Archaeologists in Vyborg, Russia have uncovered two remarkable artifacts that reshape the city’s connection to its medieval and post-medieval past. A long-lost 15th-century Swedish heraldic stone—once belonging to the influential Tott family, governors representing the Swedish crown—was rediscovered in the most unexpected place: a sewer collector near Vyborg Castle.
Shortly afterward, workers strengthening an embankment in the city center stumbled upon a 19th-century dagger resembling the traditional Caucasian kama. Together, these chance discoveries highlight how layers of history continue to emerge from beneath Vyborg’s streets, offering fresh insight into the region’s political and cultural legacy.
According to Alexander Smirnov, director of the Monrepos Park Museum and research fellow at the Center for Rescue Archaeology of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), some of the most significant finds related to Vyborg Castle were uncovered far beyond the castle walls—and purely by chance. His interview was published on November 19 by the Center’s public page “ArcheoCode.”
A 15th-Century Heraldic Stone Rediscovered After a Century
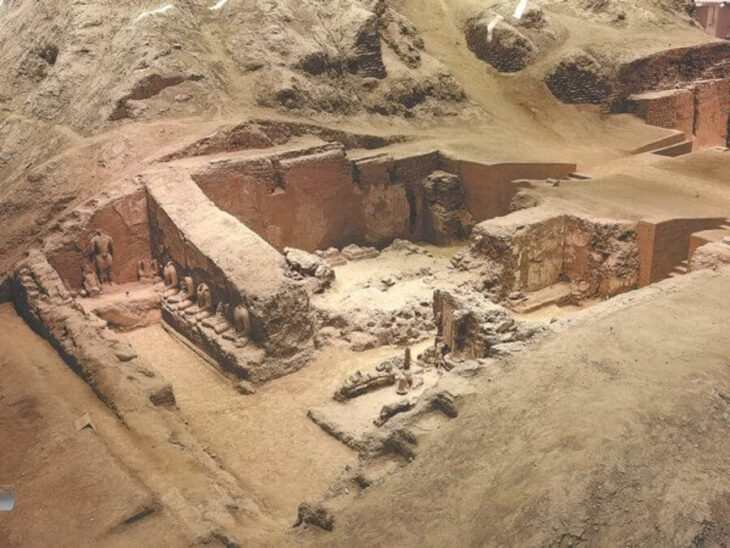
The story begins in the late 19th century, when young researcher Alfred Hackman conducted the first systematic archaeological assessment of Vyborg Castle. During his work, he sketched a mysterious stone slab embedded in one of the castle’s walls. Though his drawing survived, the stone itself was believed lost for more than 100 years.
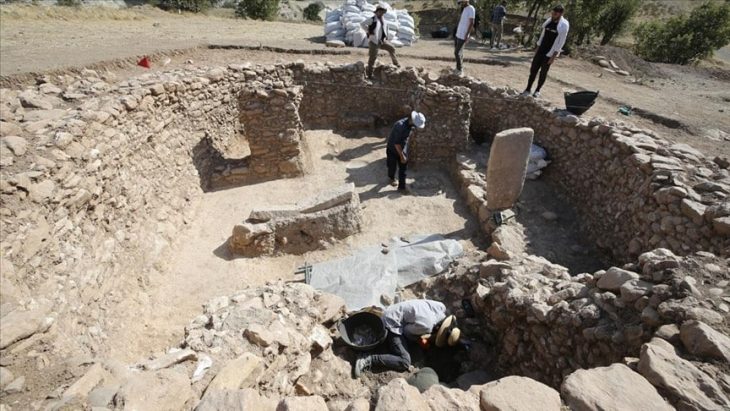
That changed when archaeologists examined a one-story building from the 1770s located across the water from the castle. During routine excavation, they uncovered a sealed sewer collector. When the heavy stone lid was turned over and cleaned, the team made a stunning realization: the slab was in fact the long-lost heraldic stone of the Tott family, governors of the Swedish king in Vyborg. The stone originally adorned the royal chambers in the 1450s.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This knightly coat of arms, with its helmet and feathers, likely reflects a 15th-century regional style that may differ from the more commonly depicted Tott family emblems.
“A real knightly coat of arms, complete with a helmet and feathers,” Smirnov explains. “Hackman didn’t fully understand what he had found, but his pencil drawing matches the rediscovered slab perfectly. A 15th-century knightly emblem—this is genuine, high-quality Medieval heritage that deserves a central place in the museum.

