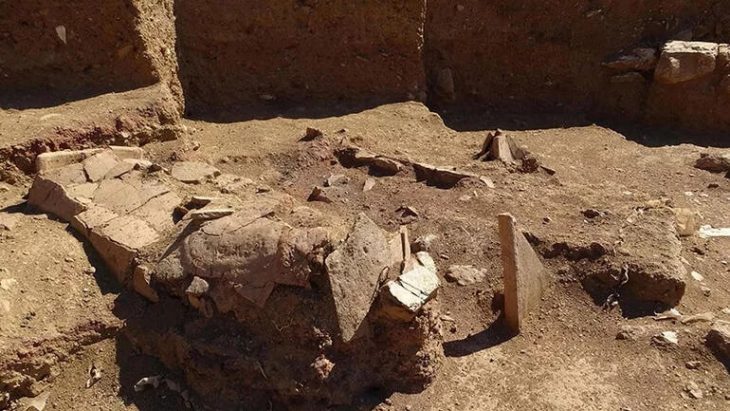
While bronze vessels were the most visible implements used in the Shāng dynasty (approximately 1600-1050 BCE) ancestor rites, actual communication with ancestors took place through oracle bones. These bones, primarily cattle shoulder blades and turtle undershells, were dried and holes were drilled in them at regular intervals.
A question was directed to an ancestor by applying a hot poker to these holes to make the surface crack. Specialists, usually a king or members of a ruling family, would then read the appearance of the cracks to obtain the ancestor’s response. Both the question—in positive and negative forms—and the results were written on the surface of the oracle bone.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

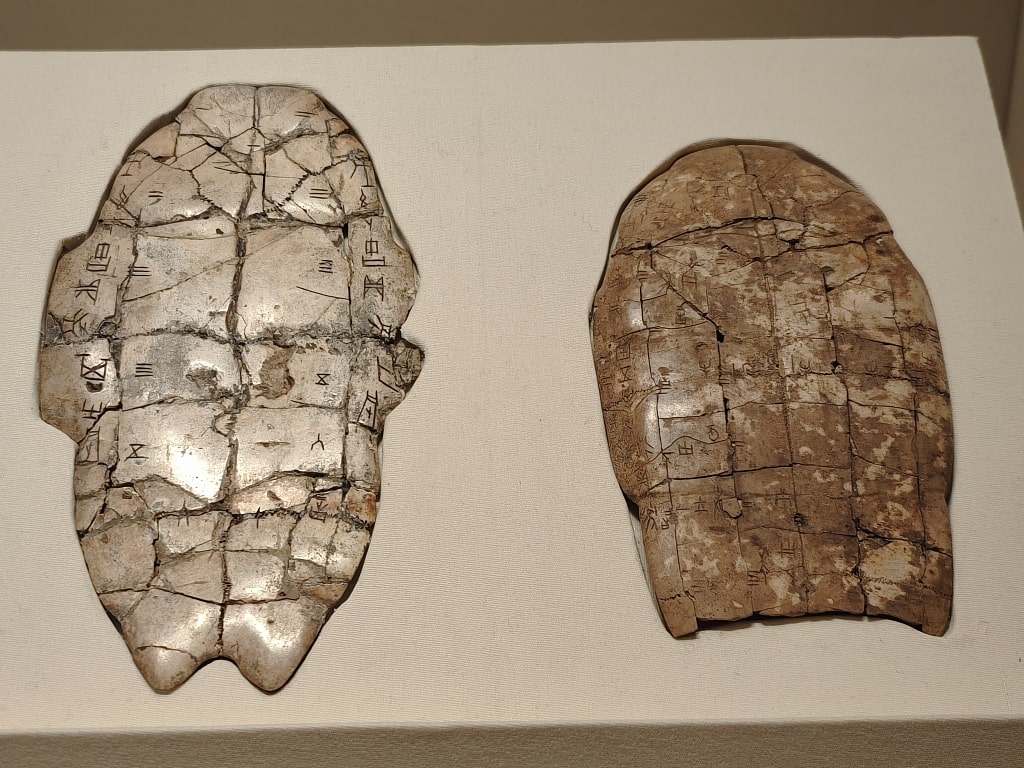
A vast “library” of these bones has been found near the Shāng dynasty capital of Anyang in Henan province, China. More than forty-five thousand of them have been published so far. Most foretell births, deaths, rainfall, good harvests, the outcome of hunts and battles, and the meanings of dreams.
The Oracle bone script is an advanced writing system. Paleographers can decipher only about 1,400 of the 2,500 known oracle bone script logographs by matching them with later Chinese characters.
The late Shāng oracle bone writings, along with a few contemporary characters cast in bronzes in a different style, constitute the earliest significant corpus of Chinese writing, which is critical for studying Chinese etymology because Shāng writing is directly ancestral to the modern Chinese script. It is also the oldest and ancestor of the Chinese script family.

According to researchers, oracle bone inscriptions are the only ancient writing systems that, despite historical changes and social development, have survived thousands of years later in the evolved Chinese characters. This is in contrast to other world’s most famous ancient writing systems, such as the hieroglyphs from ancient Egypt, the cuneiforms from ancient Babylon, and the Mayan glyphs from Mesoamerica.
Lack of archaeological evidence prevents addressing the related questions of how long before that time writing developed and in what contexts, or whether writing in China developed gradually or rapidly, and whether it developed exclusively in a religious context or, as in the ancient Middle East, it was tied to court administration.
Cover Photo: National Museum Scotland