The story of the saints in the catacombs of Northern Europe is a peculiar story. It is rooted in the crisis of faith after the Reformation, prompting people to dramatically return to decorative materialism in the practice of worship.
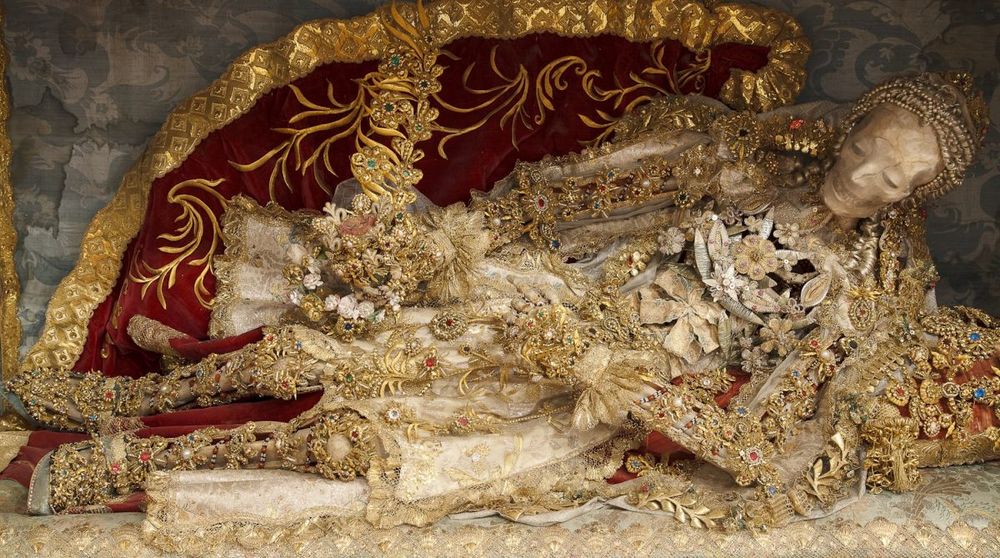
The jeweled skeletons were discovered in catacombs under Rome in 1578 and given as replacements to churches that had lost their saint relics during the Reformation in the idea that they were Christian martyrs. However, for the most part, their identities were unknown. The receiving churches subsequently spent years lavishing diamonds and gold clothing on the respected skeleton strangers, even filling their eye sockets and sometimes decorating their teeth with finery. However, when the Enlightenment arrived, they were rather humiliating because of the huge amount of money and luxury they symbolized, and many were hidden away or vanished.
On May 31, 1578, vineyard workers in Rome discovered a passage leading to an extensive network of long-forgotten catacombs below Via Salaria. The Coemeterium Jordanorum (Jordanian Cemetery) and the surrounding catacombs were early Christian burial grounds, dating back to between the 1st and 5th centuries AD.
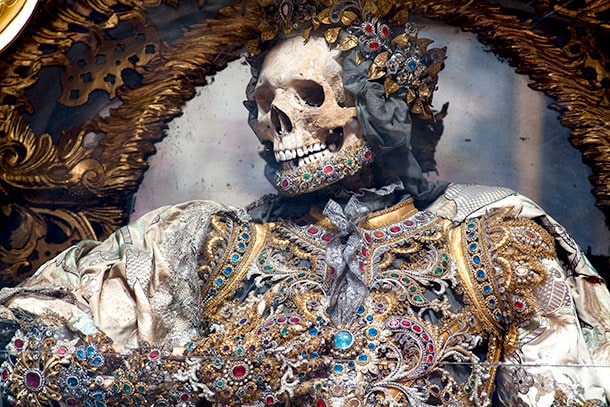

The Catholic Church had been fighting the Reformation for decades when these catacombs were discovered. Despite the fact that certain human remains had been revered as hallowed relics for centuries*, Protestant Reformers saw retaining relics as idolatry. Bodies, even the bodies of saints, were to decompose into dust. Countless relics were interred, defaced, or destroyed during the Reformation.
Relics have long been popular among the laity, and the Counter-Reformation used the shipment of fresh holy relics into German-speaking nations as a strategy. They needed to replace what had been lost, but where would they find new saints?
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
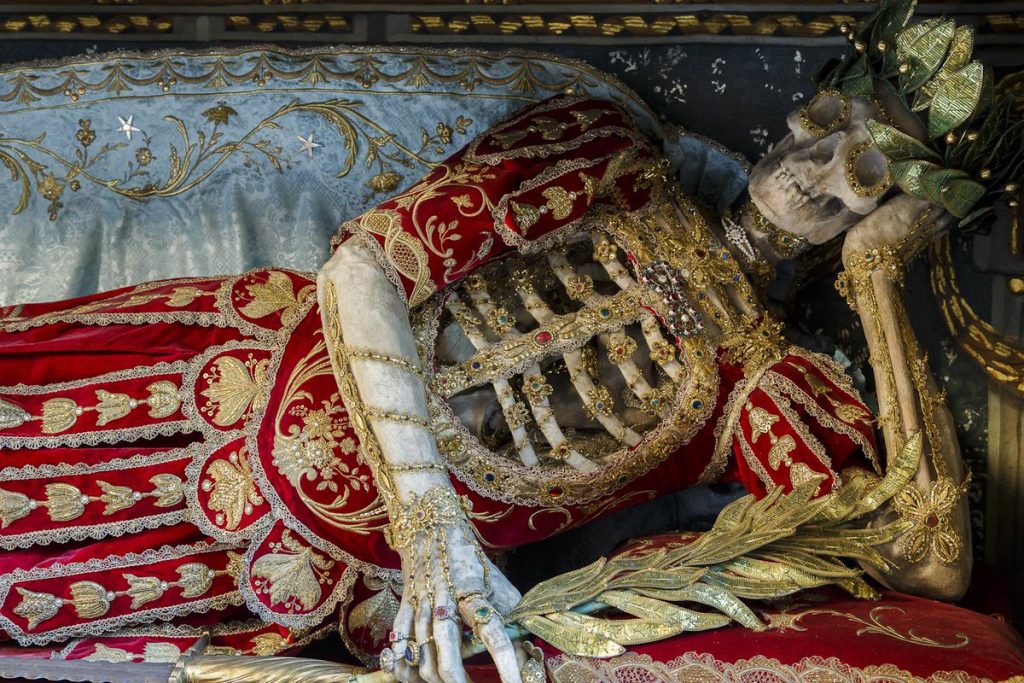

