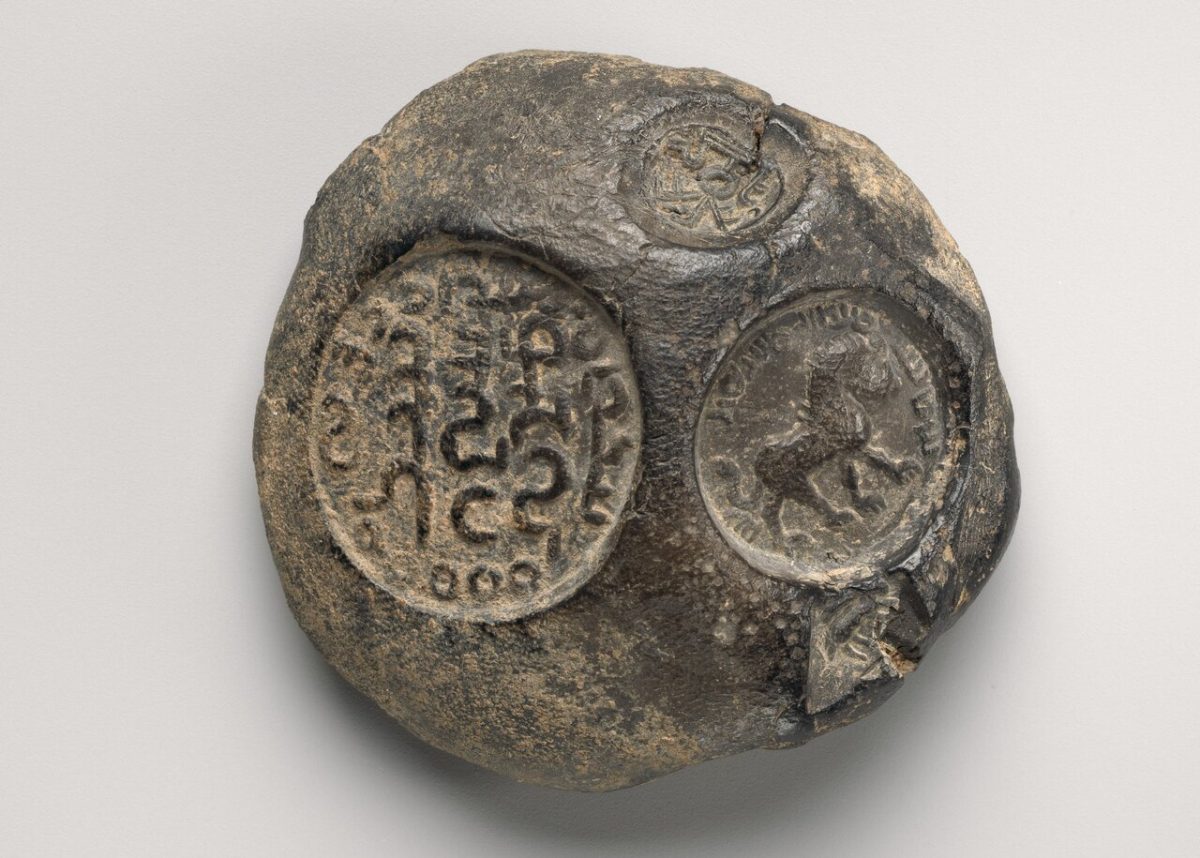
In a stunning archaeological find, the name “Shiraz” was identified on a clay sealing from the Sassanid era written in Pahlavi script.
The Sassanid Empire‘s (224-651CE) territory encompassed all of what is now Iran, Iraq, Armenia, Afghanistan, eastern parts of Turkey, and parts of Syria, Pakistan, Caucasia, Central Asia, and Arabia.
The Sassanids called their empire Eranshahr “Empire of the Aryans (Persians)”. Ardashir I established the Sassanid Empire or Sassanian Dynasty following his victory over Artabanus IV Ardavan, the final Parthian (Arsacid) monarch. It came to an end when Yazdegerd III (632–651), the final Sassanid Shahanshah (King of Kings), lost his 14-year struggle to expel the growing Islamic empires.
