Archaeologists examining the mustatil stone remains in the northwest of Arabia think that these stone remains may have been used for 7,000-year-old cattle cult.
A new research group has discovered the prehistoric rectangular stone structures known as mustatils discovered in northwestern Saudi Arabia are older than traditionally thought, perhaps predating the pyramids.
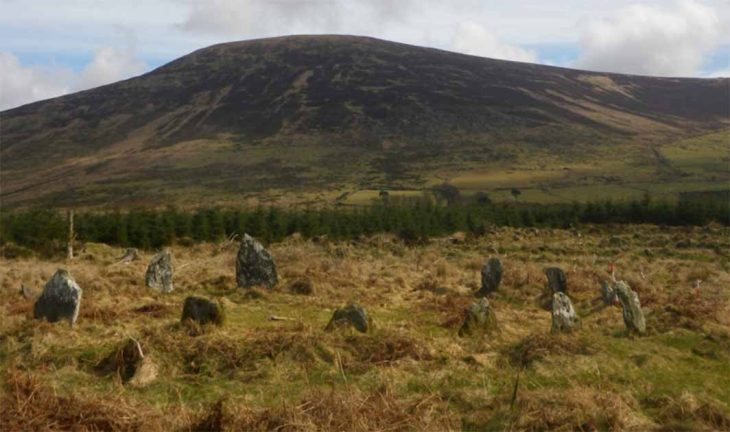
The mustatils are discovered to be among the world’s oldest monuments, according to archaeologists. The discovery was assigned this name by the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU), which is the plural version of the Arabic word for rectangles.
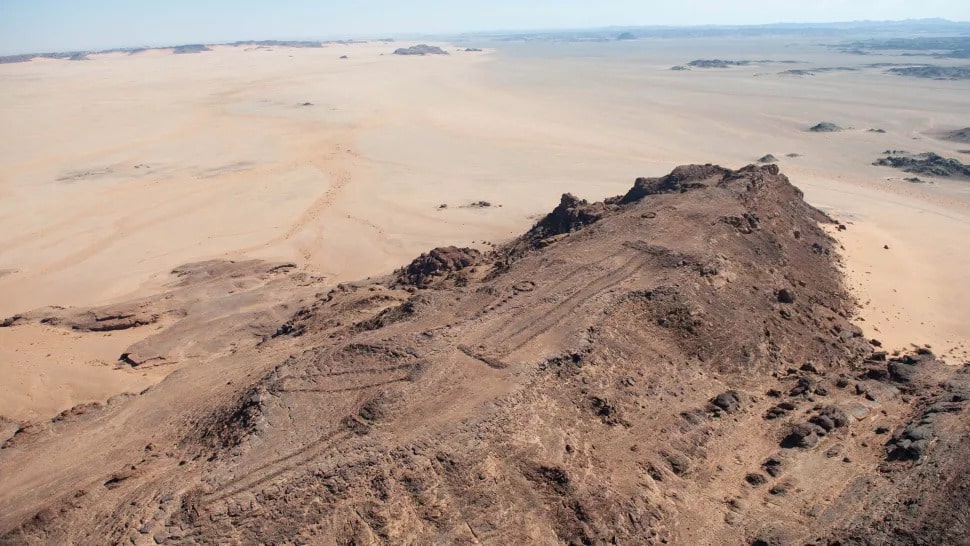
While the presence of the mustatils was previously recognized, the analysis suggests that the team counted more than 1,000 stone rectangular-shaped monuments, nearly double the number previously found.
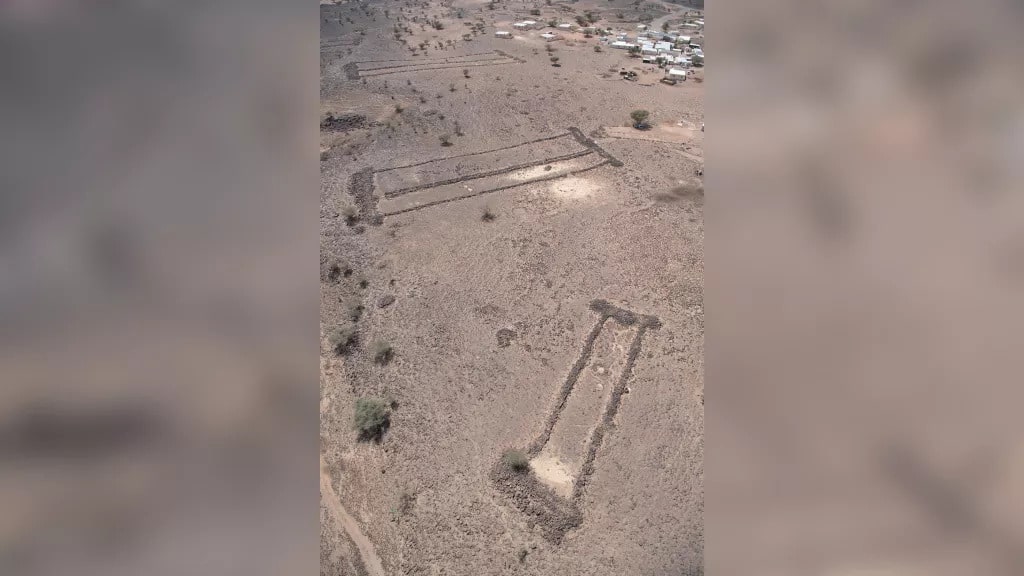
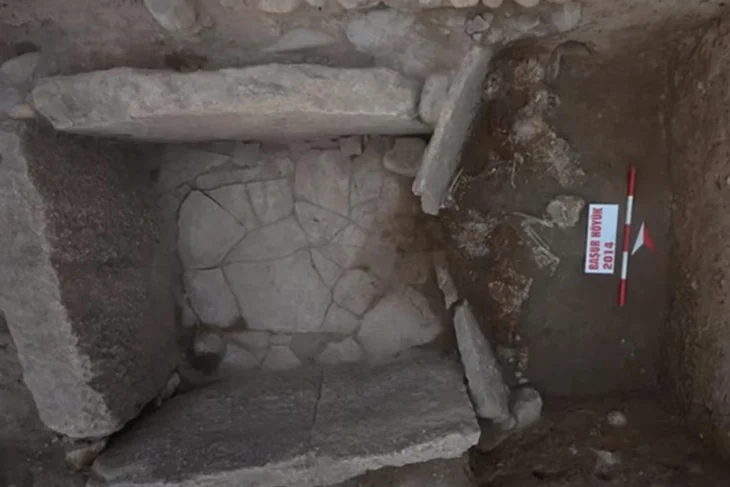
Each mustatil is made up of two thick-walled ends joined by two or more long walls to form a series of massive rectangular courtyards varying in length from 20 meters to over 600 meters. Outside the mustatil’s main entrance, circular/semi-circular cells have been built.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to the research, about 1,000 of these mustatils occupy an area of 200,000km2 and have very similar shapes, implying that they are all from the same time span.

The dissertation on this find is part of the University of Western Australia’s archaeological program in the provinces of AlUla and Khaybar.
“We think of them as a monumental landscape,” said Melissa Kennedy, an archaeologist at the University of Western Australia in Perth and an author of the study, NBC reported her as saying. “We are talking about over 1,000 mustatils. These things are found over 200,000 square kilometers [77,000 square miles], and they’re all very similar in shape … so perhaps it’s the same ritual belief or understanding.”
Scientists are baffled as to why the ancient civilizations who created the mustatils built so many of them around what is now Saudi Arabia’s desert. Kennedy theorizes that certain mustatils were only used once, or that different groups of people created and used different mustatils in close proximity to one another.
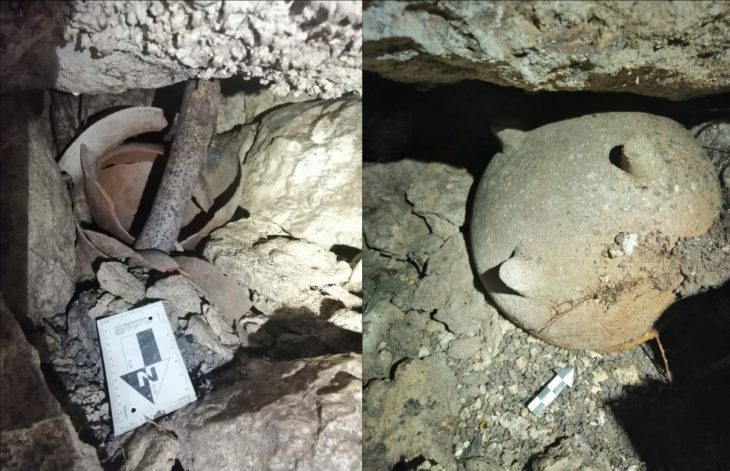
One clue to their purpose is the discovery of a small chamber or niche on the headwalls of certain mustatils, which seems to have been used for animal sacrifices.
According to Kennedy, 900-year-old archaeological evidence of a cattle cult was found in the south of Arabia, and the mustatils may have been an early manifestation of that belief. Any mustatils may have been developed to stake territorial claims on productive herd pasture.