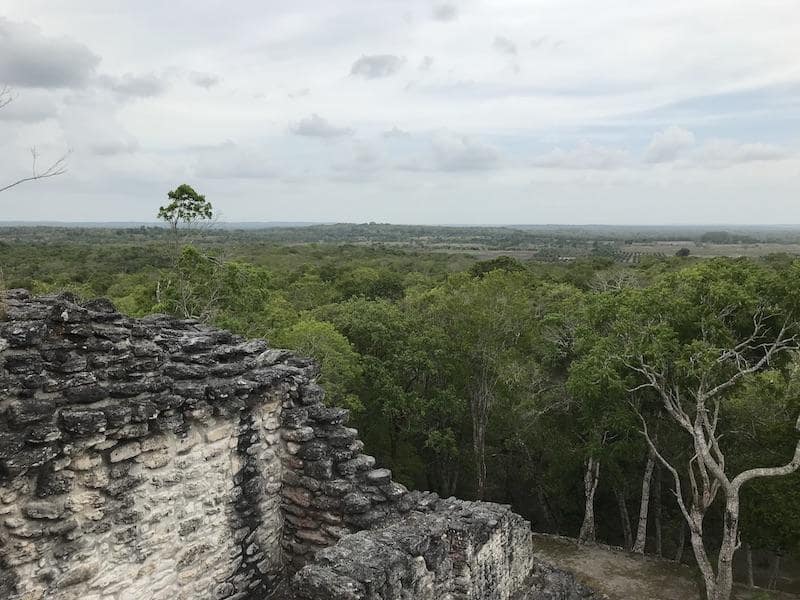
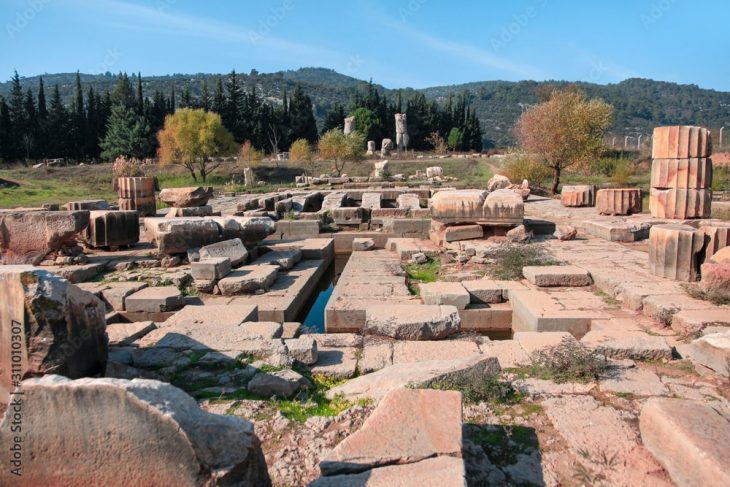
Tulane University researchers used laser-guided imaging to uncover vast unexplored Maya settlements in Campeche, Mexico, revealing more than 6,500 pre-Hispanic structures, including a previously unknown large city with stone pyramids.
The ability to examine large regions from the comfort of a laboratory thanks to Light Detection and Ranging (Lidar) technology has revolutionized the way archaic researchers study ancient civilizations in recent years.
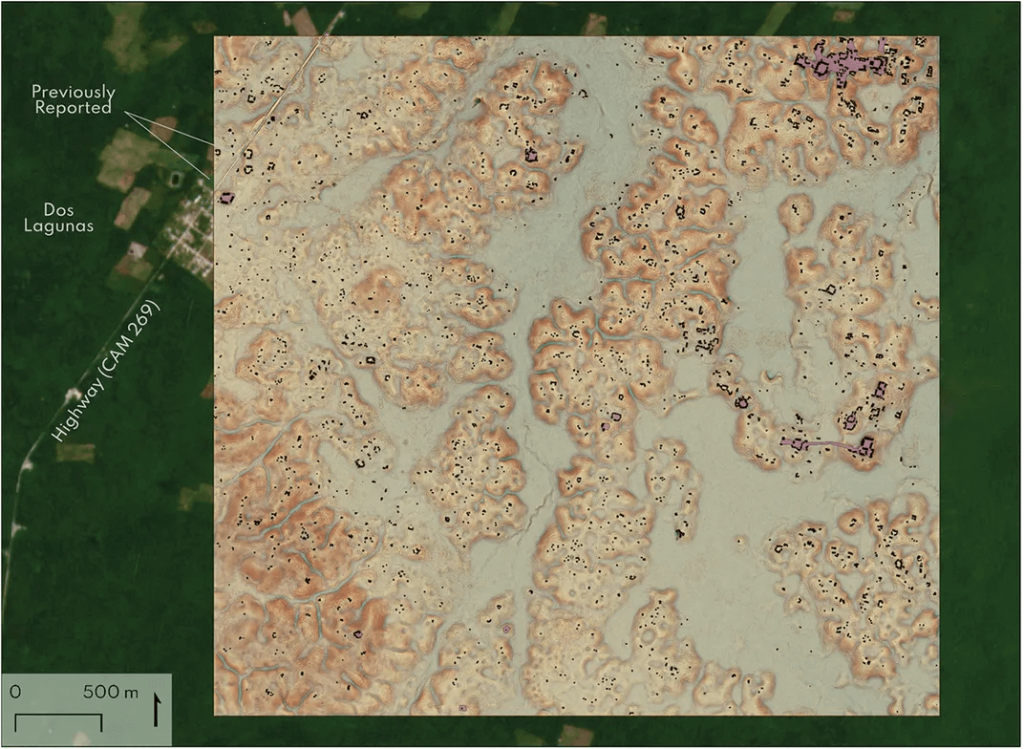
The research project, led by doctoral student Luke Auld-Thomas alongside his advisor, Professor Marcello A. Canuto, both affiliated with Tulane’s Middle American Research Institute (MARI), used Lidar technology to study an area of 130 square kilometers in Campeche.
