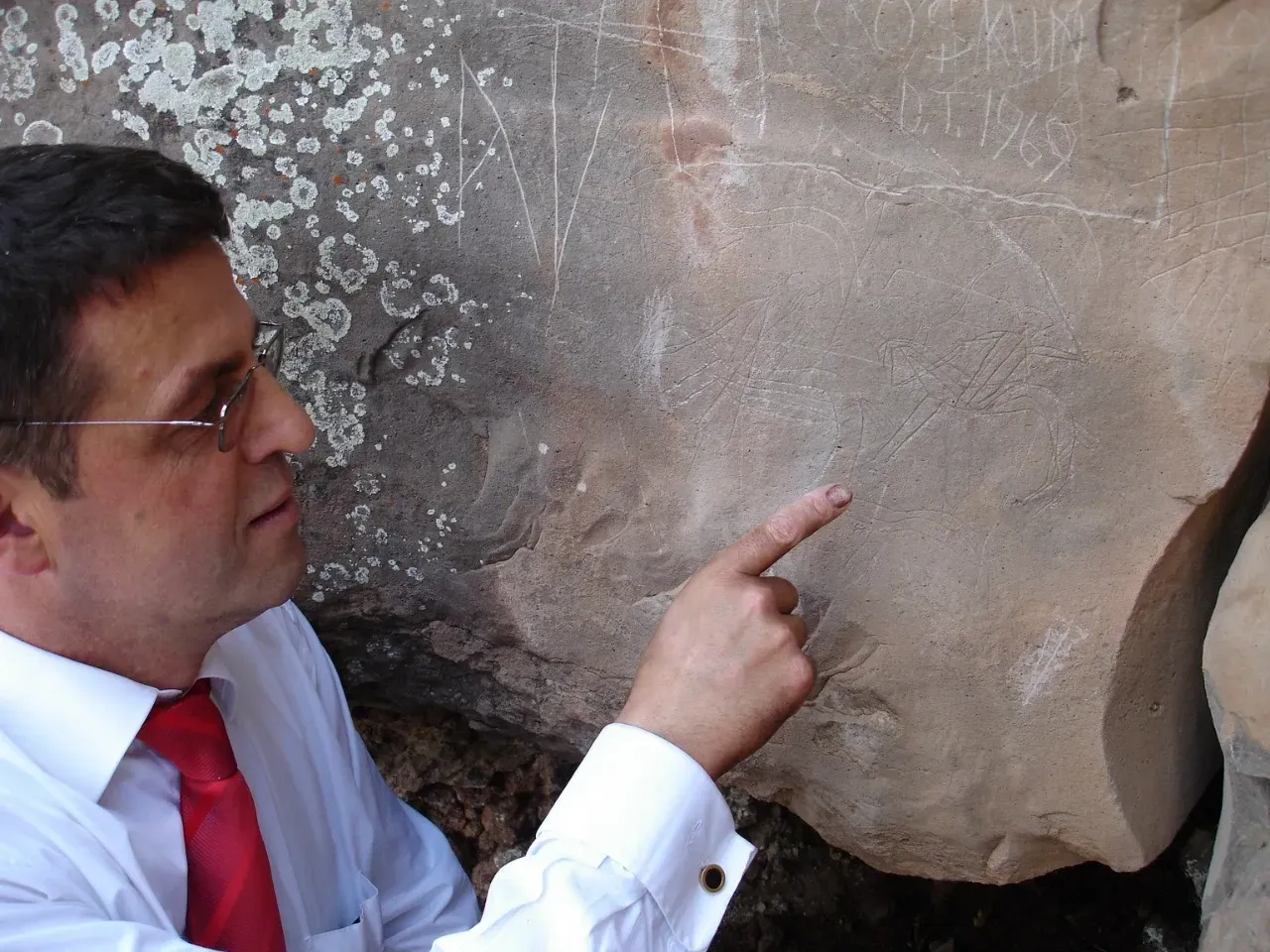
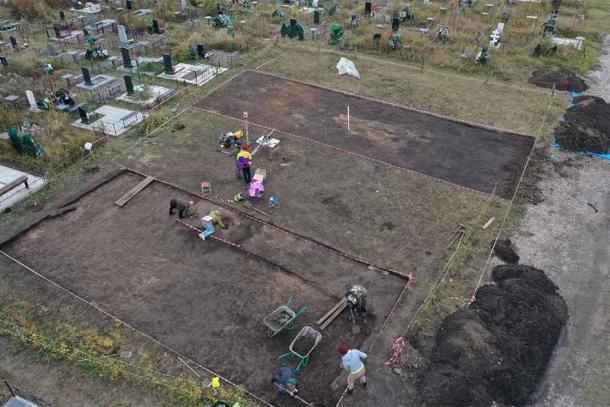
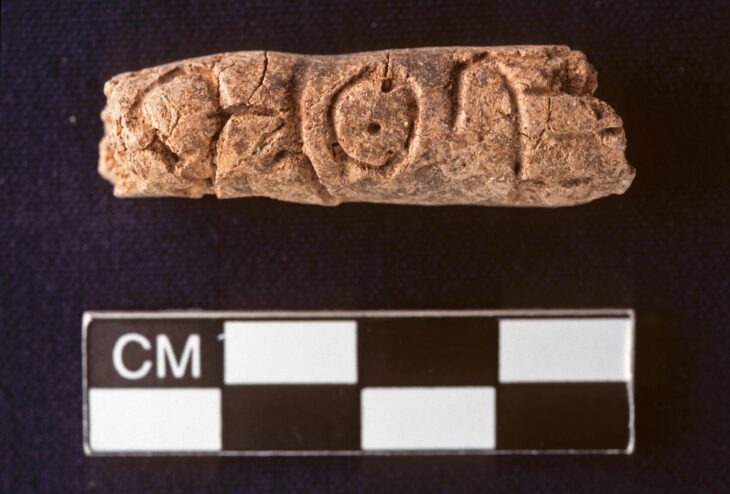
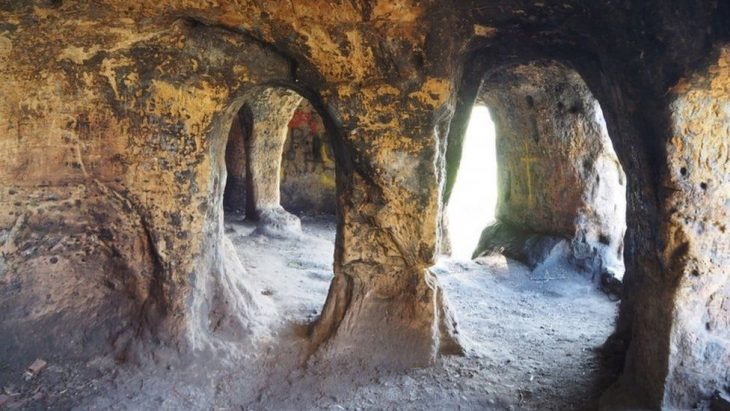
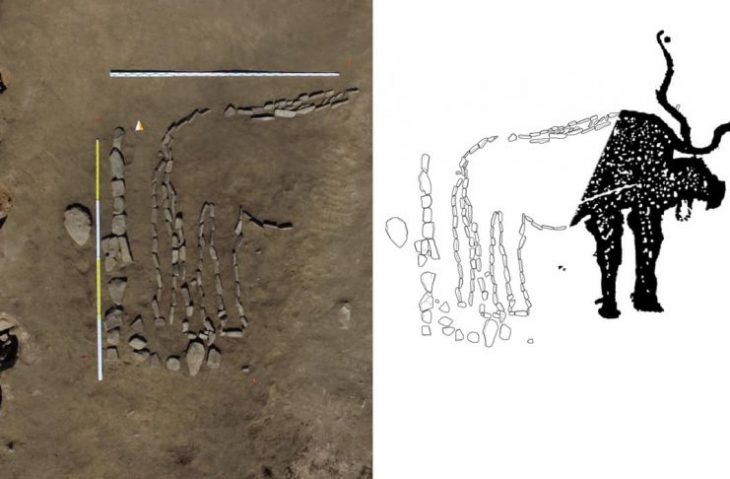
Researchers made a significant discovery during field research conducted in 1994 in Esatlı village, Mesudiye, Ordu. They introduced a series of remarkable rock carvings and Esatlı Kaya Inscriptions.
