The Moche civilization and the Mochico culture were one of the pre-Inca civilizations that developed in the north of present-day Peru.
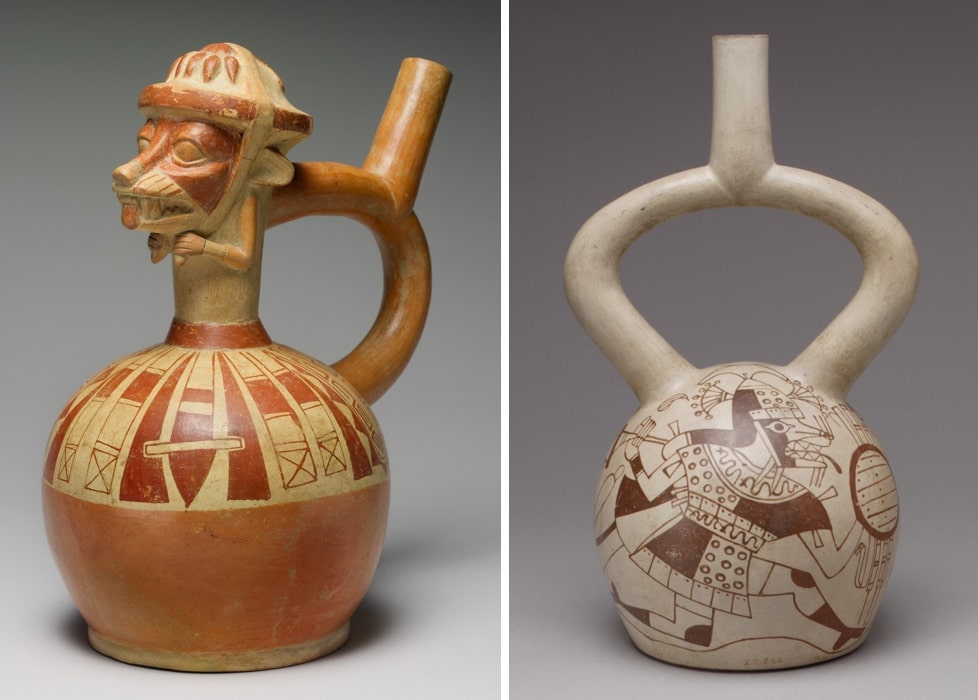
The Moche people were a civilization that thrived along Peru’s northern coast from roughly 100 AD until 700 AD. They were essentially a farming society. They also possessed excellent workmanship, as seen by their ceramics and jewelry. They are known for their monumental constructions (huacas) and irrigation systems.
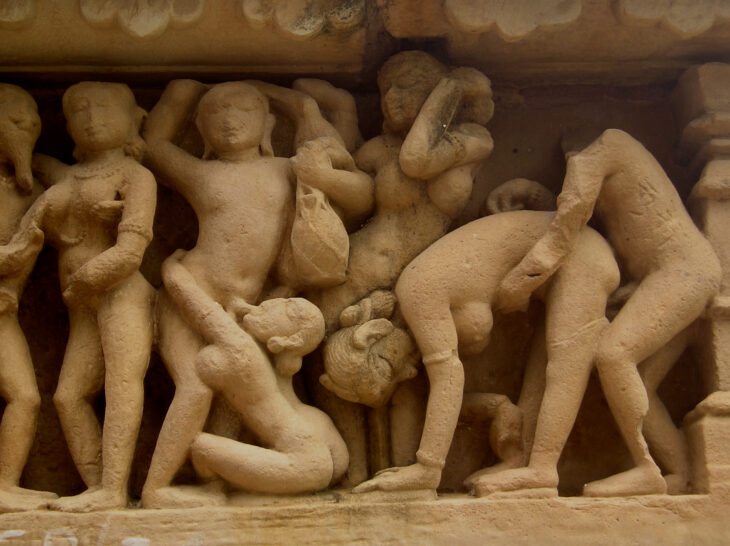
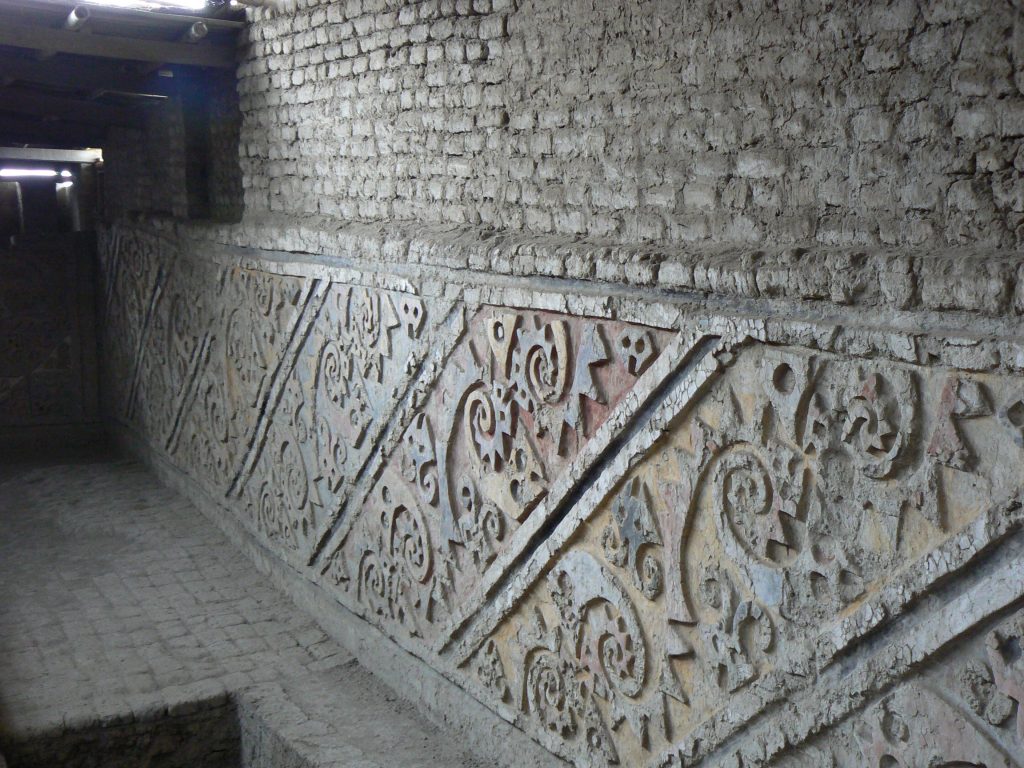
Of these monumental structures, Huaca del Sol is the largest pre-Columbian building in Peru. Near this building, which was partially destroyed in the 16th century, Huaca de la Luna is better preserved. The nearby Huaca de la Luna is better preserved. Its interior walls contain many colorful murals with complex iconography. The iconographies, the ceramics, the pottery, and the stories depicted on the walls of their temples, all show a great deal of violence, and vibrant cultures and rituals.
The Moche people participated in sex, violence, and sacrifices, according to what can be determined about their society. They celebrated life and nature, and they valued both life and death equally.

Lady of Cao
The Moche are likewise a remarkable people in that their iconography, pottery, and other features were extremely developed, yet one part of their civilization is noticeably absent. They have no written documents, unlike other known civilizations.
The Lord of Sipan was the first Moche mummy discovered. As a result, it was considered that the Moche civilization was a patriarchal or male-dominated society, but these beliefs were refuted with the discovery of Lady of Cao.

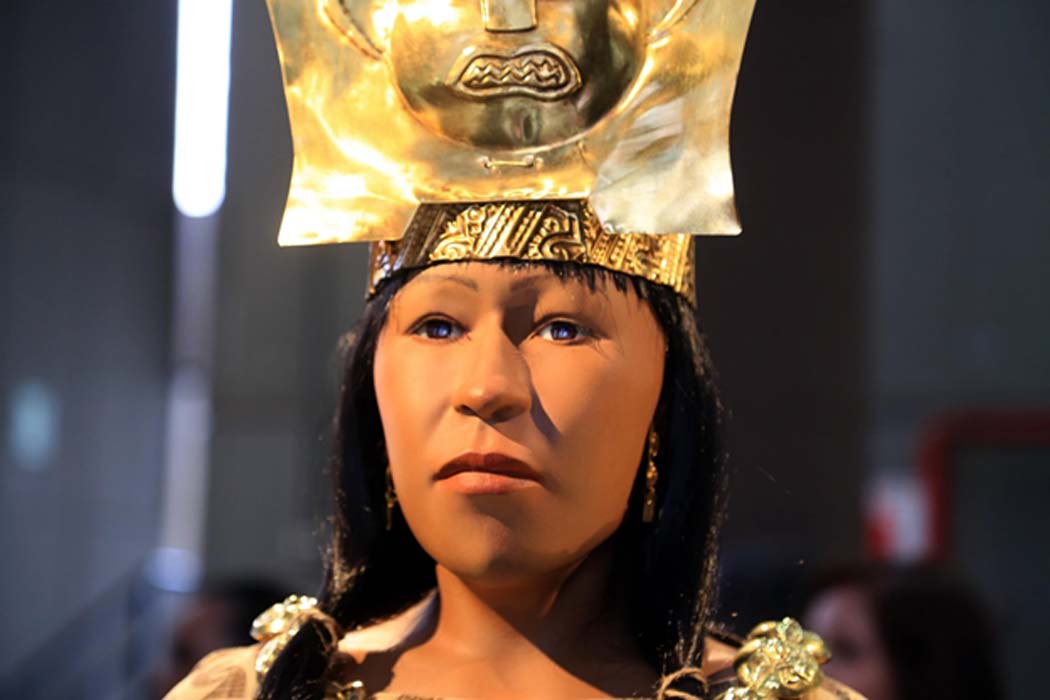
It is Peruvian archaeologist Regulo Franco, who in 2006, together with the Wiese Foundation, uncovered the discovery of the Lady of Cao, the first known woman with absolute power in the Moche civilization.
For 1,700 years, the remains of this woman with almost semi-divine powers were hidden in a splendid tomb at the Cao Viejo temple within the El Brujo archaeological complex some 60 kilometers (36 miles) from the city of Trujillo on Peru’s northern coast.
The Huaca el brujo was the Lady of Cao’s final resting place. The hallowed burial location of Huaca el Brujo is also known as Wizard’s Hill. All archaeologists were surprised to locate a female mummy in Huaca el brujo because it was considered that only males were buried there.
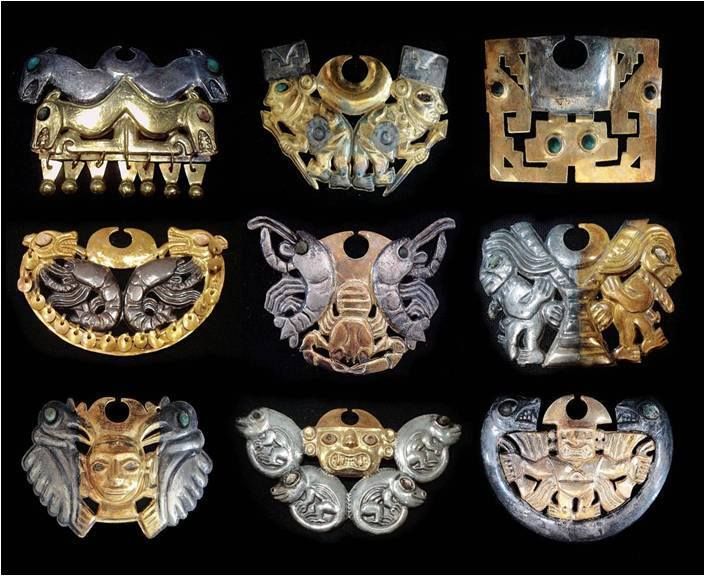

When her burial things, including the body, were retrieved, no archeologist could have guessed that the person enclosed among the surrounding 25 layers of fine fabric, cotton, and copper plates was a lady.
She had been buried there with her wealth and jewelry, along with five other people, including two priests, two bodyguards, and a teenage girl, in a room 275 square meters (almost 3,000 square feet) in size, decorated with murals depicting Moche cosmology and various divinities in the form of various animals.
She is estimated to have lived around 450 CE, and she died in her mid-twenties. It has been confirmed that she died during childbirth due to various complications.
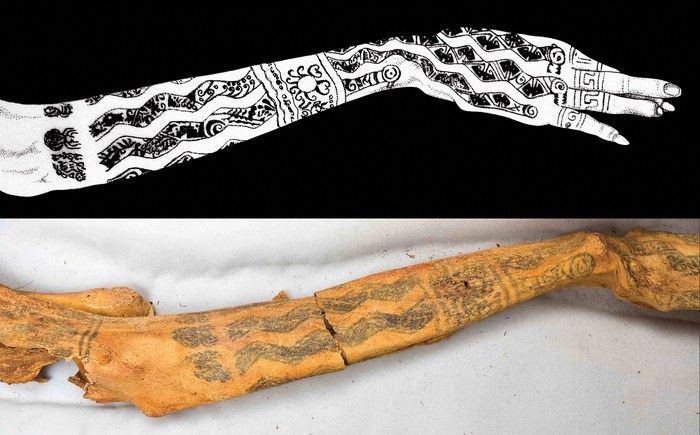
The mummy’s corpse was in good condition, due to the saline ocean in which it was most likely washed and then anointed with cinnabar (mercury sulfide) during the burial ceremonies. Furthermore, the Lady of Cao’s forearms and hands were covered with gorgeous tattoos of serpents, an indication of her religious authority as a healer and probably also as an oracle, and spiders, highlighting her ability as a weaver.
Lady of Cao was buried with gold, silver, and gilded copper jewelry. The many pieces of jewelry indicate that she may have been a high-ranking member of society. Because the Moche tribe did not intentionally mummify their deceased, it is considered that the Lady of Cao was an exception.
This had clearly changed the outlook of a male ruled Moche society. In subsequent years, as many as eight other priestess queens’ remains have been unearthed from the Moche burial sites.
El Brujo also has the unique feature that it’s an enclave that was first occupied 14,000 years ago.
Considered the most powerful woman in ancient Peru, the Lady of Cao rewrites the history of pre-Hispanic civilizations, although she continues to keep many secrets.