The bones themselves came from the re-discovery of the Roman catacombs in c 1578. For the following several decades, the underground catacombs were found, robbed by tomb robbers, and the bones, skeletons, clavicles, and other relics of victims were sold to various Catholic churches as relics of martyrs.
The hardworking, compassionate nuns associated with those churches were highly accomplished ladies, and it was they who created the garments for the catacomb bare-bones (called in German katakombenheiligen)and put the valuable and cut stones for adornment. Who knows whose old bones were adorned in such away. The bones arrived from Rome in a box with the name of the slain saint.
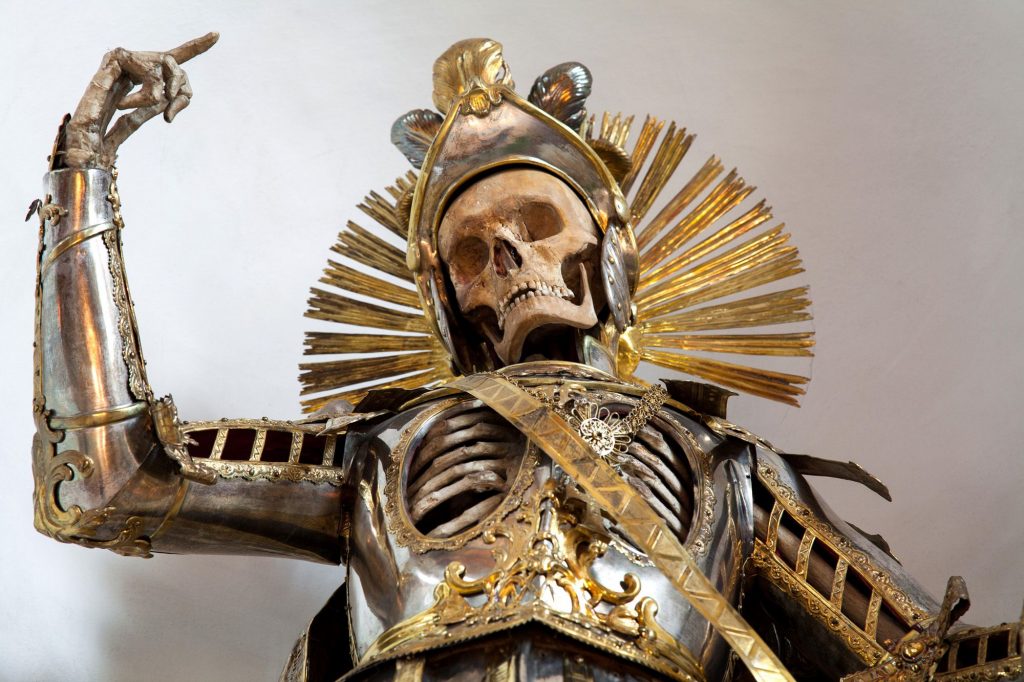

They were unquestionably prestige symbols. The skeletons were given Latin names and were covered in gold and diamonds from the cranium to the metatarsal. The decorations varied, but they were frequently elaborate. The skeletons wore velvet and silk robes embroidered with gold thread, and the gems were real or costly imitations. Even silver plate armor was provided to a select few.

Given the time, finances, and commitment required to build the saints, it is sad to contemplate how few have survived to the present day. During the nineteenth century, many were stripped of their jewels and hidden or destroyed since they were deemed morbid and humiliating. Of all of the catacomb saints that once filled Europe, only about ten percent remain, and few can be viewed by the public.
For more on the Katakombenheiligen, be sure to check out Paul Koudounaris’s Heavenly Bodies: Cult Treasures & Spectacular Saints from the Catacombs.













![Upper molar of a Brontothere mammal of Asian origin [Credit: Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Upper-molar-of-a-Brontothere-mammal-of-Asian-origin-min.jpeg)

