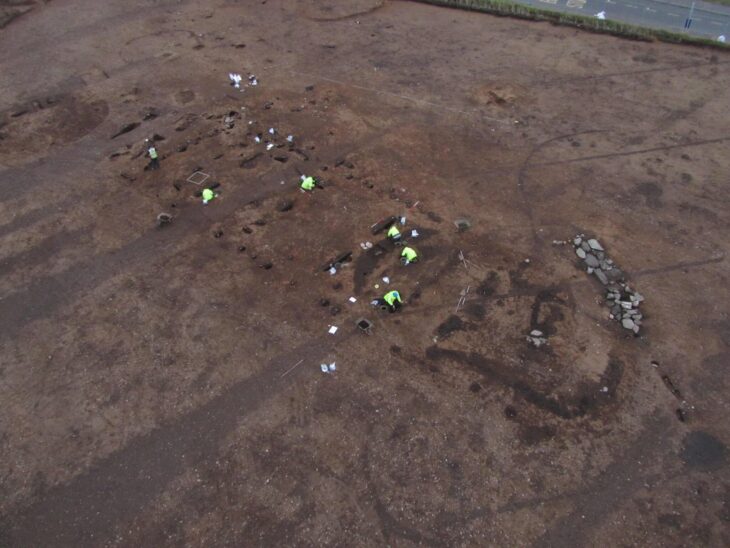
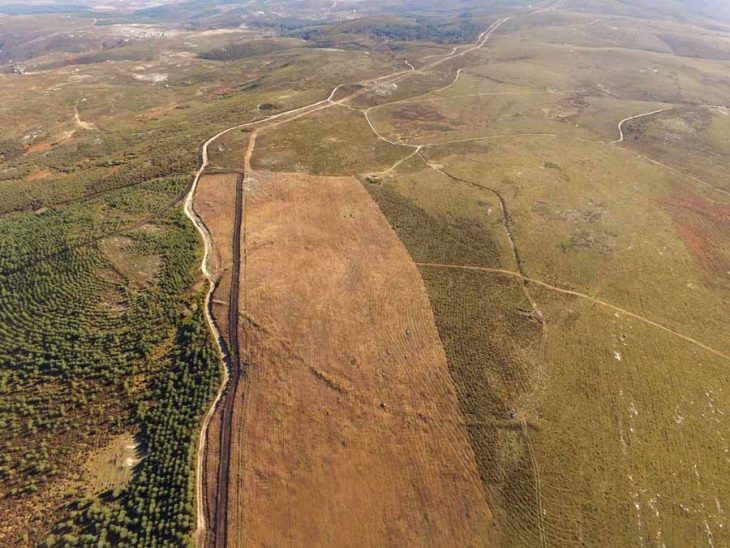
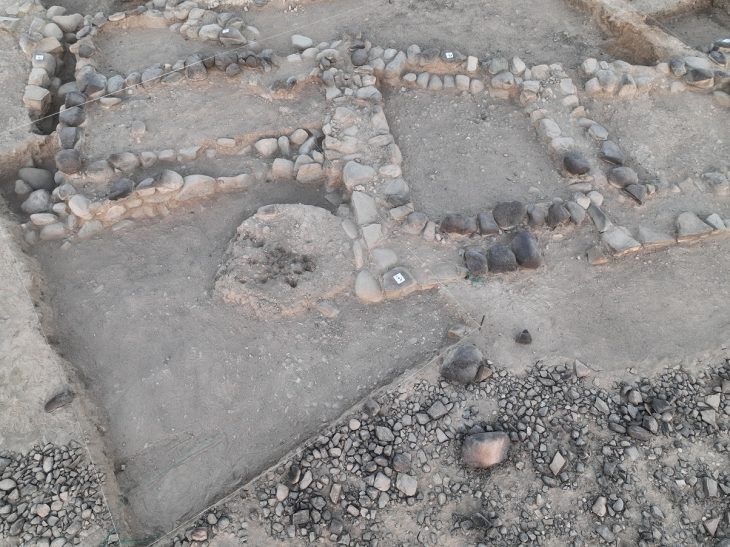
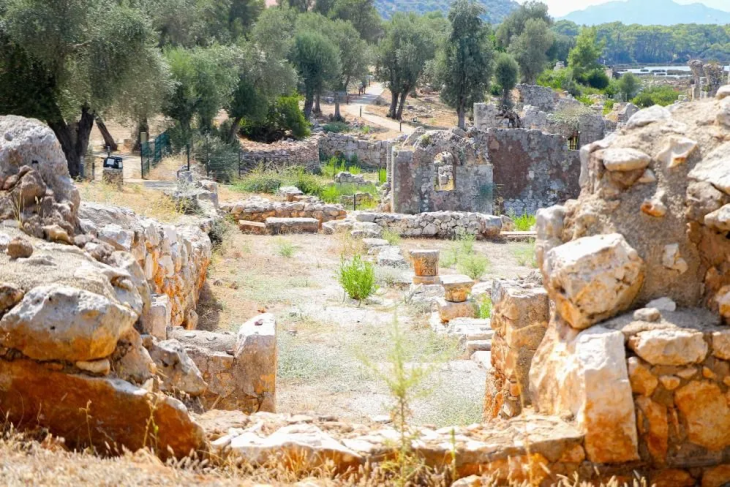
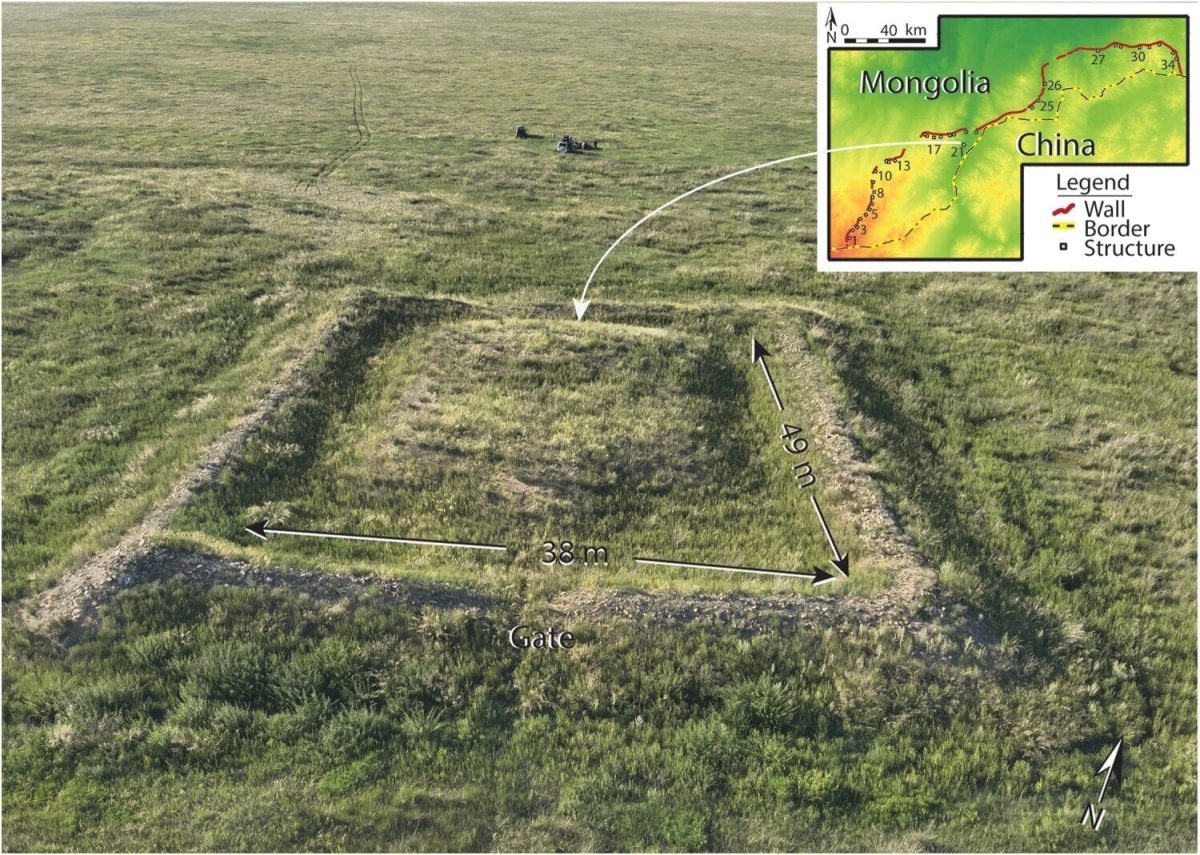
Researchers have studied the 405-km wall system in eastern Mongolia known as the Mongolian Arc to learn more about its history and purpose. The “Mongolian Arc” consists of an earthen wall, a trench, and 34 structures.
This section of the Great Wall of China that extends into Mongolia has been analyzed for the first time, allowing them to present some speculative insights into the history and function of this enormous structure.
Running roughly parallel to the border between China and Mongolia, the ancient barrier extends from Sukhbaatar Province to Dornod Province in northeastern Mongolia, where winter temperatures often fall as low as -25 degrees Celsius (-13 degrees Fahrenheit).
Based on historical records, researchers suggest that the entire system was built between the 11th and 13th centuries AD, but archaeological studies to date are insufficient to more accurately date the construction times of its different parts.
The study authors analyzed the wall and its associated structures using satellite images, Chinese atlases, and Soviet maps in addition to direct field observations, noting that “the Mongolian Arc, despite its magnitude, has been largely overlooked in existing academic discourse.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In their paper published in the Journal of Field Archaeology, the team describes the techniques and technology they used to study the wall.
Researchers’ most striking finding was that the Mongolian Arc contains numerous large gaps, suggesting that it was built in a hurry and therefore never fully fortified. There is also evidence that suggests the wall was built as a means of controlling the movement of people or animals or perhaps as a part of a taxation scheme.
“One possible explanation for the gaps, which were points of vulnerability in the system, is that the Mongolian Arc was hastily built during the final years of the Jin dynasty as a defense against the expected invading Mongol armies,” write the researchers.
Such theories arose as it became clear that the wall would not have served as much of a barrier—many of its outposts, for example, were in locations with limited views into the surrounding territory.
The entire wall system to which the Mongolian Arc belongs has received different names in the research literature. It has been called the “Jin border trench”, the “Jin long wall,” and the “Liao-Jin Wall”.
It is also one of the most enigmatic long wall and trench systems in Chinese and Mongolian history. Despite its size and complexity, it is unclear when it was constructed, who built it, and for what purpose.
It is not even clear whether the entire array of walls was built at the same time or if, as researchers hypothesize, it is an accumulation of different projects built over a long period of time.
Researchers believe the Mongolian Arc has received much less attention than other long wall (or Great Wall) constructions in the history of this region, possibly due to the uncertainties associated with its construction and use, the fact that it is located in remote areas, and the fact that it is not visually impressive.
The study authors are currently unable to make any definitive statements regarding the purpose of the Mongolian Arc, although they are planning to conduct more extensive excavations of some of the structures in an upcoming field season. This, they hope, will help them to determine the wall’s “construction dates and duration of use, and shed light on the activities of the people stationed in these enclosures.”
DOI: 10.1080/00934690.2023.2295198
Cover Photo: Drone photo of Khaltaryn Balgas (MA21). Photo: Journal of Field Archaeology