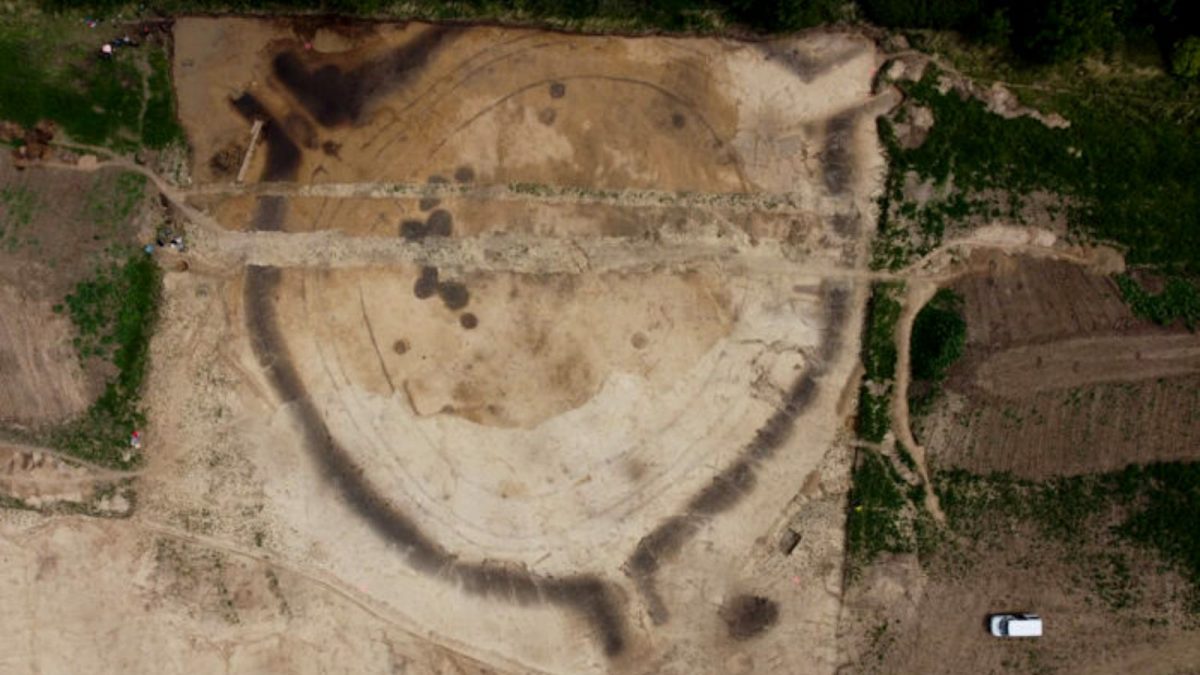
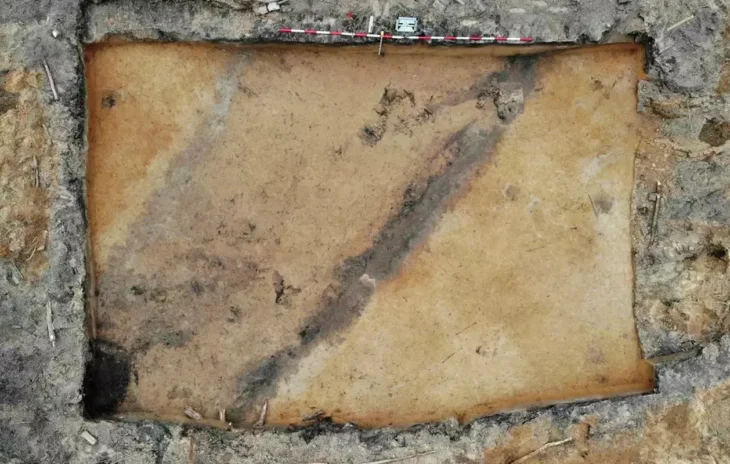
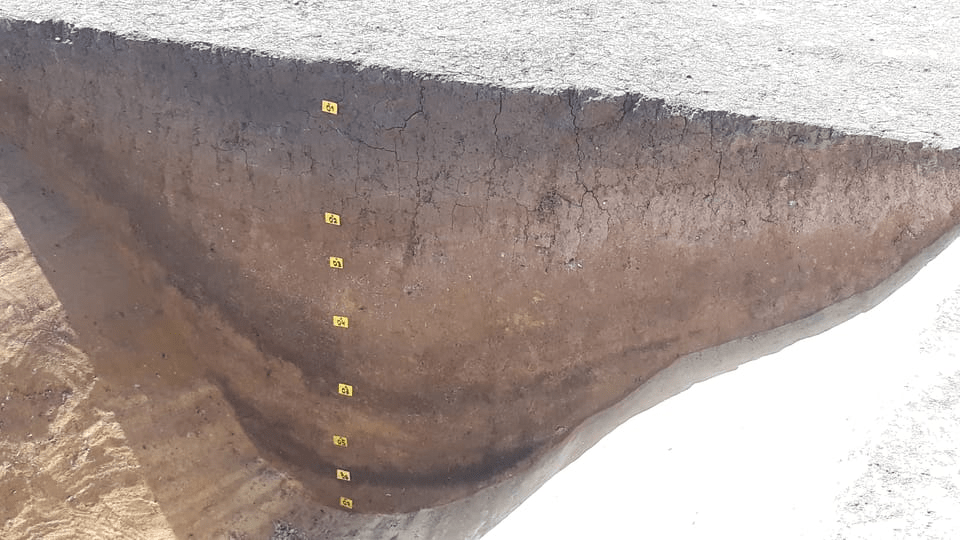
Archaeologists are investigating a 7,000-year-old so-called roundel (known as ‘rondely’ in Czech), and monumental structure located in the Vinoř district on the outskirts of Prague, Czech Republic.
The ancient Neolithic structures’ function is still unknown, but scientists are hopeful that more research will clarify why the monumental structures were built and who and how they were used.
Roundels are large circular Neolithic structures that were built between 4600 and 4900 BC. They are therefore far older than England’s Stonehenge or the Egyptian pyramids, making them the oldest monumental structures in all of Europe. However, these intriguing ancient structures are extremely well-preserved.
Most people in the West have heard of Stonehenge in England, which is thought to have been built between 3000 BC and 2000 BC, and some may have heard of Newgrange (3200 BC) in Ireland. But very few people know about Central Europe’s ‘roundels’. And these Neolithic circular enclosures have secrets to reveal.

“The so-called roundels are the oldest evidence of architecture in the whole of Europe. They are a series of circular ditches and they are always arranged in a circle with two, three, four or more entrances to the center, four being the most common. The circular ditches usually number between one and three, or very rarely four. The whole structure reaches an average of between 30 to 240 meters, but you most commonly find them in the range of 60 – 80 meters. Perhaps I should emphasize that these ditches are usually around one and a half meters wide, but we know of ditches up to fourteen meters wide and six meters deep,” Jaroslav Rídký from the Institute of Archaeology of the Czech Academy of Sciences in Prague told Radio Prague International.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Miroslav Kraus, the research’s principal investigator, notes that despite these findings, it is still not clear what function these structures have served:
“One of such theory is that it could have been used as an economic centre, a centre of trade. It could also have been a centre of some religious cult, where rites of passage or rituals connected to the time of year were performed.

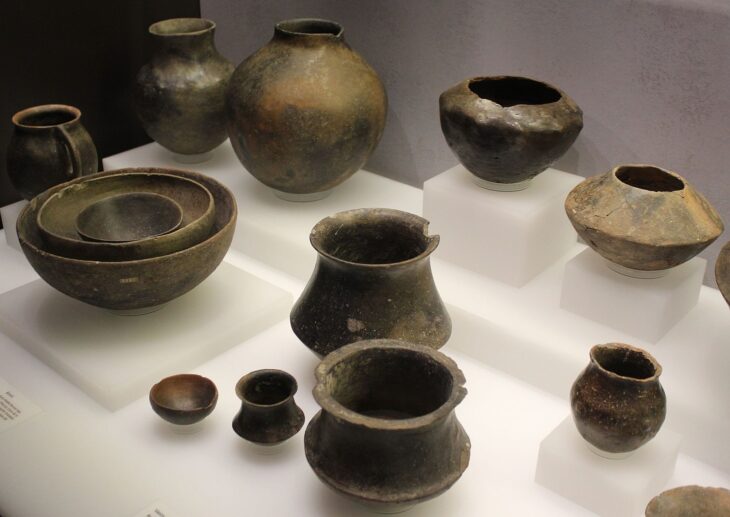
“Roundels were built during the Stone Age when people had not yet discovered iron. The only tools they could use were made of stone and animal bones.”
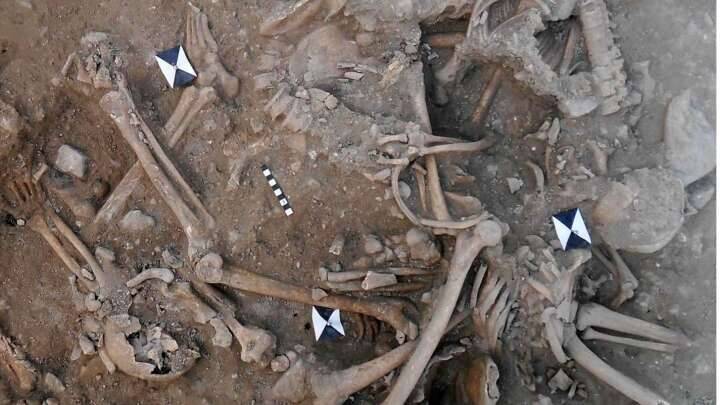
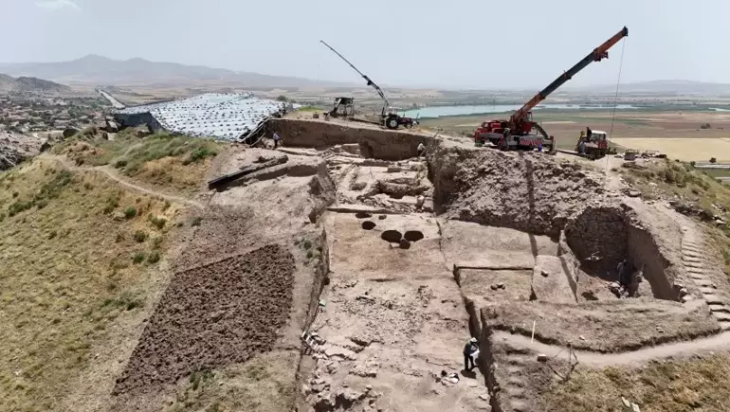
To date, around 200 roundels have been found all over central Europe, with 35 of them located on the territory of the Czech Republic. The roundel in Vinoř, which measures 55 meters in diameter, has an unusual floor plan with three separate entrances. The current investigation of a roundel in Prague’s district of Vinoř can provide scientists with more information about the structures’ purpose.
According to Mr. Kraus, the research is special because archaeologists have nearly completely uncovered the structure.
“We have the opportunity to uncover nearly the whole structure, or rather what remained of it. At the same time I should note that part of the structure was revealed back in the 1980s, during the laying of gas and water pipelines,” Kraus said.

Scientists will now take samples for analysis and the results should provide researchers with more information about the original structure.
“It would be great to discover something that would indicate the actual function of the building. However, it is very unlikely, since none of the previously researched roundels had revealed such information.
“It would also be great to find something that would suggest its real age. So far, radiocarbon dating of samples collected from roundels has put their age somewhere between 4900 years to 4600 BC. That is a pretty wide time span.”
The Vino roundel research is expected to continue until the end of September. Archaeologists previously discovered a Neolithic settlement northeast of the roundel that had been in use for 300 to 400 years.