These images and figures, believed to have been created in the early centuries of Christianity, are considered among the most important examples of their kind, spanning a geographical range from Siberia to France and Portugal. Surrounding these inscriptions, which are thought to have been crafted by Turks practicing Tengriism (Shamanism), are ancient tumuli that indicate old Turkish settlements and burial sites.
The petroglyphs and inscriptions found in Esatlı hold additional significance as they illustrate the evolution of written communication. This site provides a unique opportunity to observe the progression from petroglyphs to ideograms, pictograms, markers, syllables, semi-syllables, and letters. It serves as a vital link in understanding the stages of development from primitive rock carvings to the formation of written language.
However, these important inscriptions are now facing the threat of disappearance, highlighting the urgent need for preservation efforts to protect this invaluable cultural heritage.
Prof. Dr. Necati Demir, a faculty member at Gazi University, has made significant statements regarding the Esatlı Kaya Inscriptions (Esatlı Rock Inscriptions) located in Mesudiye, Ordu. He emphasized that these inscriptions are not only an important cultural heritage of the region but also a crucial part of Turkish history. According to Demir, the Esatlı Kaya Inscriptions are among the areas with the highest concentration of Turkic script, second only to the Göktürk inscriptions. These inscriptions provide valuable insights into prehistoric Turkish migrations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

In his field studies conducted in the 1990s, Demir identified the Esatlı Kaya Inscriptions among other significant cultural findings. He noted that these inscriptions consist of both written expressions and rock paintings, closely resembling those found in Kyrgyzstan, which further enhances their historical importance.
The inscriptions are written in the Göktürk alphabet, one of the earliest known Turkic scripts, which dates back to the 7th century. This script was used by the Göktürk Khaganate and is characterized by its angular shapes and distinctive characters. Prof. Dr. Demir explained that the inscriptions are in the handwritten form of the Göktürk alphabet, which he has successfully deciphered. He pointed out that these writings have a similar structure to the inscriptions found on the ceiling of the Hagia Sophia Church in Trabzon. However, he lamented that the deterioration of the inscriptions complicates the deciphering process.
Highlighting the urgent need for protection, Demir stated that many of the inscriptions have been damaged over time. He has urged authorities to declare the region a protected area, but so far, no concrete steps have been taken. He stressed the importance of allocating more resources for the protection of cultural heritage and ensuring coordination among relevant authorities. Additionally, he called for international recognition and protection of the Esatlı Kaya Inscriptions, emphasizing the crucial role of UNESCO in this effort.
Demir also pointed out the potential for the Esatlı Inscriptions to be included in the UNESCO World Heritage list, noting that serious efforts are needed in this regard. He expressed concern that without prompt action, Turkey risks losing this significant part of its history, especially as other countries, like Iran, are actively protecting similar inscriptions.

Furthermore, he highlighted the tourism potential of the Esatlı Inscriptions, suggesting that they could attract visitors from around the world if the area were transformed into a museum and declared a protected site. He compared the potential of Esatlı to Gobustan in Azerbaijan, which draws thousands of visitors annually.
Demir also addressed the need for archaeological excavations in the region, stating that while treasure hunters have already caused damage, careful excavations could yield valuable findings that would help establish the exact dating of the inscriptions.
In conclusion, Prof. Dr. Necati Demir called for an urgent action plan to protect the Esatlı Kaya Inscriptions, emphasizing their significance not only for Ordu but for all of Türkiye. He warned that failure to act could result in the loss of this invaluable heritage and the severing of historical ties.
In his article titled “The Petroglyphs and Inscriptions in Esatlı Village (Ordu-Mesudiye) and Their Historical Background,” Professor Necati Demir provides further insights into the significance and historical context of these remarkable inscriptions. For more detailed information on the subject, you can read his article.
This article is based on an interview conducted by Mertcan Deniz for the local media outlet Ordu Olay newspaper.
Cover Image Credit: Ordu Olay – Mertcan Deniz