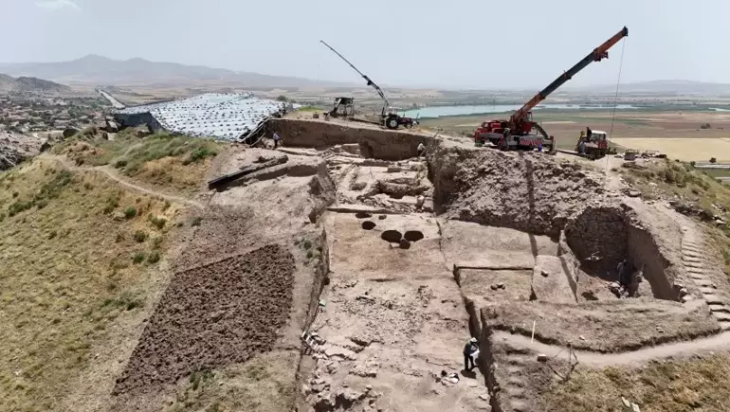
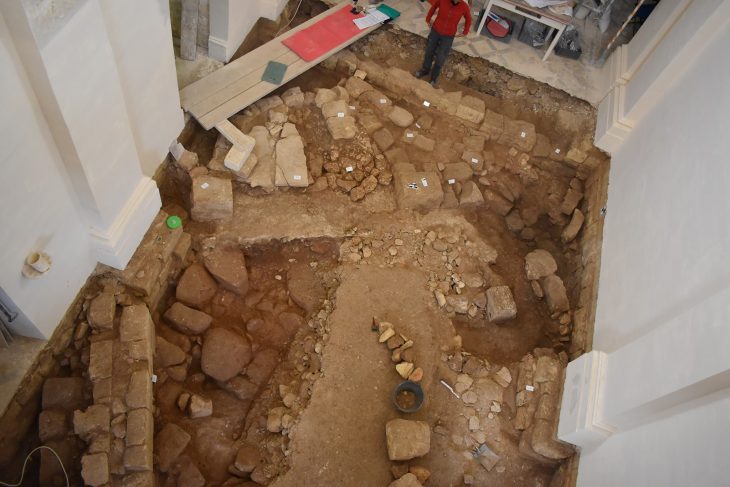
Archaeologists from the University of Illinois Chicago have uncovered a temple complex constructed by the Wari Empire 1,200 years ago at the Pakaytambo site in southern Peru (A.D. 600-1000).
The Wari were a Middle Horizon civilization that flourished in the south-central Andes and coastal area of modern-day Peru. The Wari people spoke their own language and created beautiful tapestries and weavings that have survived and can be seen in museums today.
The Wari, who had Huari as their capital, used their wealth of landscapes to build an empire with provincial capitals linked by an extensive road system. Their empire-preserving strategies and artistic style would have a significant impact on the subsequent Inca civilization.
This is one of several recent finds of Wari D-shaped temples across Peru, where Wari state expansion and influence previously were unclear.
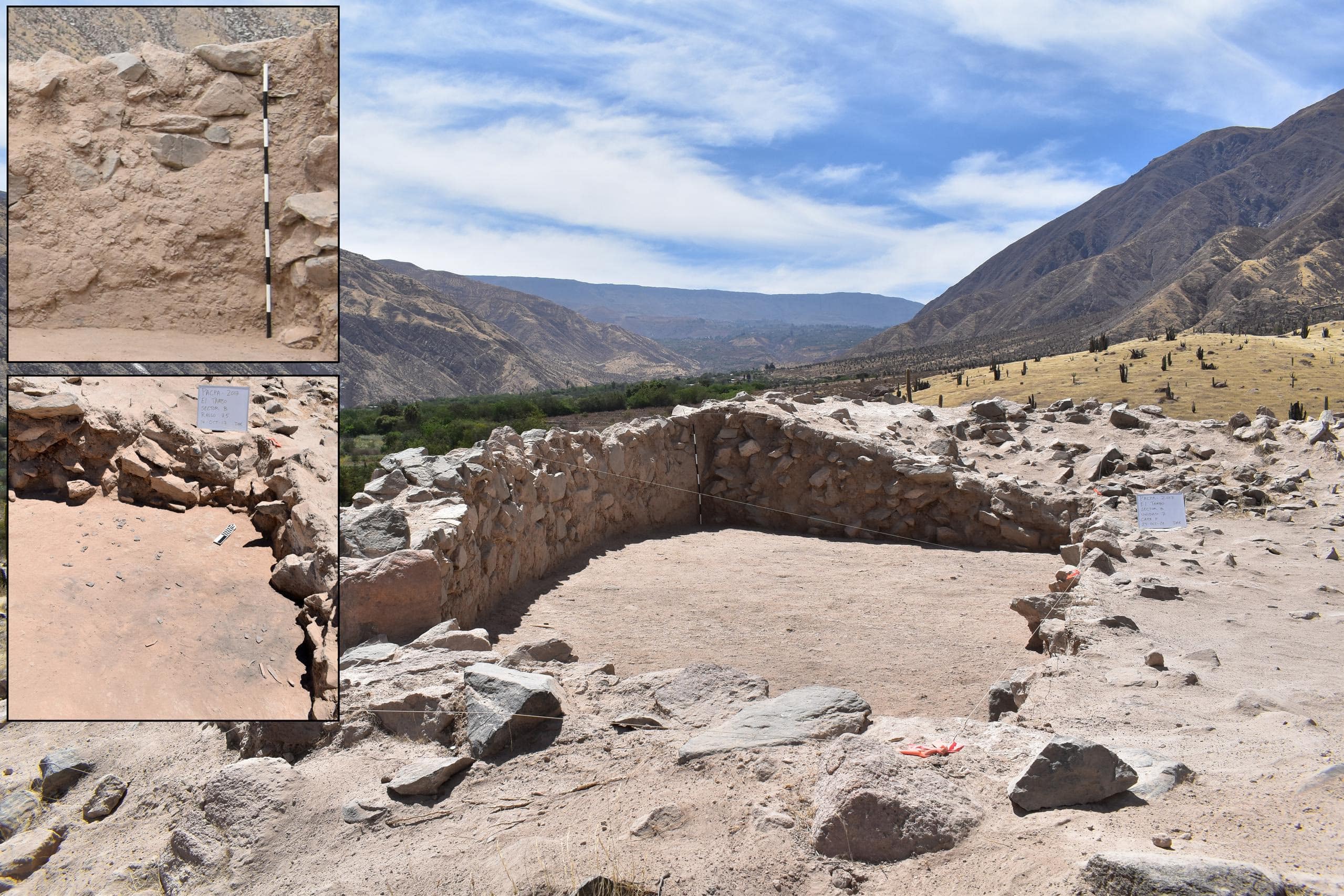
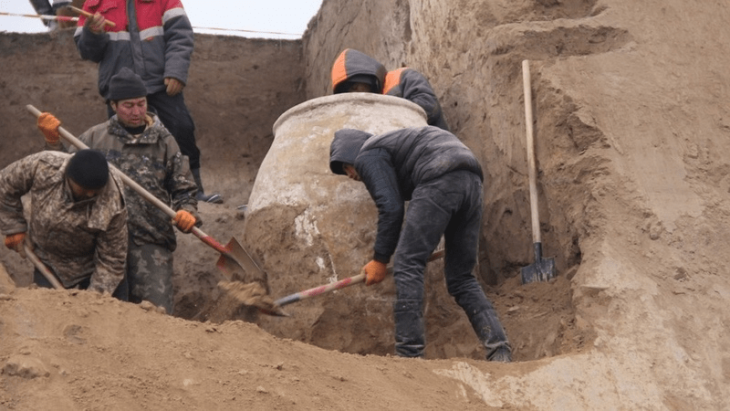
A Wari ritual complex with a D-shaped temple, patio-group architecture, several supporting buildings, and a massive platform construction has been discovered during excavations.
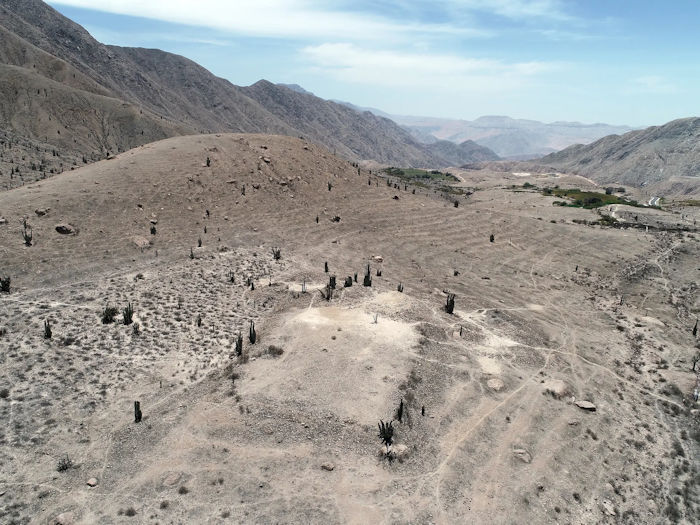

As reported in the Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, the D-shaped temple was built on top of a large, monumental platform with adjoining structures that would have housed Wari religious officials and people linked to the Wari Empire.
“One of the most effective ways of bringing people into the empire was through shared beliefs and religious practices,” David Reid, UIC postdoctoral research associate in anthropology and the study’s author said. “Open plaza spaces associated with the temple complex at Pakaytambo would have allowed local communities to participate in ritual gatherings organized by the Wari.”
He also notes that such ceremonial events would have been critical in maintaining political authority across great distances of the Wari Empire.
“Temple complexes of premodern states served critical roles beyond that of a religious function. Both political and economic activities were often embedded within state-sponsored rituals, ceremonies, and events organized by temple institutions. Although we may not fully know how Pakaytambo was integrated within the broader Wari political economy, its geographic location and archaeological record provide some insight,” researchers write in their study published in the Journal of Anthropological Archaeology.
The research was financed with support from the Wenner-Gren Foundation and the National Science Foundation.
Cover Photo: Excavation of D-shaped temple. Top insert: plastered interior wall. Bottom insert: abandonment feature on structure floor. Photo: UIC