The Sassanid era is regarded as one of Iran’s most significant and influential historical periods. Persia had a significant impact on Roman civilization during the Sassanid era, and the Romans only granted equal status to the Sassanid Persians.
The finding is important due to cementing the history of Shiraz, which is situated some 60 km south of Persepolis, once the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (c. 550–330 BC).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
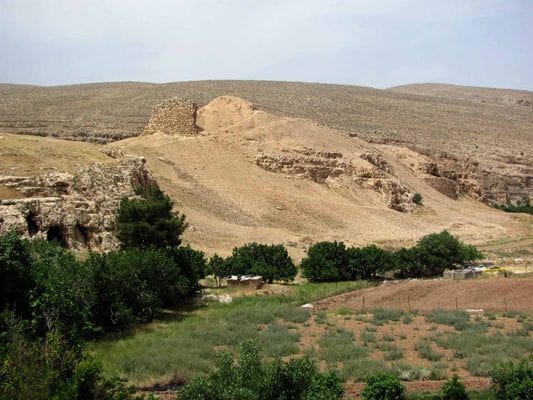

The sealing is being kept at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York. These sealings were unearthed during three seasons of archaeological excavations by experts from the Metropolitan Museum of Art, conducted from 1932 to 1935.
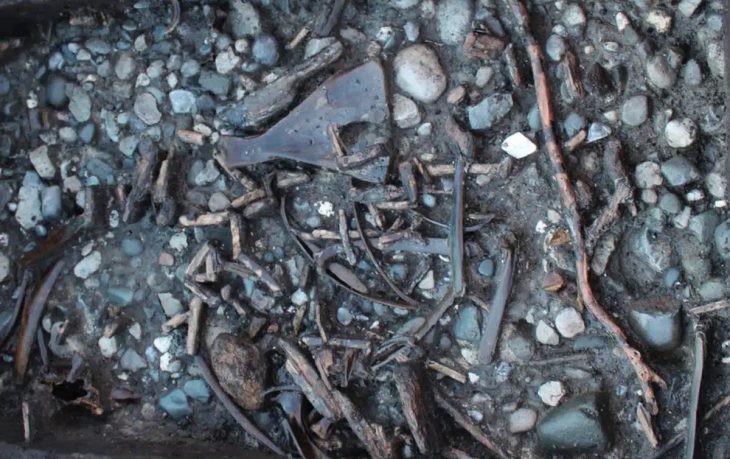
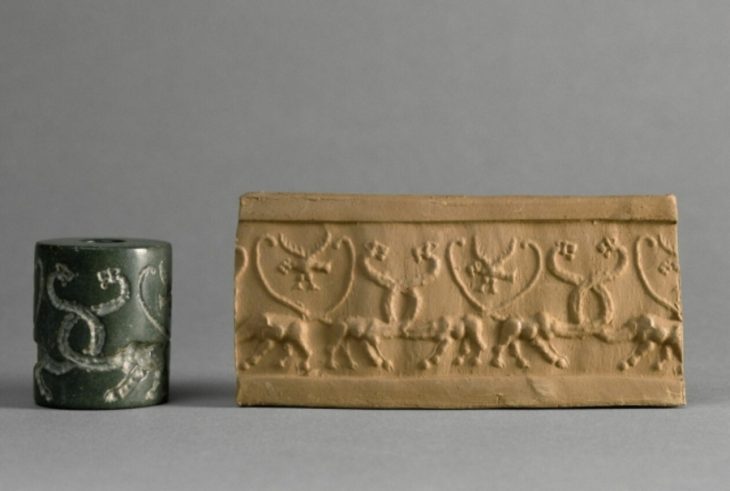
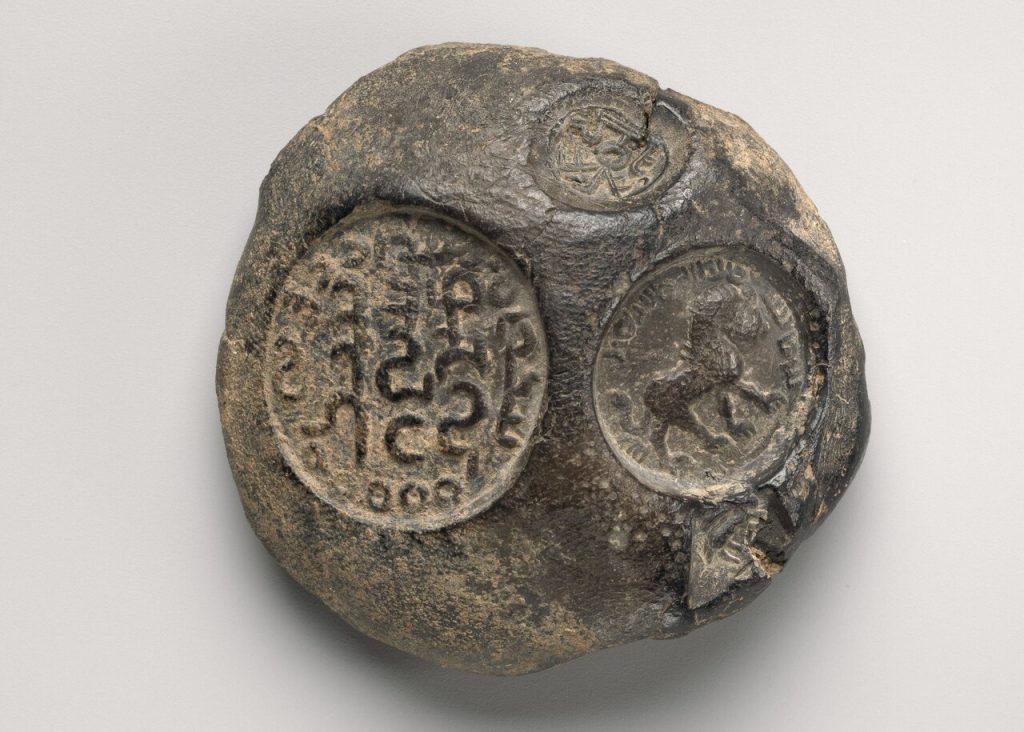
According to the Met Museum, this sealing was impressed with four seals of varying sizes. The imagery on the seals depicts a lion walking right, a monogram, an inscription, and a horned quadruped.
This sealing was one of more than five hundred that were unearthed from the Sasanian stronghold located at Qasr-e Abu Nasr. The building burned, baking the clay and preserving the seal impressions, which is how the cache survived.
Iranian archaeologist Mohammadreza Nasab-Abdollahi said that based on the research he has done, he has identified the name of Shiraz in the Pahlavi script (Middle Persian) on the “Sasanian clay seal”, which were obtained nearly a century ago from the archaeological excavations in the “Qasr-e Abu Nasr” in the east of Shiraz.
On 6 April, Iranian archaeologist Mohammadreza Nasab-Abdollahi affirmed to ISNA news agency that the inscription “Mugh-e Shiraz” has been deciphered on these Sassanid clay sealings.

According to Nasab-Abdollahi, archaeological investigations indicate that Qasr-e Abu Nasr in Shiraz exhibits a cultural sequence from the Achaemenid to the Abbasid period, with its primary settlement dating back to the Sassanid era.
“The archaeological findings from Qasr-e Abu Nasr reveal a wide spectrum of administrative systems, techniques, and defensive structures,” the archaeologist remarked.
Furthermore, he emphasized that archaeological evidence from the Sassanid period, including such clay sealings, as well as artifacts from the Achaemenid era such as inscribed bricks from Persepolis, corroborates that the city known today as Shiraz bore the same name in antiquity and was among the significant cities of ancient Iran.