The role of culture in human spread: Digital data collection contains 150 years of research.
Human history in one click: For the first time, numerous sites relating to the early history of mankind from 3 million to 20,000 years ago can be accessed in a large-scale database.
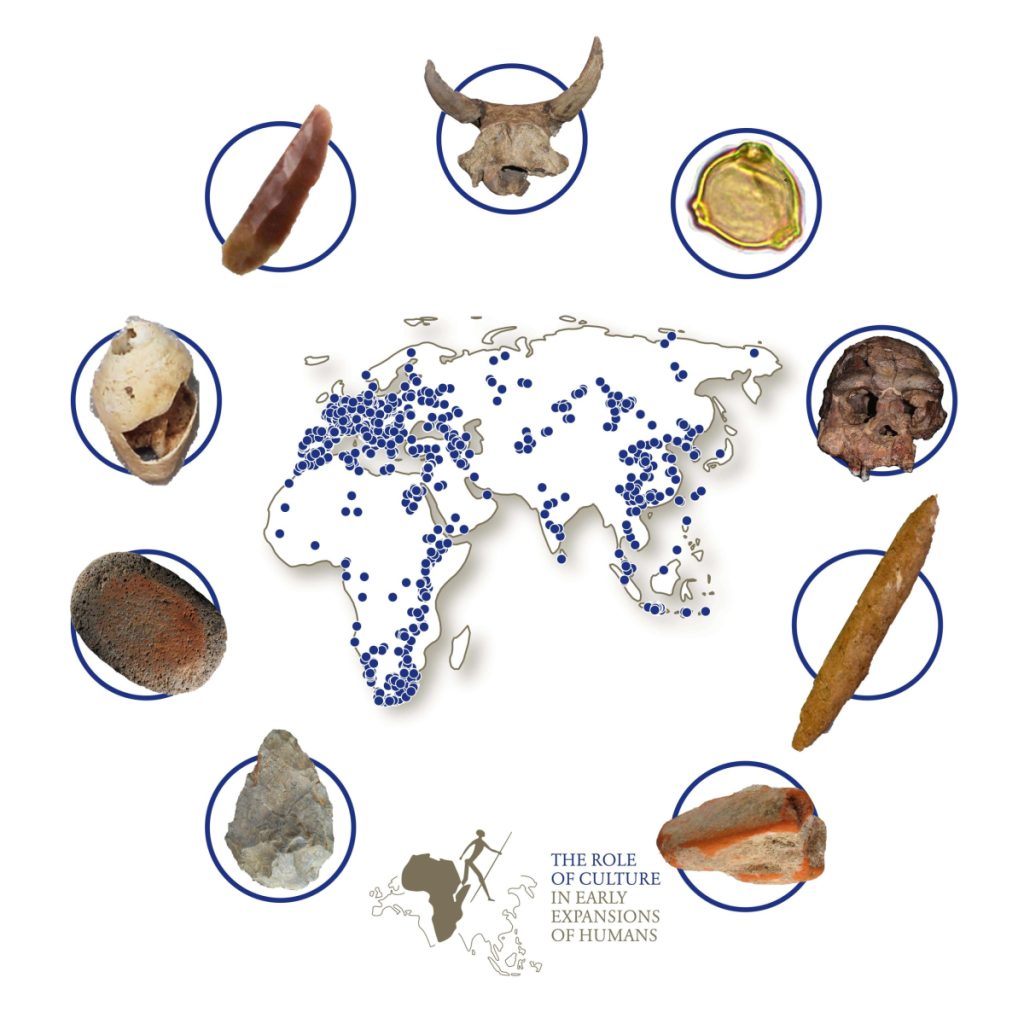
Scientists from the research center ROCEEH (“The Role of Culture in Early Expansions of Humans”) have compiled information on 2,400 prehistoric sites and 24,000 assemblages from more than 100 ancient cultures. The digital data collection is available for free to scientists and amateurs and was recently published in the journal PLoS ONE.
The research center is located at the University of Tübingen and the Senckenberg Society for Nature Research, sponsored by the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences and Humanities, and funded in part through the Union of German Academies.
ROAD, the “ROCEEH Out of Africa Database”, represents one of the largest digital collections of information about archaeology, anthropology, paleontology and botany based on 150 years of research history, says Dr. Andrew Kandel, University of Tübingen. By joining information about cultural remains, human fossils, animal bones and plants into a unified geographical and chronological framework, the team created a tool that helps analyze the complex aspects of human evolution.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Since 2008 an international team of six scientists and dozens of research assistants painstakingly compiled the data. More than 5,000 publications in multiple languages were analyzed, including Chinese, Russian, English, German, French, Italian, Spanish and Portuguese.
An easy-to-use map interface shows the distribution of sites across the globe. It also allows users to graphically present the results of simple queries, so a user can make their own map by selecting a specific culture, period or region of interest. In addition, a user can also download a PDF “ROAD Summary Data Sheet” containing a site summary.
“Scientists can use ROAD to formulate advanced queries”, says Kandel. “For example, a query can help establish the presence of different categories of stone tools across Africa, or the distribution of specific animals, like horse, rhinoceros or reindeer during periods when the glaciers advanced or retreated. Such queries provide researchers with large quantities of data which they can further study using various methods of visualization and analysis.”
ROCEEH designed ROAD to better understand the deep history of our human past. “We examine the multi-faceted relationship between culture and environment and observe its impact on human expansions.” In the spirit of open science, the team makes this data freely available to the general public, students, and researchers across the globe.
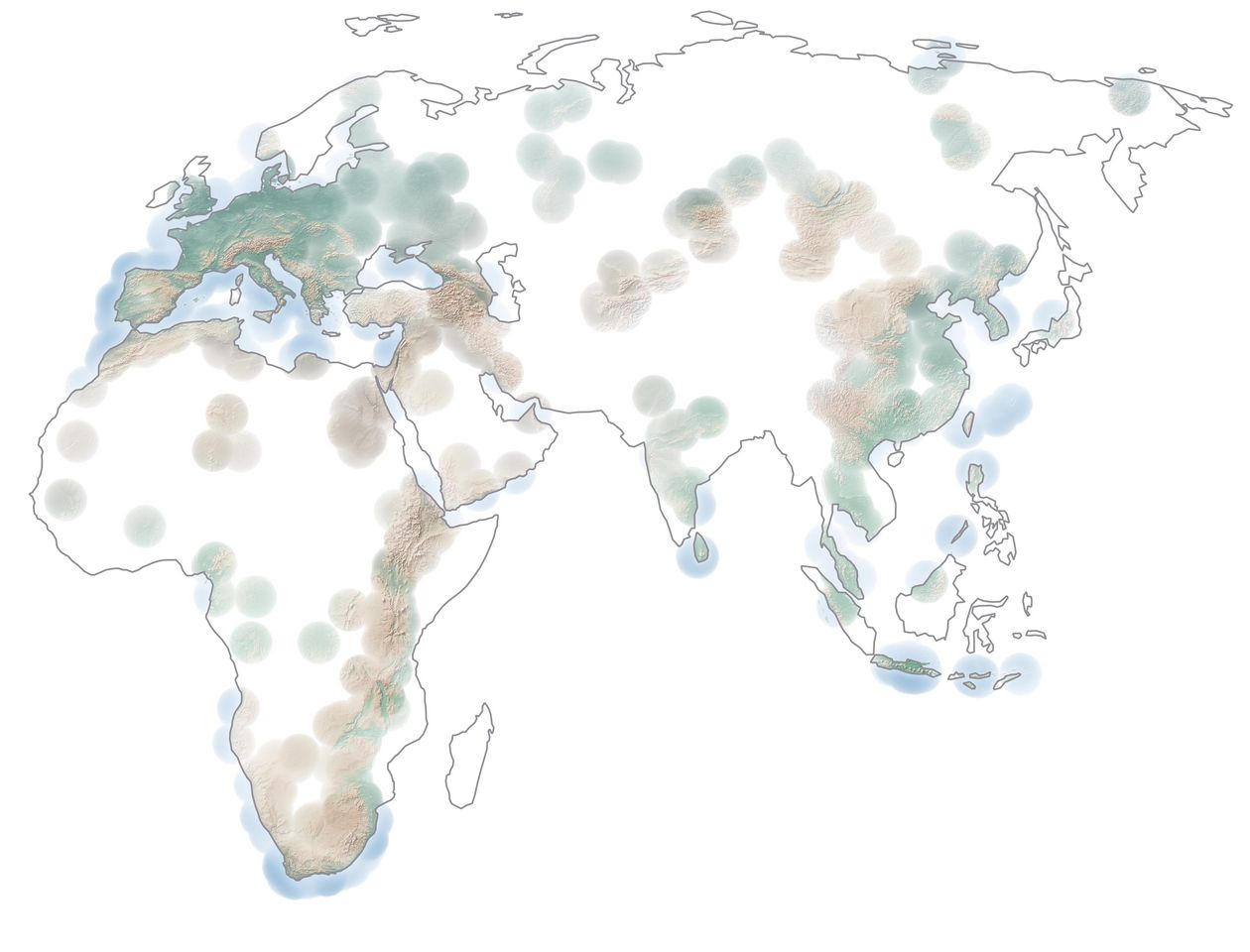
The collection of these data has already shown that much of the scientific knowledge about our past comes from just a few, very well-studied regions such as Southern and Eastern Africa and Europe, as well as Central and East Asia. However, Oceania was not part of the study. The blank spots hint at the expectation of exciting future discoveries about our species’ past from the fields of archaeology and anthropology.
Free Database ROAD: https://www.roceeh.uni-tuebingen.de/roadweb/
“The Role of Culture in Early Expansions of Humans” (ROCEEH): www.roceeh.net
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0289513
Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen
Cover İmage: The majority of the prehistoric world remains uncharted, as shown by the blank areas of this map. This visualization is based on a Kernel Density Estimate of assemblages in ROAD. Sites with higher densities of assemblages appear more intense in color. Oceania is not within ROAD’s scope. Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen