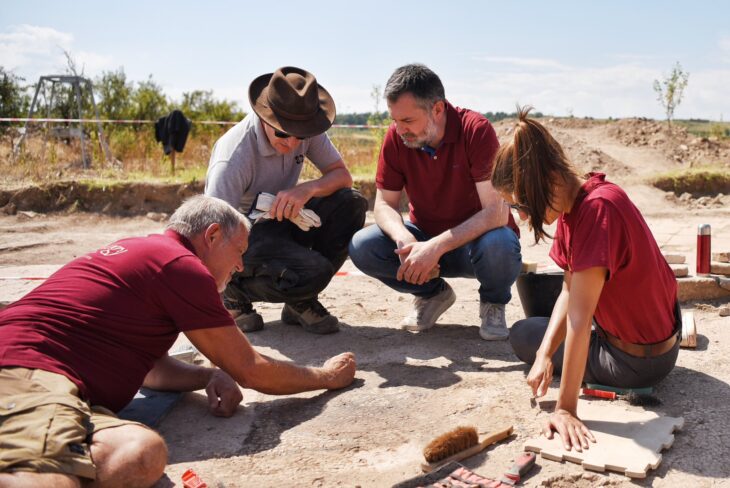
From the 12th to the 16th century, the Kaltenborn monastery near Allstedt was a religious, cultural, and economic center of the southeastern Harz foreland. Today the abbey has wholly disappeared from the cultural landscape. Current excavations by the State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt (LDA) bring to light impressive relics of the monastery church, but also many evidence of the destruction of the complex in the Peasants’ War of 1525.
The Augustinian monastery of Kaltenborn near Emseloh (Mansfeld-Südharz) was founded in 1118. The founders were the Saxon-Thuringian Count Wichmann and his wife Kunigunde, the daughter of the famous Ludowinger Ludwig the Springer. Favored by the high nobility and richly endowed with donations, Kaltenborn developed into one of the most prosperous and influential monasteries in the region.
The prosperity and power of the monastery, as well as its vigorous collection of taxes, aroused resentment in the affected population – refusal of services by Kaltenborn subjects has been reported as early as the mid-15th century. When the Peasants’ War broke out in central Germany, the Augustinian monastery was plundered and devastated by insurgents from the nearby villages of Riestedt and Emseloh in April 1525. Many monks fled and did not return. The monastery did not recover from this and was finally abolished in 1538. Later, the church, cloister and all other buildings were removed so thoroughly that today only small rests of ruins have remained of the once magnificent abbey.
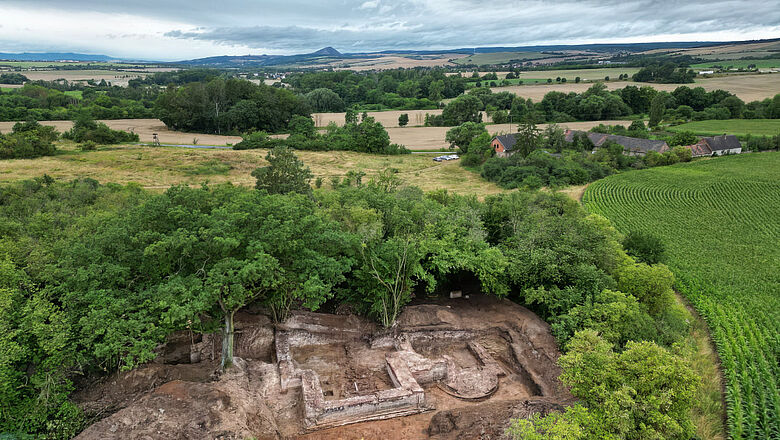

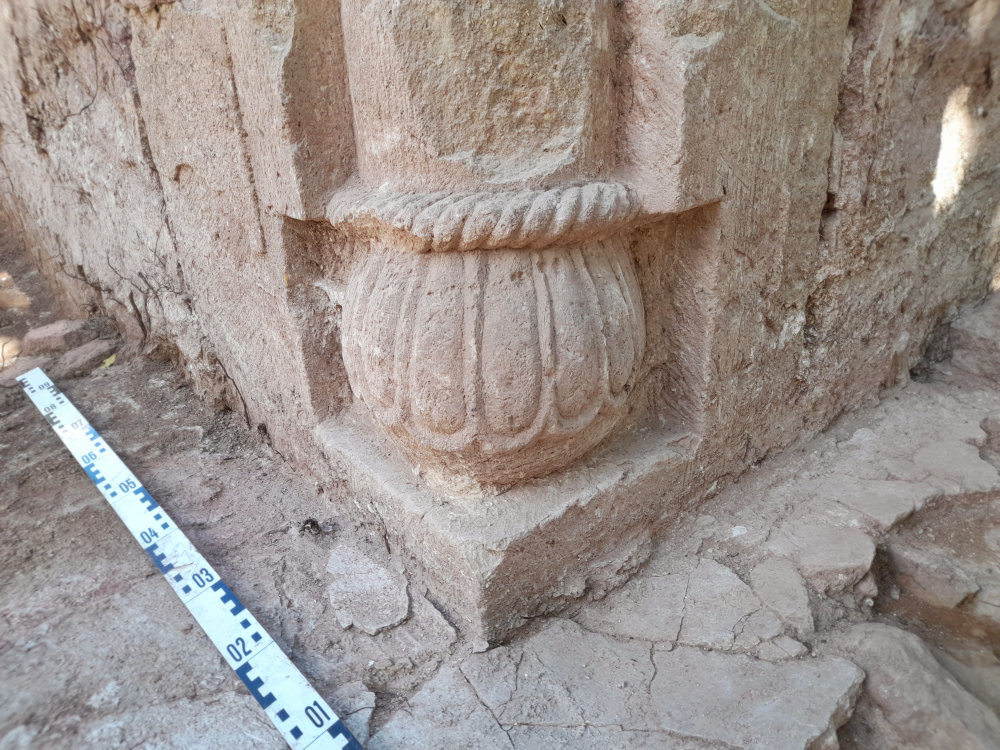
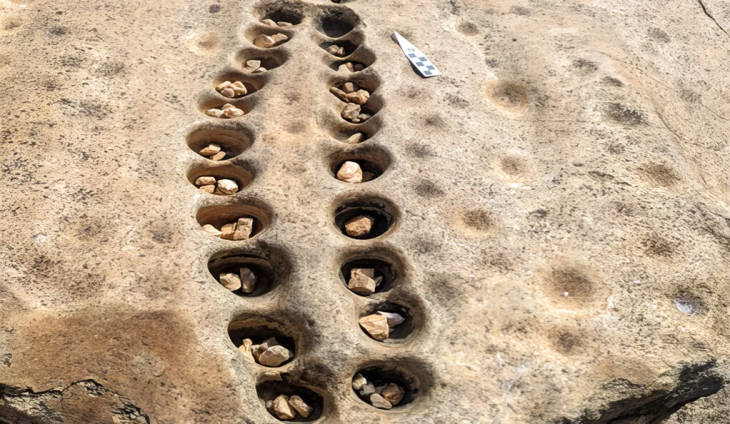
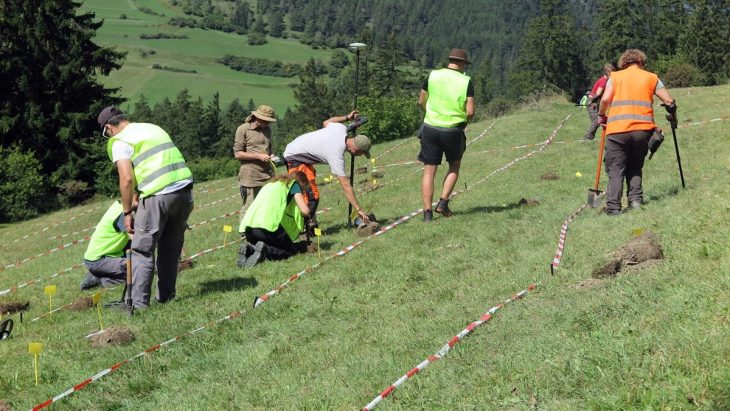
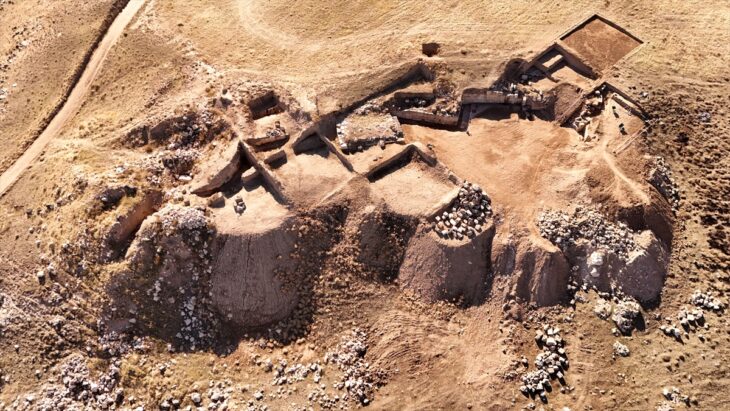
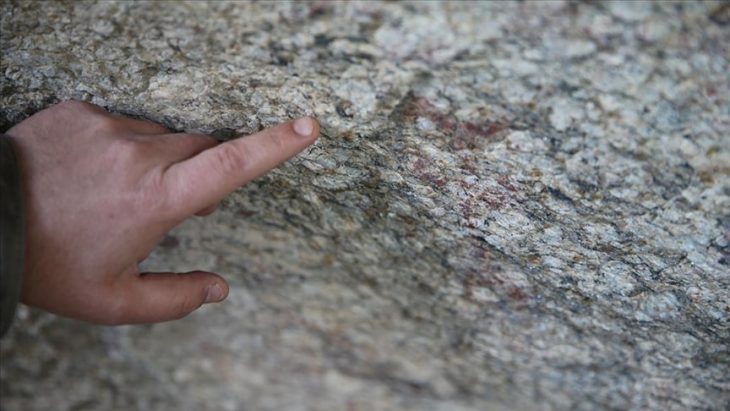
Current geophysical investigations, metal detector surveys and excavations under the direction of Prof. Dr. Felix Biermann (LDA) have now produced surprisingly rich relics of the monastery. The walls of the abbey church have been partially preserved under enormous masses of rubble up to a height of two meters. The stately three-aisled basilica with transept, rectangular main apse and semi-circular side apses was built in Romanesque forms in the first half of the 12th century and later expanded in Gothic style. In the south, the cloister buildings connected to a large, walled, roughly rectangular courtyard with a diameter of up to 230 meters, in which various buildings were located. Particularly impressive are the Romanesque architectural and decorative elements of the church, which include magnificent column bases, lintels with floral motifs and round arches with friezes – the latter with close parallels to the Ulrichskirche in nearby Sangerhausen, which has survived to this day and is one of the main works of Romanesque art in Saxony-Anhalt.
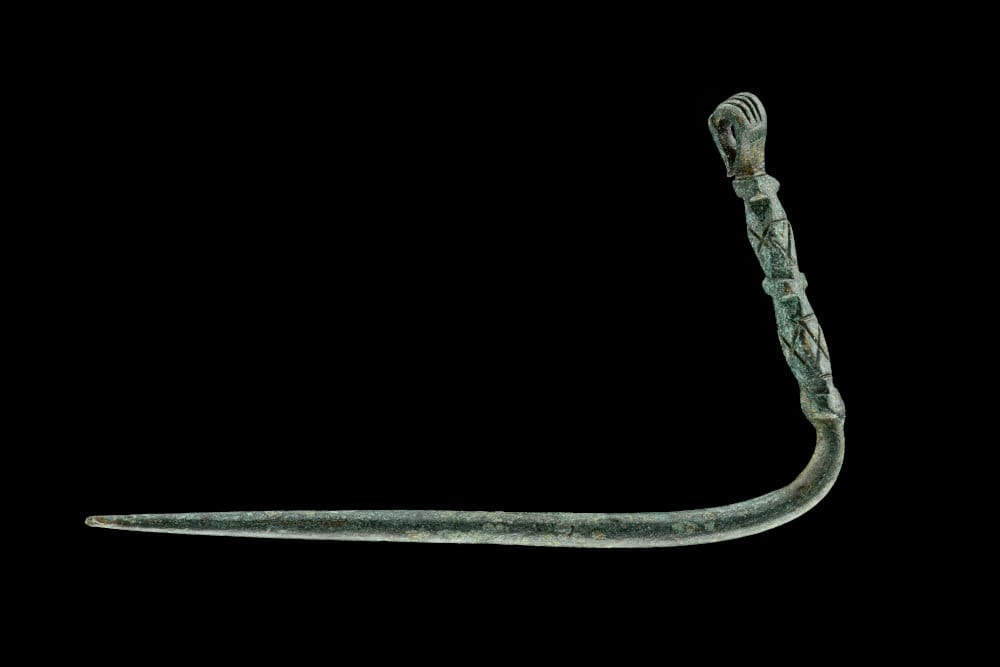
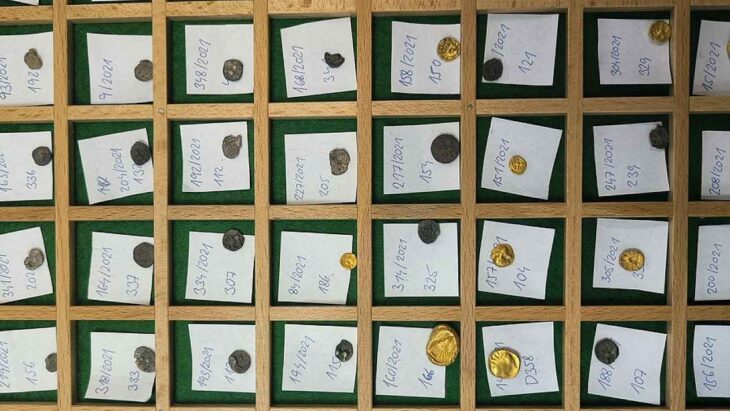
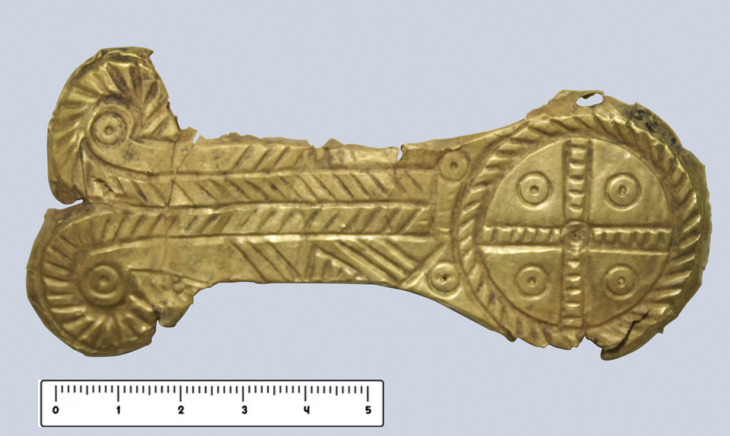
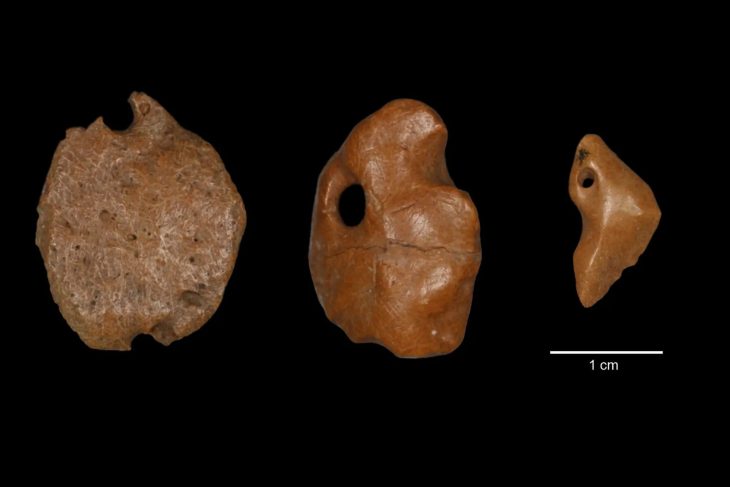
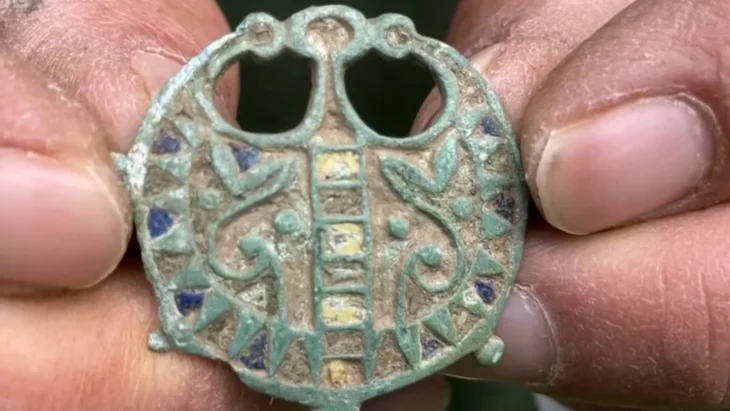
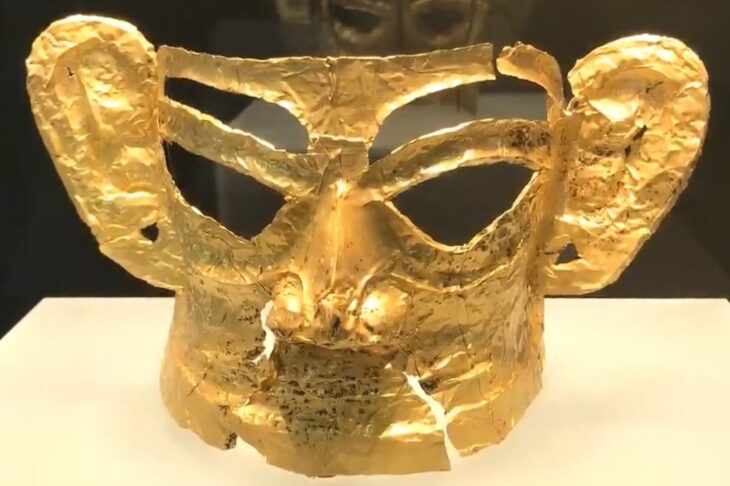
These architectural relics and a rich ensemble of small finds – coins, book fittings, belt buckles, pieces of jewelry, scales, signet rings, pens, and the like – shed light on the monastery’s proud early days. Other finds tell of its eventual downfall.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Numerous fragments of stove tiles from the 15th and early 16th centuries, including colorful glazed ones with figurative and floral decorations, attest to the comfort and even luxury that a monastic community did not look good on. Such finds manifest a dissolution of traditional monastic discipline and asceticism, which explains why the monasteries were only able to offer little resistance to the Reformation. The furor of the rebellious peasants resulted in layers of fire and debris with smashed ceramic vessels, broken glass from windows, tiles, and metal objects melted in embers as a result of massive destruction.
State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt (LDA)
Cover Photo: Romanesque column base in the main apse of the monastery church. © State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt (LDA), Felix Biermann