A new study of early Bronze Age examples from Luxembourg and Britain, led by researchers from the universities of Mainz and Ferrara, finds indications of a patrilineal descent system for western Eurasian Bell Beaker communities. / Family relationships that link Britain to Luxembourg.
Poignant prehistoric burials containing the remains of an adult and child laid in the grave as though embracing in death have long fascinated archaeologists. A new study of early Bronze Age examples from Luxembourg and Britain provides insights into family relationships in prehistoric communities and the transition from collective to individual burial in 3rd millennium BC Western Eurasia. The results provide the first genetic evidence that Bell Beaker communities in Northwest Europe buried children with their biological mothers and other close biological relatives.
Astonishing similarities between a double burial in Luxembourg and a British grave 500 kilometers away
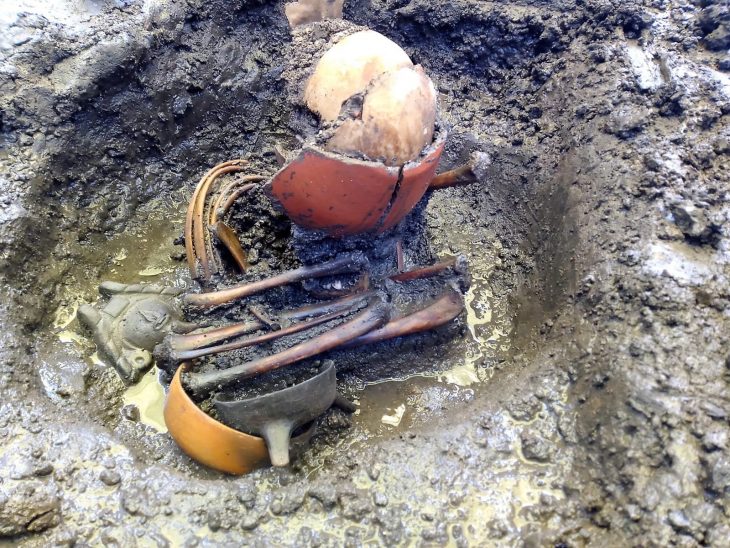
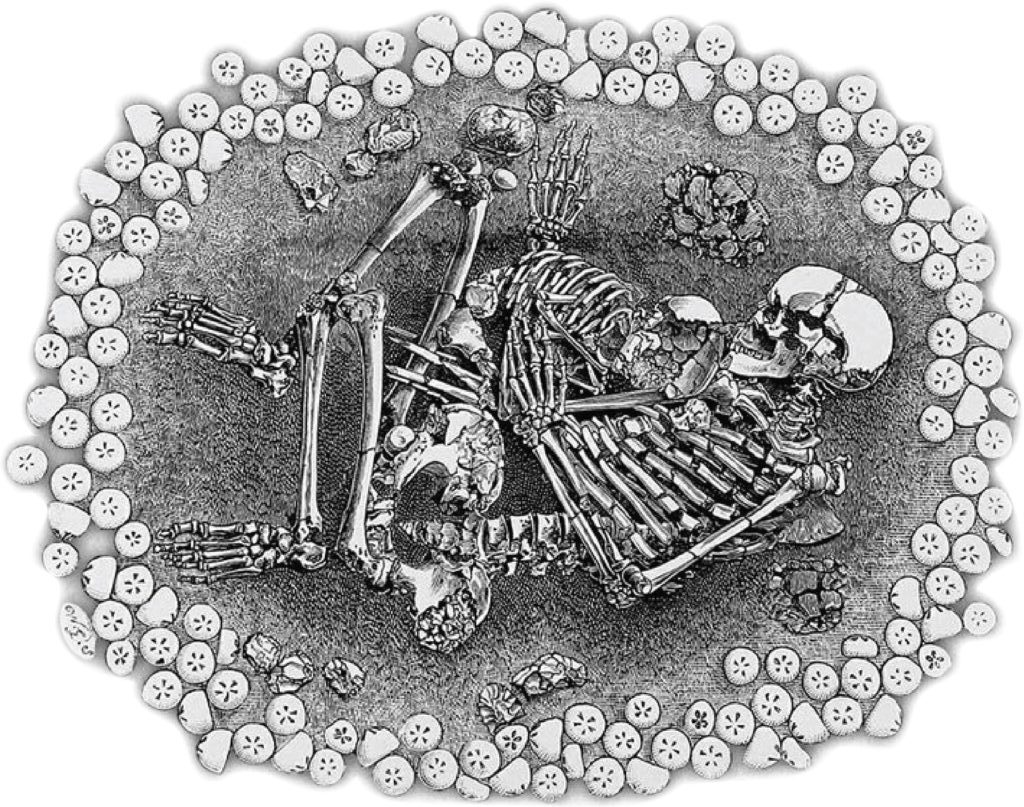
In 2000, archaeologists from Luxembourg working on the construction of a highway in the south of the country at Altwies ‘Op dem Boesch’, discovered graves dated to the Bell Beaker period (2450 – 1800 BC). One grave contained the skeletons of a woman and child, buried facing each other, the adult holding the head of the dead child in her hand in a final gesture of maternal love.
As part of a new project on the prehistory of Luxembourg, this ancient family tragedy has now provided a team of European researchers with an opportunity to answer wider questions about Bronze Age burial practices and family relationships in Europe using archaeology, anthropology, and ancient DNA. For the burial was not unique. Work by Dr Foni Le Brun-Ricalens, Director of the Institut National de Recherches Archéologiques (INRA) and one of the instigators of the study, uncovered another hauntingly similar grave from a round barrow at Dunstable Downs in Bedfordshire in Britain – more than 500 kilometers away from Altwies.
This burial, uncovered in 1887, led archaeologist Dr. Maxime Brami of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), one of the lead authors of the study, to investigate whether the two graves were connected in some way. What was the particular significance of the double burial? Did the adult and child die together, perhaps violently? Did these families know each other? Why were the burial rituals so similar? To answer these questions, a team was put together to analyze and compare the grave goods and skeletal remains from the graves in Britain and Luxembourg.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Ancient DNA analysis reveals that adults and children were closely related
The bones from Dunstable Downs were traced to Luton Cultural Trust with the help of Elise Naish, Head of Heritage and Collections at Luton Cultural Trust, and Dr. Katie Meheux from the UCL Institute of Archaeology Library. Despite their early excavation date in the late 19th century, the provenance of the skeletons was well-documented and the bones were in a good state of preservation. Anthropologist Dr. Nicoletta Zedda from the University of Ferrara, a lead author of the study, was able to examine the remains. Together with geneticists from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), she was able to analyze the genomes of all four skeletons from the two adult-child burials.
The DNA revealed fascinating insights into shared ancestry and culture in Early Bronze Age Europe. All four individuals, although separated by hundreds of kilometers, traced most of their ancestry from steppe populations that migrated from Eastern and Central Europe in the 3rd millennium BC. Perhaps more significant was the intriguing family relationships revealed. “The skeletons from Altwies were of a woman and a boy of around three years of age, and DNA analysis revealed that they were indeed mother and son,” explained Dr. Nicoletta Zedda. “The picture looks different for Dunstable Downs: a young woman and a girl about 6 years old, but DNA revealed they are in fact paternal aunt and niece.”
Genetic data suggest a patrilineal descent system
In continental Europe, the orientation of Bell Beaker graves followed strict rules based on the sex of the individual. In Altwies, the orientation of the grave was aligned with the sex of the child, a male, and not that of his biological mother. At Dunstable Downs, the adult and child were second-degree related on the paternal side, suggesting that here a paternal aunt perhaps played the role of substitute parent or primary caregiver for the child, at least in death. “The data might hint at a patrilineal descent system for western Eurasian Bell Beaker people,” affirmed archaeologist Dr. Maxime Brami. “And our findings suggest that – at least in some Early Bronze Age communities – extended families lived and buried their dead together, placing emphasis on biological and kin relationships.”
A highly codified burial practice with a lost meaning
The cause of death and reasons for joint burial are still unknown. No marks of violence were found on the skeletons. Further research for the project uncovered over a hundred joint burials of adults and children similar to the ones described here across Eurasia, dating from the 3rd and 2nd millennium BC. The researchers could propose many explanations for joint burial and simultaneous death, perhaps violence, infections, or pandemics, but the astonishing similarities between the burials from Luxembourg and Britain suggest that communities, indeed perhaps families, in Bell Beaker Europe mourned their dead according to widely held and closely followed formal rituals. “The body of a woman, lying as though sleeping, clasping a child in her arms, is poignant and emotive. Although that peaceful image may be deceptive, it still reflects a lost meaning retained across thousands of miles and amongst many diverse cultures,” emphasized Dr. Maxime Brami.
Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-45612-3
Cover Photo: Skeletal remains of an adult and a child at Dunstable Downs (ill./©: illustration from the book “Man, The Primeval Savage” (1894) by Worthington Smith