Over 1,300 archaeological sites in Azerbaijan were systematically surveyed and documented in two field campaigns in 2021 and 2023 by researchers from Kiel University’s ROOTS Cluster of Excellence and colleagues from the Academy of Sciences of Azerbaijan.
Researchers publish the results of interdisciplinary research on burial customs and settlement structures in the Southern Caucasus from the 4th to 1st millennium BCE. They have now published the results of their latest research campaign in the international journal Antiquity.
The article is a follow-up of an overview of the results of the 2021 field campaign, which was published in the journal Archaeological Prospection earlier this year.
Spanning more than 1000 kilometres in length and up to 5600 metres in height, the mountain ranges of the Caucasus stretch between the Black and Caspian Seas. What appears to be a huge natural barrier was however an important contact and exchange zone between the highlands of West Asia and the Southeast European steppes for thousands of years. Despite this importance, archaeological data from the Caucasus and neighbouring regions remains fragmentary.
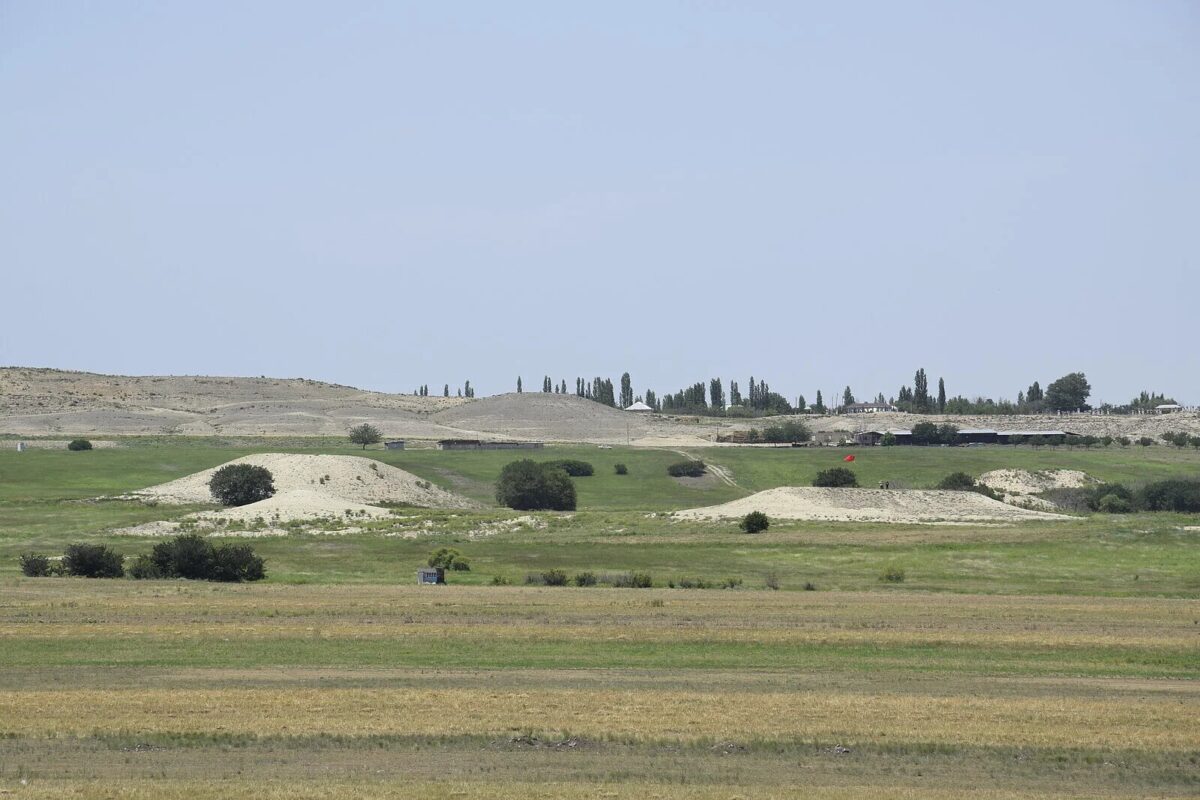
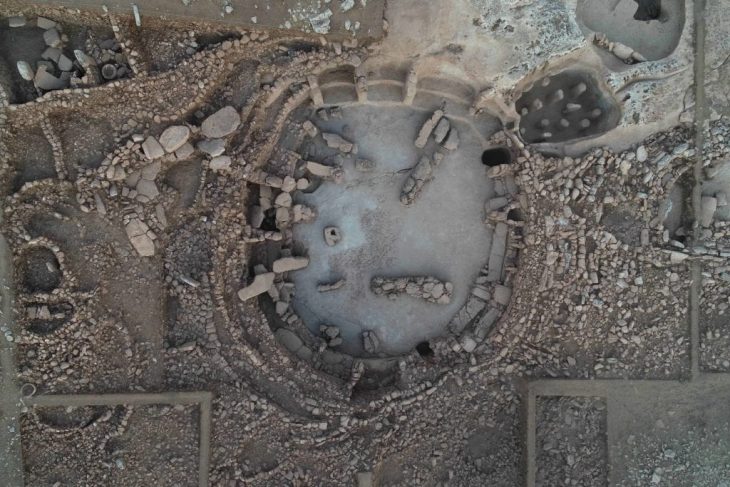
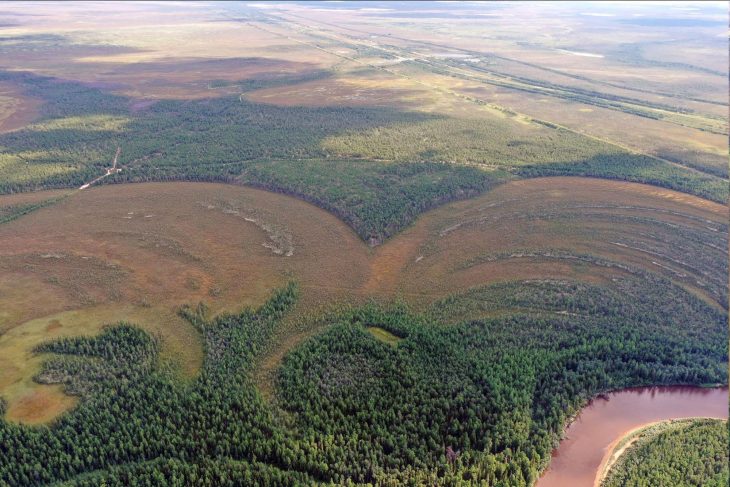
The research of the ROOTS team focuses on two areas in the administrative district of Goranboy in Western Azerbaijan, along the margins of the piedmont of the Lesser Caucasus. Burial mounds, known as kurgans, are a typical landscape feature of the region. However, there has been a lack of systematic documentation of the archaeological sites to date. “We can only draw conclusions about socio-cultural developments in the past if we have precise data on the number, type, size, distribution and age of burial mounds and other archaeological sites,” says Andrea Ricci, archaeologist and head of the project within the ROOTS Cluster of Excellence.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
During the two field campaigns, the team used a combination of different methods for the investigations, ranging from remote sensing to on-site geophysical measurements.

Satellite images helped the researchers to gain an overview, analyse landscape structures and identify potential archaeological features. Comparing very early satellite images from the 1960s and 1970s with current images also revealed modern changes to the landscape. “Prior to the fieldwork, the analysis of these images confirmed the presence of a considerable number of mounds, which are probably kurgans.”
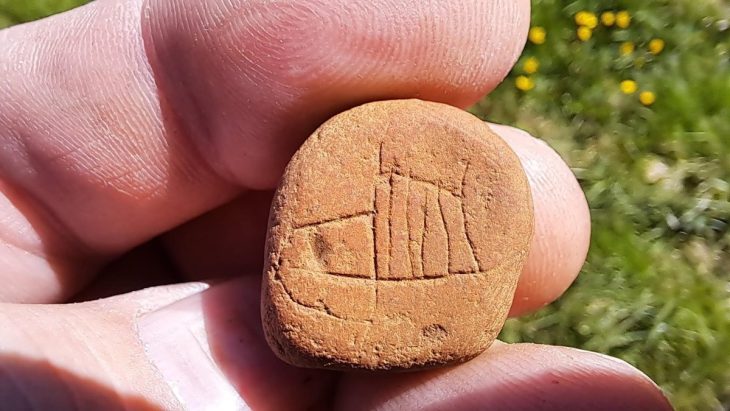
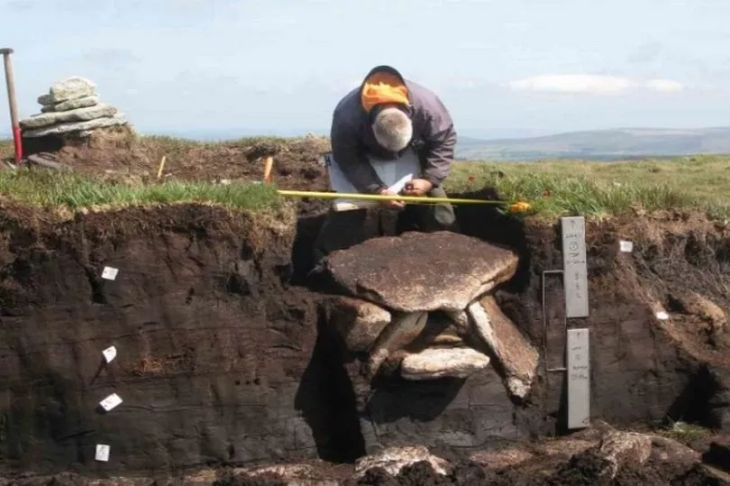
On-site, geological and geomorphological investigations were carried out and archaeological features were documented. Where available, the team members collected artefacts on the surface in order to date the sites.
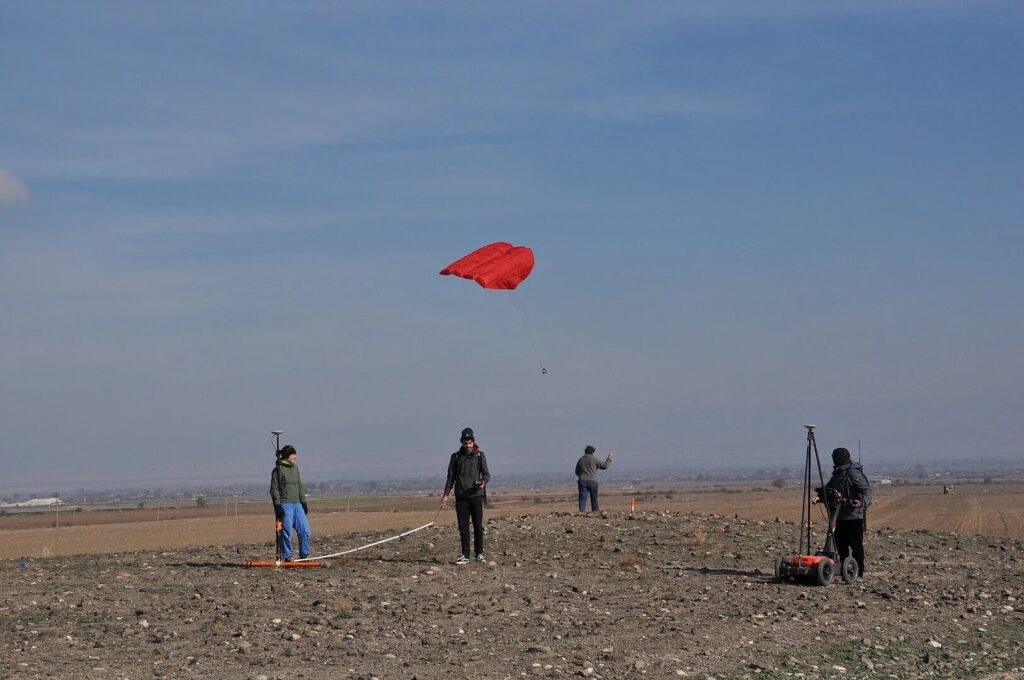
Using a camera attached to a kite, the team also photographed selected areas covering several hectares in order to create 3D landscape models from the acquired images. “These integrated methods allow us to document the dimensions and spatial relationships of the kurgans with an intensity and precision never reached before, revealing that kurgans were often arranged in clusters,” explains Dr. Bakhtiyar Jalilov, archaeologist from the National Academy of Azerbaijan (Baku) and cooperation partner of the project. Geomagnetic and electromagnetic measurements and the use of ground-penetrating radar expanded the investigations on the Earth’s surface into the ground to document the shape and size of specific kurgans.
On the Uzun-Rama plateau alone, the team was able to identify more than 1,200 kurgans. Of these, only around 200 were previously known. Another 85 kurgans were added along the Qaraçay River Valley. They date from the 4th to 1st millennium BCE. The detailed investigations revealed different structures over the millennia.
In addition to the kurgans, the team identified burial sites or individual graves from the Late Bronze Age/Early Iron Age, as well as sites dating to the Chalcolithic (5th-4th millennium BCE) and the Middle Ages (10th-15th century CE).
Ricci A, Fiori S, Huseynov M, Jalilov B, Kneisel J, Raese H. The archaeological record of the Qaraçay River Basin along the northern piedmont of the Lesser Caucasus. Antiquity. Published online 2024:1-8. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.182
Cover Image Credit: Kurgans are a common feature of the landscape in many places in West Azerbaijan. Credit: Andrea Ricci