The Roman Empire’s aqueducts are magnificent specimens of the art of architecture. Although centuries have passed since these aqueducts were built, they continue to teach us new things in terms of both construction techniques and aesthetics.
Scientists from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) studied the Aqueduct of Valens that supplied Constantinople with water and discovered new information on how this system was protected.
The architectural talents of the Roman Empire were undoubtedly far ahead of its time. The theaters, harbors, temples, and roads they built for Roman citizens were quite impressive.
“However, the most ground-breaking technical achievement of the Roman Empire lies in its water management, particularly its long-distance aqueducts that delivered water to cities, baths, and mines,” said Dr. Gül Sürmelihindi from the Geoarchaeology group at Mainz University.
The Romans were not the first to invent aqueducts, but it was they who popularized it. More than 2,000 long-distance Roman aqueducts are known to date, and many more are awaiting discovery.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
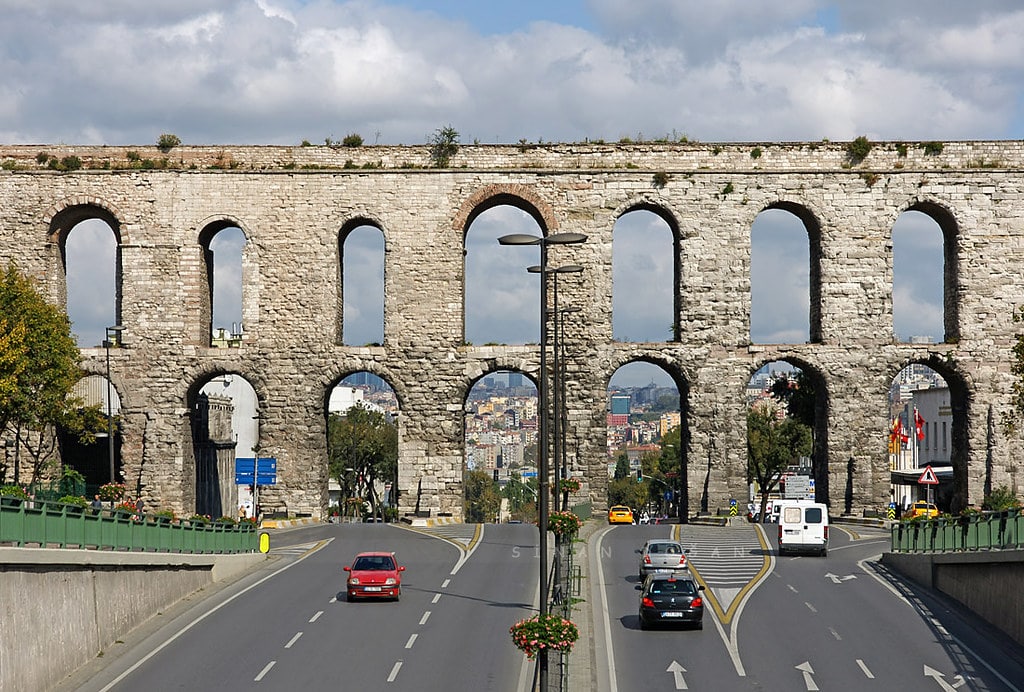
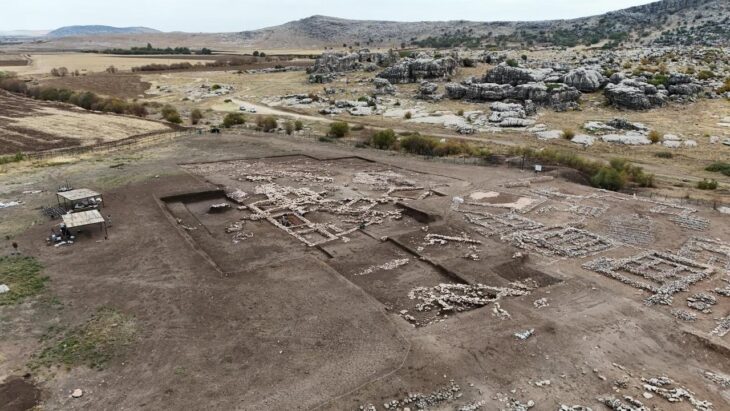
Dr. Gül Sürmelihindi’s and her research team dissertation focuses on the most impressive late-Roman aqueduct, the water supply lines of Constantinople, now Istanbul in modern-day Turkey.
