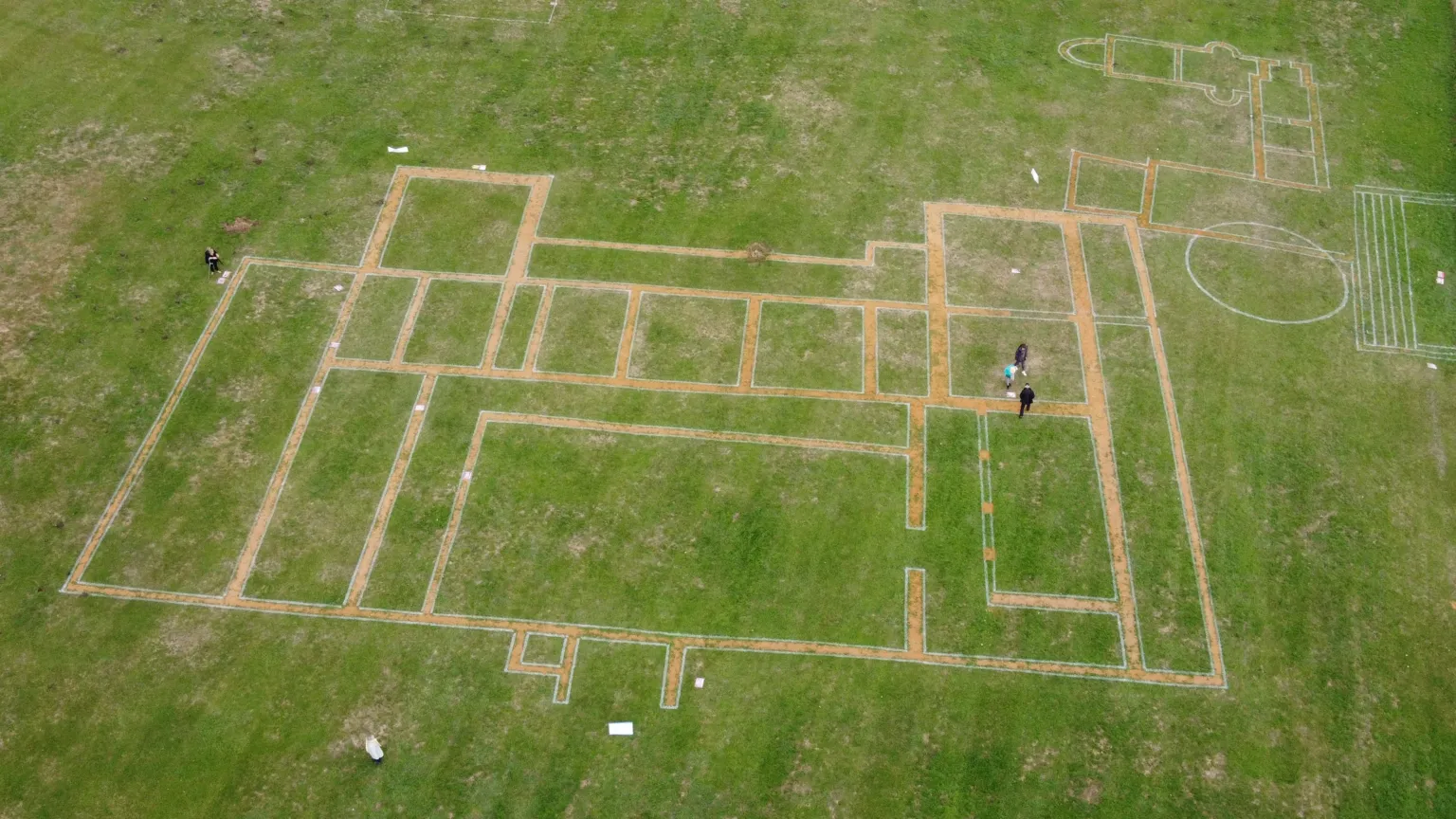
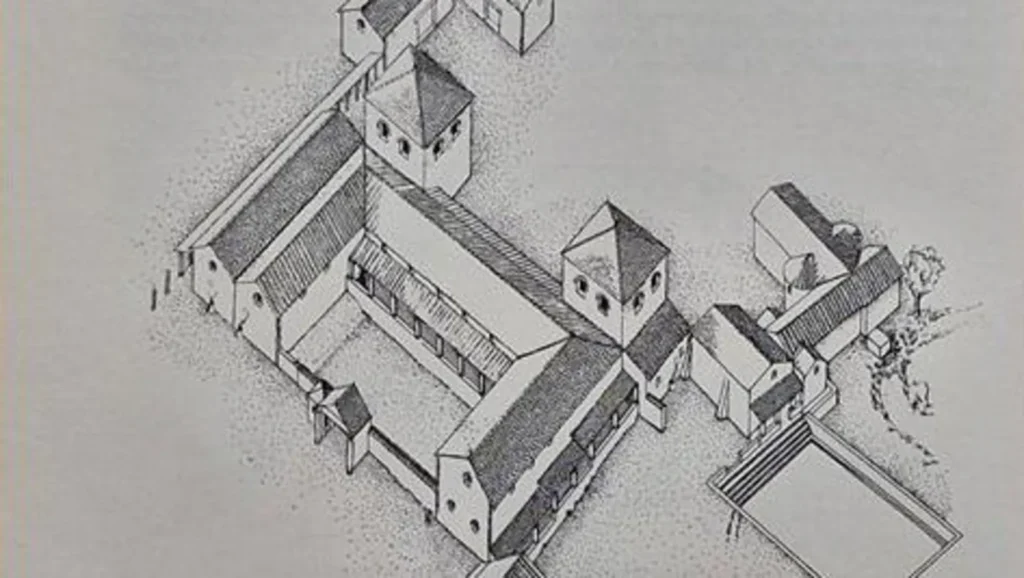
Beneath the grass and walkways of Gadebridge Park lies one of England’s most extraordinary Roman relics: a villa complex with a swimming pool so large it ranks second only to the Great Bath at Bath in private Roman Britain.
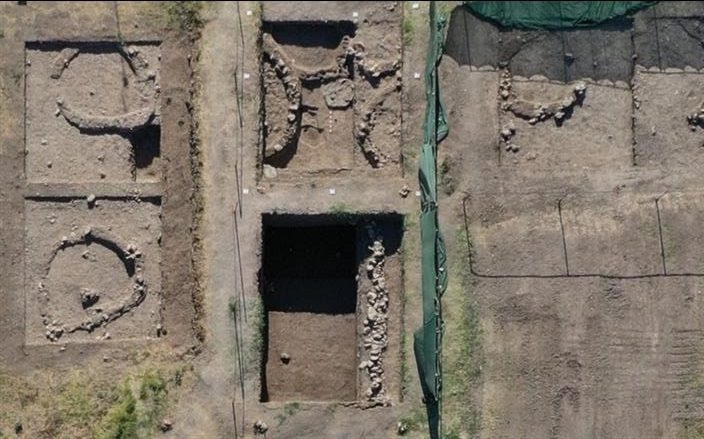
After decades of being buried and largely forgotten, the footprint of this ancient marvel was given new life this month, as local archaeologists and community groups marked out its outline for public viewing—and reminded residents of the grandeur that lies underfoot.
A Discovery in the 1960s: From Farmstead to Luxury Villa
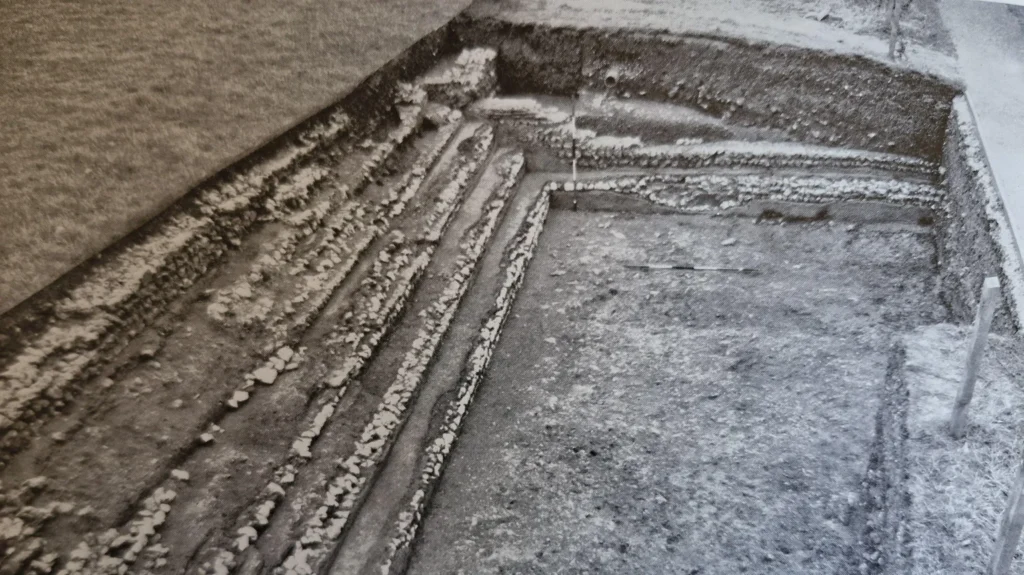
The story began in the early 1960s, when road construction works uncovered masonry beneath the soil. Excavations led by archaeologist Dr. David S. Neal between 1963 and 1968 revealed a site that had been occupied for more than 300 years.
What started as a modest timber farmstead soon after the Roman conquest of AD 43 grew into a lavish stone villa. During the Antonine period in the 2nd century, extensions included corridors, bathhouses and grand wings, turning the complex into one of the largest and most impressive rural estates in the region.
The Grand Pool
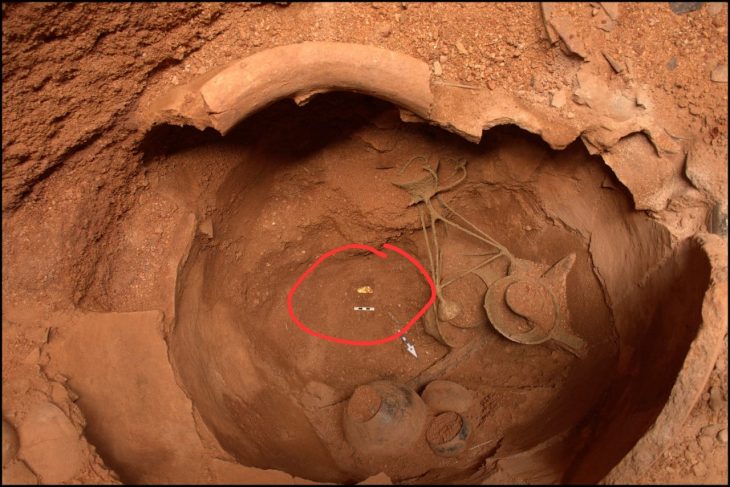
By the early 4th century, the villa reached its height of luxury. A huge swimming pool measuring approximately 21 metres by 12 metres was constructed as part of an elaborate bathhouse. Visitors would descend five broad steps—one designed as a bench-seat—into the water. Ingeniously, holes in the base allowed fish to escape, hinting that the pool was fed naturally by water from the nearby River Gade.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This remarkable feature makes it the largest private swimming pool ever discovered in a Roman villa in England, surpassed only by the monumental baths at Bath.
Decline and Burial
Around AD 350, the villa was deliberately dismantled, possibly during political unrest. Evidence shows that grand living quarters gave way to simple agricultural use, with animals and small outbuildings replacing fine mosaic-floored rooms. Over centuries, the site disappeared beneath farmland, and later, a modern road. To preserve its remains from weather damage, much of it was reburied under protective sheeting and paving.
Bringing History to Life: Heritage Open Day
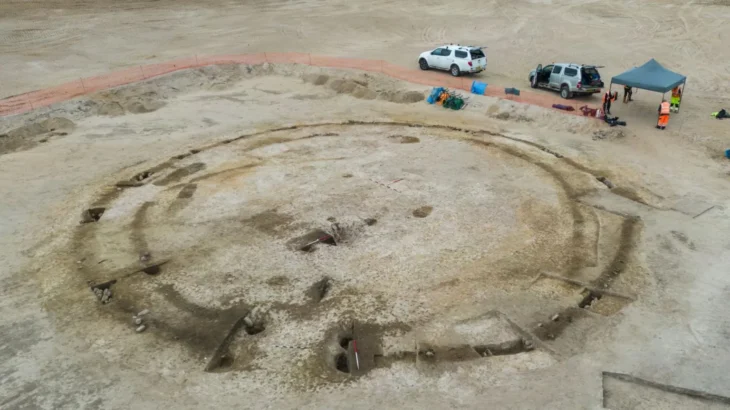
On 13 September, Dr Neal returned to Gadebridge Park not to excavate, but to guide visitors across the marked outlines of the villa. Paths, rooms, corridors and the famous pool were traced in the grass, allowing people to walk where Roman families once lived and bathed.
The event drew large crowds, many with personal memories of the original excavations. For many visitors, the highlight was standing at the spot of the pool steps, vividly recalling photographs from the 1960s dig. Seeing the outlines marked across the park brought the villa back to life in a way that written reports never could.
Why It Matters
The Gadebridge Park villa is far more than buried stone. It represents:
A window into Roman luxury: heated rooms, intricate mosaics, bathhouses and one of the grandest pools in Roman Britain.
An evolving history: from a simple farmstead to a symbol of wealth and status, and eventually to a ruin reclaimed by the land.
A community legacy: generations of local people contributed to its discovery, excavation and now its rediscovery as living heritage.

In Summary
What was once uncovered, then forgotten, now lives again in the heart of Hemel Hempstead. The Roman villa of Gadebridge Park, with its monumental swimming pool, is no longer just buried archaeology—it is a story the community can see, walk across, and connect with. History, quite literally, lies beneath our feet.
Cover Image Credit: The site was marked out by rollers normally used to mark out football pitches. BBC – B. Mills
















