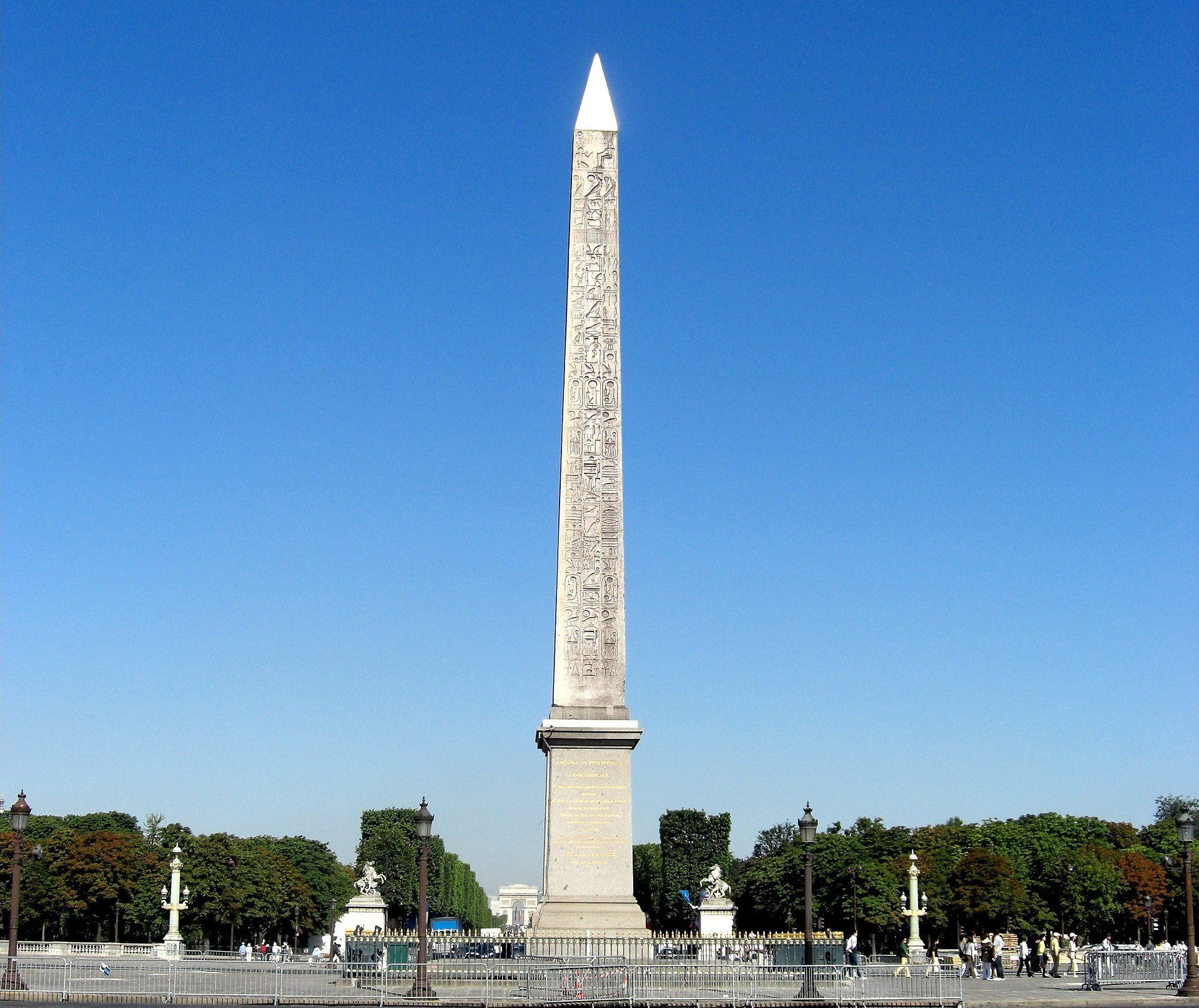
Nearly two centuries after its prominent placement in Paris’ Place de la Concorde, the 3,300-year-old Luxor Obelisk continues to yield remarkable insights into ancient Egyptian history and royal propaganda.
Jean-Guillaume Olette-Pelletier, a French Egyptologist and specialist in hieroglyphic cryptology at the Catholic University of Paris, has recently identified seven previously undocumented inscriptions near the obelisk’s summit. This significant discovery, made during a renovation in December 2021, sheds new light on the monument’s original purpose and the reign of Pharaoh Ramses II.
The scaffolding erected for the restoration provided Olette-Pelletier with an unprecedented opportunity to closely examine the higher sections of the obelisk, revealing hieroglyphs that could be read horizontally – a departure from the traditional vertical orientation. This new perspective allowed him to discern hidden messages embedded within the existing inscriptions, employing a sophisticated form of hieroglyphic cryptography designed to conceal their meaning.
According to Olette-Pelletier, only a handful of scholars worldwide possess the expertise to decipher this “3D” form of reading.
Originally one of a pair of obelisks strategically positioned at the Luxor Temple in Upper Egypt during the 13th century BCE under the aegis of Pharaoh Ramses II, this specific monolith was subsequently transferred to France in 1830 as a diplomatic gift from the Egyptian viceroy. Its initial placement along the Nile River held significance within the temple’s architectural and symbolic context.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Olette-Pelletier’s analysis revealed that one of the newly discovered messages was intentionally positioned to be visible from a 45-degree angle, specifically targeting nobles arriving by boat for the annual Opet festival, a celebration honoring the life forces of the god Amun.
The content of these hidden inscriptions serves as potent propaganda, exalting Ramses II’s divine power and urging viewers to offer tributes to appease the gods.
One notable finding includes hidden bull horns on Ramses II’s headdress, symbolizing “ka,” or the “vital force of divinity,” alongside a rectangle signifying “to appease.” Combined, these elements form a message encouraging offerings to the “ka-force of Amun.” Olette-Pelletier identified a total of seven such encrypted messages across the obelisk’s facades, each contributing to a broader narrative reinforcing the pharaoh’s legitimacy and divine status.
Ramses II, who reigned for an impressive 66 years, was known for his extensive public relations efforts, including the construction of numerous monuments to solidify his power. Olette-Pelletier’s discovery underscores the intricate ways in which ancient Egyptian rulers communicated their authority and beliefs.
The findings, which emphasize the interconnectedness of text and image in ancient Egyptian communication, are slated for publication in the journal ENiM (Egypt of the Nile and Mediterranean).
This remarkable research highlights that even well-studied historical artifacts can still hold concealed narratives, waiting to be unveiled through meticulous observation and specialized knowledge. The Luxor Obelisk, a Parisian landmark for nearly two centuries, continues to offer invaluable insights into the sophisticated world of ancient Egypt.
Cover Image Credit: Public Domain