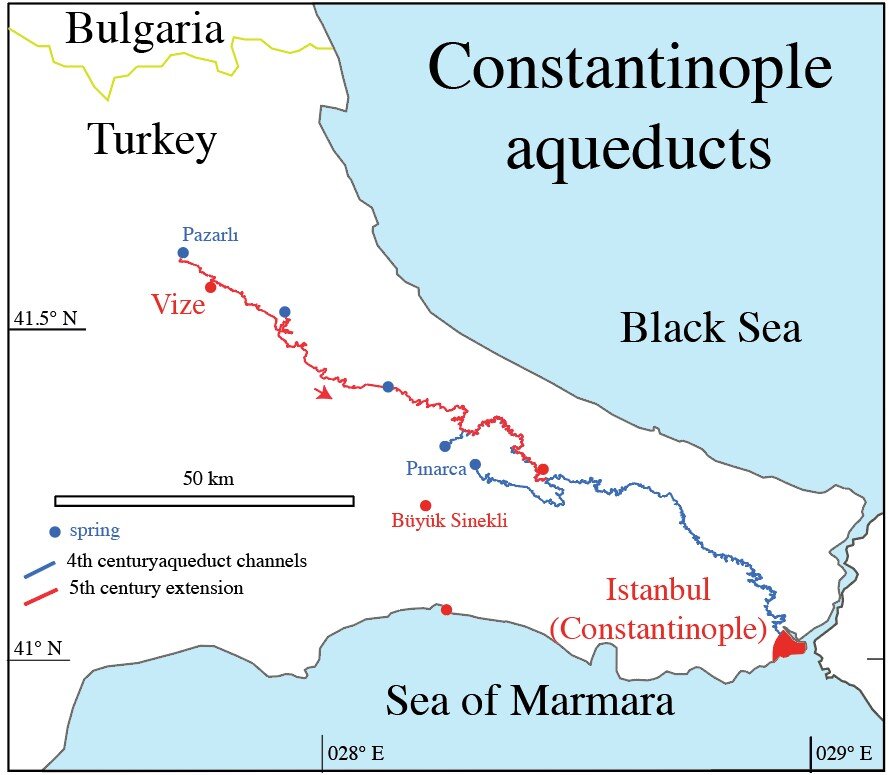
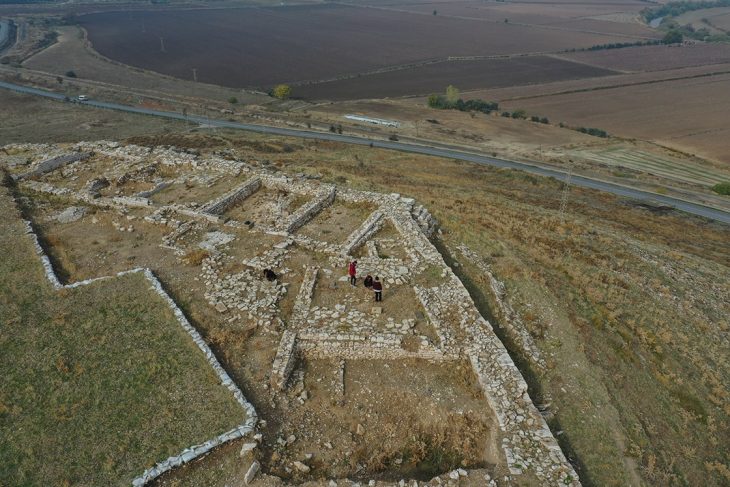
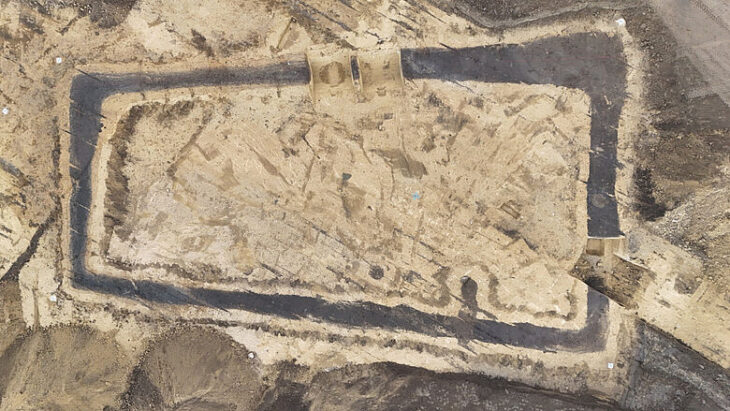
In 324 AD, the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great had an aqueduct built for Constantinople, which had difficulties in freshwater supply after making Constantinople the new capital of the Roman Empire. As the city grew, the size of the aqueduct grew. With this expansion, the total length of the aqueduct reached at least 426 kilometers, making it the longest aqueduct in the ancient world.
Sürmelihindi and her teams investigated carbonate deposits from this aqueduct, i.e., limescale shaped in flowing water, which can be used to learn about water management and the palaeoenvironment at the time. The researchers discovered that the entire aqueduct system housed only thin carbonate deposits, indicating about 27 years of use. However, according to the city’s annals, the aqueduct system operated for more than 700 years, at least until the 12th century.
In other words, it meant that the aqueduct was maintained during the Byzantine Empire. “Carbonate deposits can block the entire water supply and need to be cleaned from time to time,” said Dr. Sürmelihindi.
The carbonate used in the canal dates from the Byzantine Middle Ages, despite the fact that the aqueduct is late Roman in origin. This prompted the researchers to consider alternative cleaning and maintenance solutions since cleaning and fixing a 426-kilometer channel means it would be unavailable for weeks or months, at a time when the city’s population is reliant on its water supply. The researchers discovered that 50 kilometers of the water system’s central section is built as a double canal, with one aqueduct channel over the other and crossed on two-story bridges.
More information: DOI: 10.1002/gea.21853
Source: Phys.Org