As part of a “non-archaeological” survey, the 50-square-mile area was mapped in 2013 using lidar, a remote-sensing technology, according to a study published today in the journal Antiquity. Examining this “found” dataset, the researchers discovered the ancient city concealed in plain sight in a region teeming with Maya settlements. They found evidence of over 6,500 structures in all.
The research focuses on a part of Campeche that had previously been overlooked in traditional archaeological research.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
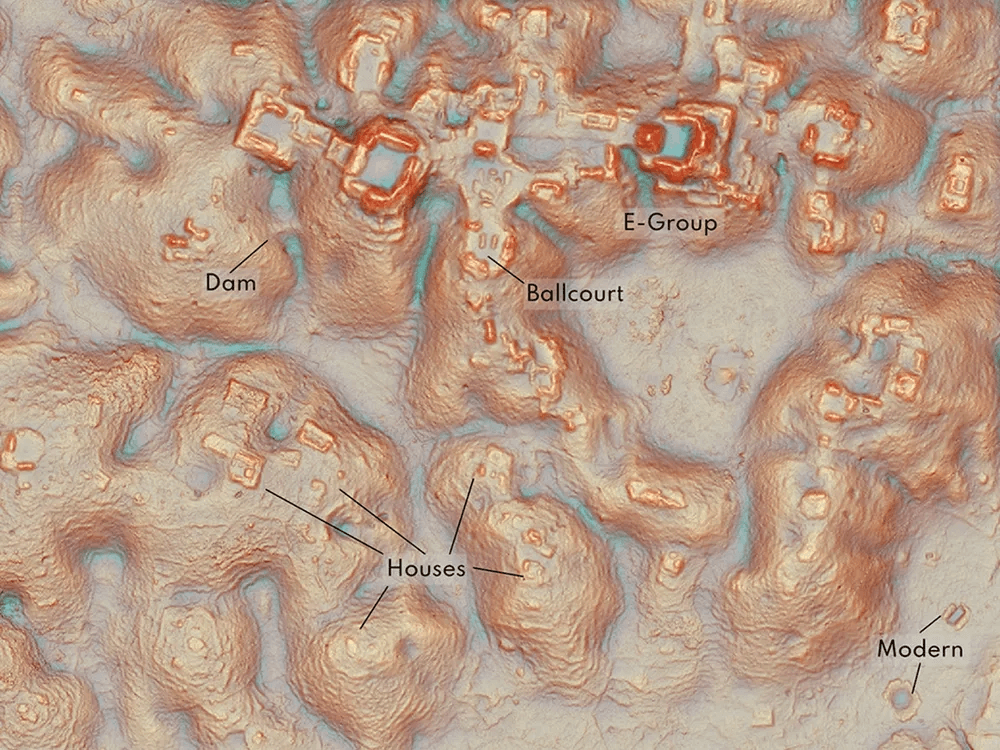
“The government never knew about it; the scientific community never knew about it,” says lead author Luke Auld-Thomas, an archaeologist at Tulane University, in a statement.
Researchers found not only rural areas and small communities but also a large city with pyramids, close to the only road in the area, near a village where farmers have been working among the ruins without the government or scientific community being previously aware of its existence.
The larger of the two “monumental precincts” that comprised the city “has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital,” according to the researchers. It included temple pyramids, a freshwater reservoir, several enclosed plazas that were connected, and a ball court where the Maya played games with rubber balls.
According to the study, Valeriana’s architectural layout indicates that some of the town was constructed before 150 C.E. It thrived during the Classic era, which roughly spanned 250–900 C.E. and was the Maya Empire’s golden age.
This discovery is particularly striking, as it underscores how much remains unknown about the Maya and that there is still much to uncover.
The researchers intend to visit Valeriana and the surrounding settlements in person to learn more about the ancient rural population of the Maya lowlands.
This study not only reveals previously unknown cities, but it also contributes to ongoing debates about the true extent of Maya settlements and their population density.
It has been contended, that prior research has mostly concentrated on sizable, well-known locations like Tikal, which may have skewed impressions of the Maya lowlands. According to some critics, the majority of the Maya region may have been rural, with big settlements being the exception rather than the rule. This perspective is called into question by the discoveries made in Campeche, which demonstrate how the Maya civilization created a network of communities in a vast tropical environment that varied in size and complexity.
“Lidar is teaching us that, like many other ancient civilizations, the lowland Maya built a diverse tapestry of towns and communities over their tropical landscape,” Canuto said. “While some areas are replete with vast agricultural patches and dense populations, others have only small communities. Nonetheless, we can now see how much the ancient Maya changed their environment to support a long-lived complex society.”
Cover Photo by Marcello Canuto
















