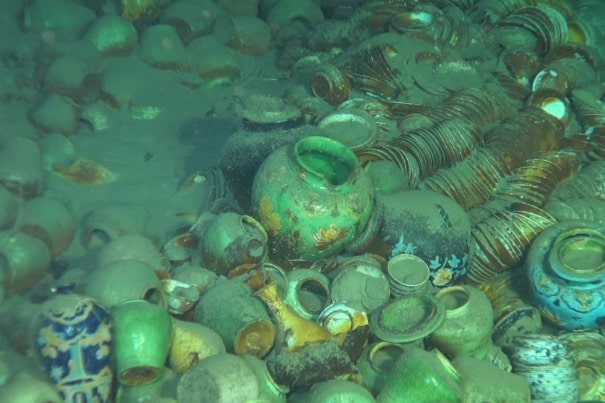
In the South China Sea, two ancient shipwrecks that date back to the middle of the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) were discovered at a depth of about 1,500 meters.
In October, a scientific research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Deep-sea Science and Engineering discovered two shipwrecks on a continental slope. It’s also the first time China has discovered a large-scale ancient shipwreck in the deep sea.
The two are named by researchers as Northwest Continental Slope No 1 and No 2 Shipwrecks in South China Sea.
The research is part of a year-long mission to scientifically assess how to preserve and protect the two shipwrecks of “world-class archaeological importance”, the National Cultural Heritage Administration said, announcing the finds on Sunday.
They would also provide important clues to the maritime section of the Silk Road, the ancient trade route connecting China to other Asian countries and beyond, the officials were quoted as saying by state-run China News Service.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The ships, which date back to the late 15th and early 16th centuries when China was ruled by the Ming dynasty, were discovered by Chinese marine researchers about 1,500 meters (4,290 feet) below the surface in the South China Sea’s northwestern region. Both were heavily laden with cargo.
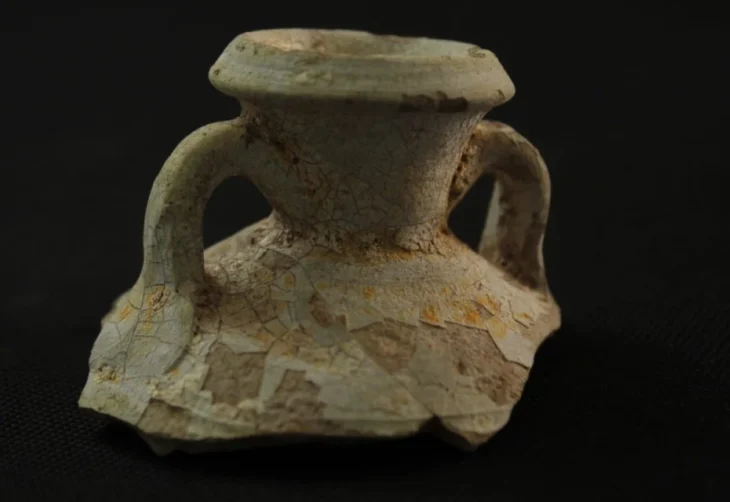
The first ship contained an estimated 100,000 items, mostly porcelain. The second, slightly older than the first, was filled with timber believed to be on its way to China, according to administration officials.
Both vessels were relatively well preserved, and archaeologists were quite certain about the era they belonged to.
“The well-preserved relics are of high historical, scientific, and artistic value,” said Yan Yalin, the director of the archaeology department of the National Cultural Heritage Administration. “It can be a world-class archaeological discovery in the deep sea. The findings are key evidence of ancient Maritime Silk Road, and is a major breakthrough study for the history of Chinese overseas trade, navigation, and porcelain,” he added. Yalin is conducting a preliminary investigation on these finds.
Among the porcelain artifacts unearthed, various types were identified, including blue-and-white porcelain, celadons, and ceramics with green glaze.
The first thorough underwater investigation of the shipwreck sites started on Saturday and is scheduled to last until June. The locations of the shipwrecks have not been made public in order to protect the artifacts.