New Theories About Vyborg’s Early Development
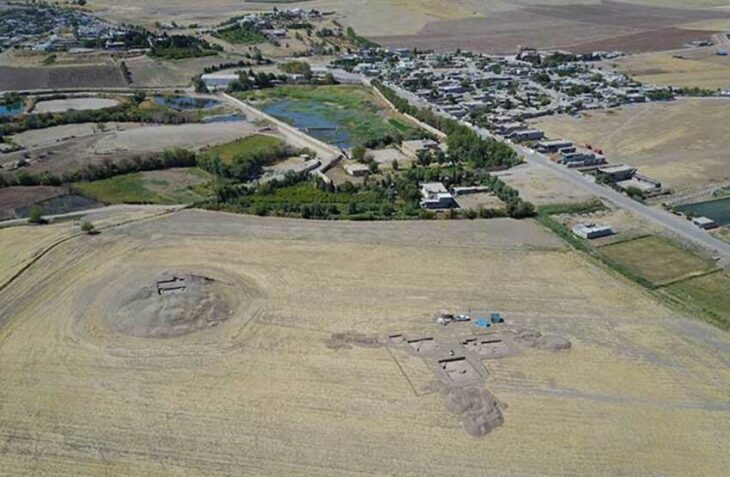
Smirnov also discussed broader archaeological research that has challenged long-held assumptions about Vyborg’s emergence as a city. Years of excavations have led archaeologists to a surprising hypothesis: at the moment Vyborg officially received city status, it may not have been a true city at all. Instead, findings suggest the presence of only the fortified castle and several impoverished fishing settlements around it.
This reinterpretation of Vyborg’s early development could redefine how historians understand the region’s political and social structure during the Middle Ages.
Conservation Efforts and Another Accidental Find
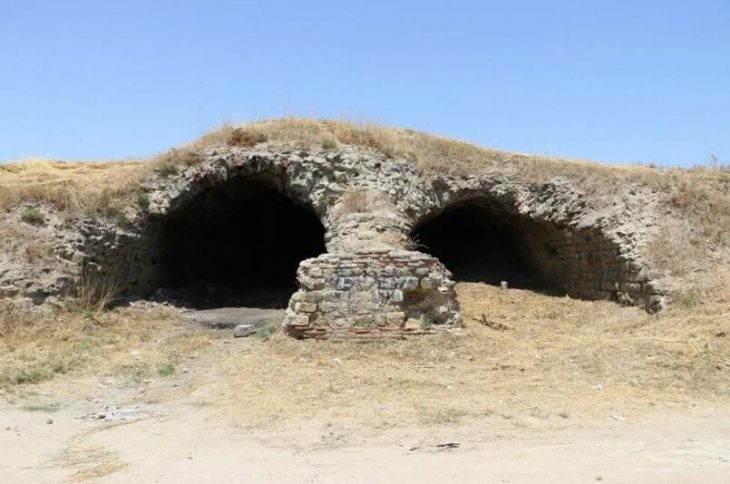
Archaeological activity continues across Vyborg. Conservation work is currently underway at the Old Cathedral, where specialists are stabilizing the ancient masonry. Meanwhile, another remarkable discovery occurred during slope reinforcement on Severnij Val Street in the city center.
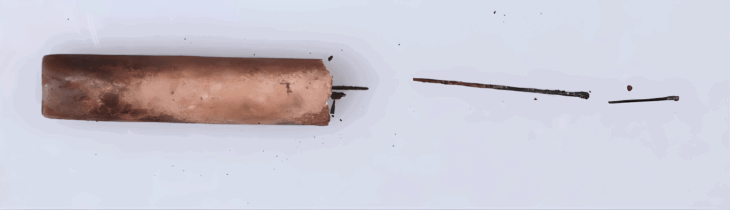
Workers uncovered an antique dagger at a depth of about one meter, prompting immediate interest from regional authorities. The Government of Leningrad Region confirmed the find on November 2.
“The dagger is now undergoing restoration and examination by specialists at Vyborg Castle,” said Vladimir Tsoy, Deputy Chairman of the regional government. “If its historical value is confirmed, it will become part of the museum’s collection and reveal yet another chapter of Vyborg’s past.”
Preliminary assessments indicate that the dagger dates back to the 19th century. Its shape resembles the Caucasian “kama,” a double-edged dagger whose name—borrowed from the Ottoman language—refers to this traditional weapon type.

A City Where History Surfaces in Unexpected Places
The rediscovery of the Tott family’s heraldic stone and the recent unearthing of a 19th-century kama-style dagger highlight the archaeological richness of Vyborg. These finds demonstrate how traces of the city’s medieval and post-medieval life continue to surface in unexpected locations—from castle fortifications to ordinary sewer structures and urban construction sites.
As research progresses, archaeologists believe even more revelations await, promising to deepen public understanding of a city whose layered history spans Swedish knights, medieval fortresses, and multicultural influence.
Cover Image Credit: Center for Rescue Archaeology of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS)