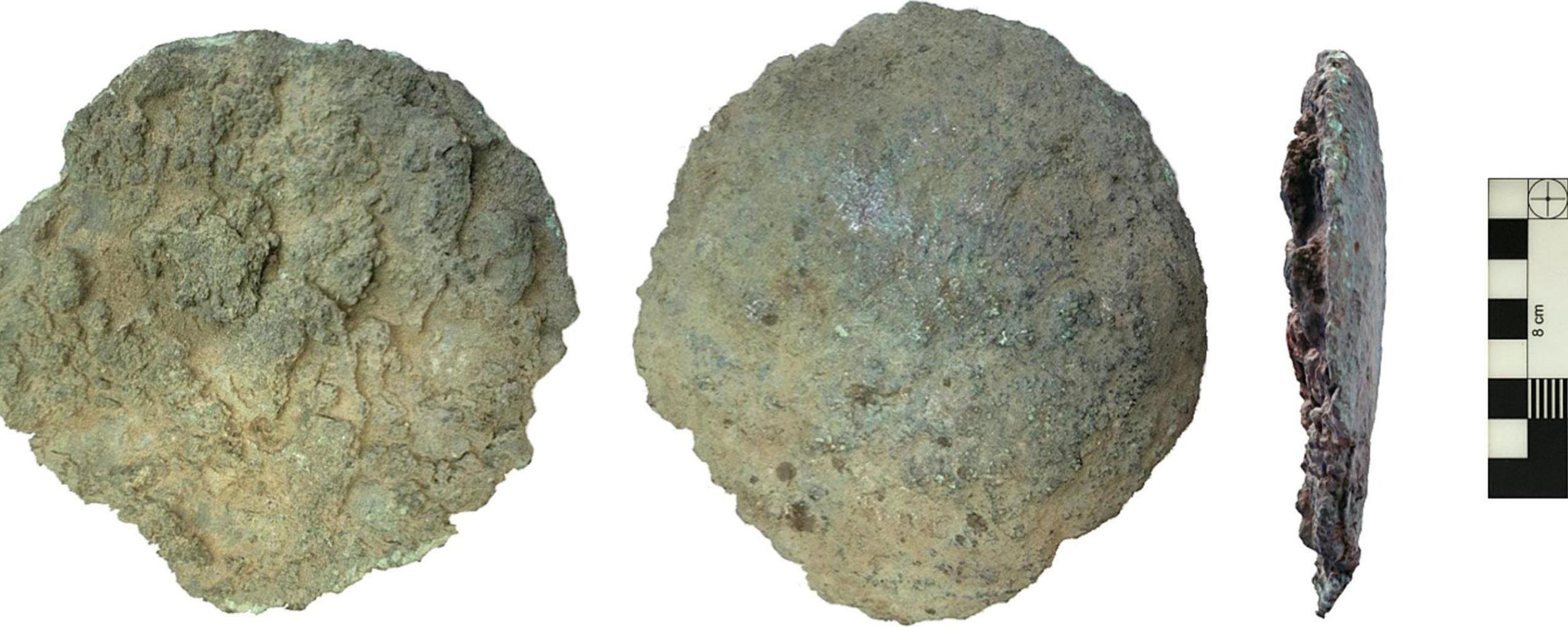
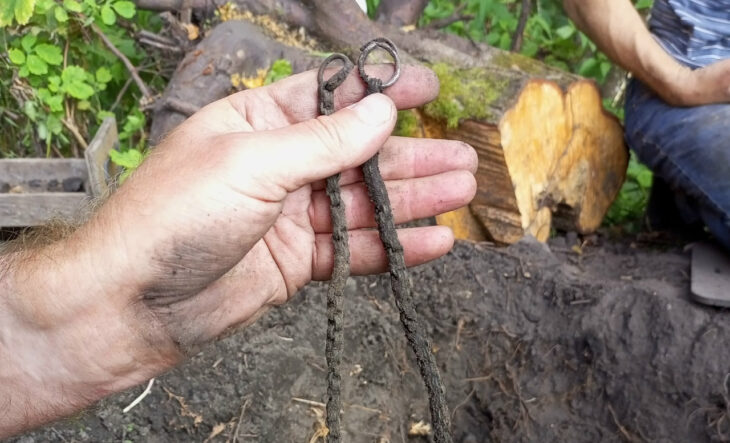
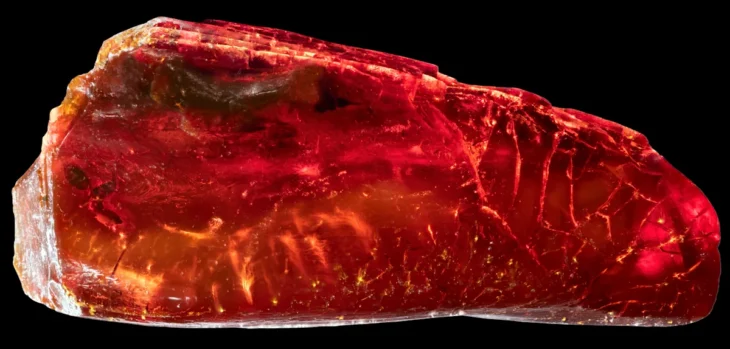
Archaeologists have discovered Sweden’s first complete plano-convex ingot, revealing Iron Age maritime trade links between the Iberian Peninsula, Scandinavia, and the Baltic Sea through advanced chemical and isotopic analysis.
The discovery was made in Särdal, Halland County, where a local family unearthed the 1.2-kilogram ingot while digging a fence post in their garden. Initially presumed to be Bronze Age, the artefact puzzled experts because it lacked an archaeological context. Researchers from the University of Gothenburg’s Department of Historical Studies launched a detailed investigation, conducting lead isotope and elemental analyses to determine its age and origin.
“Due to its shape and size, we initially assumed it was a Bronze Age artefact,” said archaeologist Dr. Serena Sabatini, who led the study. “However, the ingot turned out to be a copper–zinc–tin–lead alloy typical of the Iron Age and later periods.”
Plano-convex ingots, sometimes called “bun ingots,” were widely used as transportable metal units throughout Europe and the Mediterranean during the Bronze and Iron Ages. While such finds are common in southern Europe, this is the first time a complete example has been confirmed in Sweden.
Collaboration Unlocks a Bigger Picture
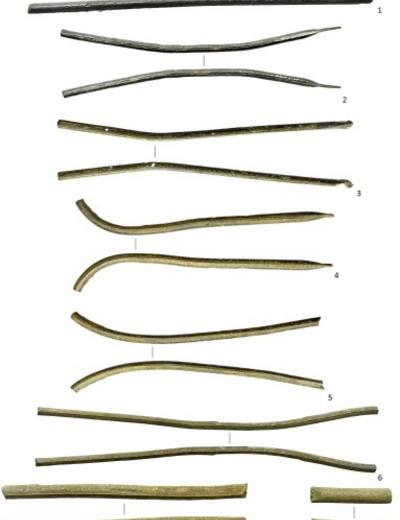
When the Swedish team compared their findings with those of Polish researchers studying hoards of rod-shaped ingots from the Iława Lakeland region in northeastern Poland, they uncovered a striking similarity. Both sets of artefacts were made of the same quaternary alloy and traced back to copper ore deposits in southwestern Spain’s Iberian Pyrite Belt, a region exploited for copper, silver, and lead since the Bronze Age.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Networking and international collaboration are key,” Sabatini emphasized. “By combining isotopic data with historical and archaeological knowledge, we were able to place this unique find in a broader context. Without our Polish colleagues, we would not have reached these conclusions.”
Tracing Ancient Trade Routes
Lead isotope analysis indicates that the Iberian mines supplying Scandinavia in the Bronze Age continued exporting copper well into the Pre-Roman Iron Age (c. 500 BCE–0 CE). The ingot’s maritime discovery location, close to Sweden’s west coast, suggests that trade routes established during the Late Bronze Age remained active for centuries, connecting Iberia to Scandinavia and the Baltic.
This finding strengthens earlier hypotheses that southern Scandinavia was deeply integrated into Atlantic and Baltic maritime networks, not only exchanging goods but also sharing cultural practices, technologies, and even burial customs.

Scientific Methods Drive New Insights
The study employed advanced archaeometallurgical techniques, including Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM-EDS) and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS), to analyze the ingot’s microstructure and alloy composition. These tests revealed high purity and deliberate alloying practices rather than accidental contamination.
The Polish ingots, discovered between 2013 and 2015 in Iława and Łanioch, were also studied using the same methods, confirming that they belong to a chemically and isotopically homogeneous group.
“Our results suggest that these artefacts represent ready-made alloy ingots circulating during the Iron Age,” said Sabatini. “They offer tangible evidence of a sophisticated, interconnected metal trade system across northern Europe.”
Redefining Isolated Finds
Traditionally, isolated finds like the Särdal ingot are considered difficult to interpret due to their lack of archaeological context. This study demonstrates that a multidisciplinary approach, combining chemistry, geology, and archaeology, can unlock their stories.
“These results show that single finds, when studied in depth, can significantly contribute to our understanding of ancient economies and long-distance trade,” Sabatini added.
A Glimpse into Northern Europe’s Early Globalization
The discovery highlights a period of early globalization in northern Europe, when metal circulated across vast distances, linking mining hubs in Spain with elite societies in Scandinavia and the Baltic. This research not only fills gaps in Iron Age history but also illustrates the value of data sharing among scientists.
The plano-convex ingot is now part of the Halland Museum of Cultural History collection, and the Polish rod ingots are housed at the Museum of Warmia and Masuria in Olsztyn.
Sabatini, S., Nordvall, L., Nowak, K., Stos-Gale, Z., Oudbashi, O., Sobieraj, J., Karasiński, J., & Wranning, P. (2025). Iron Age metal trade between the Atlantic and the Baltic Sea: New insights from the first complete plano-convex ingot found in Sweden and ingot rods from the Iława Lakeland in northeastern Poland. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 66, 105312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2025.105312
Cover Image Credit: The plano-convex ingot from Särdal, Halland, Sweden. Credit: Sabatini et al., 2025, Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports