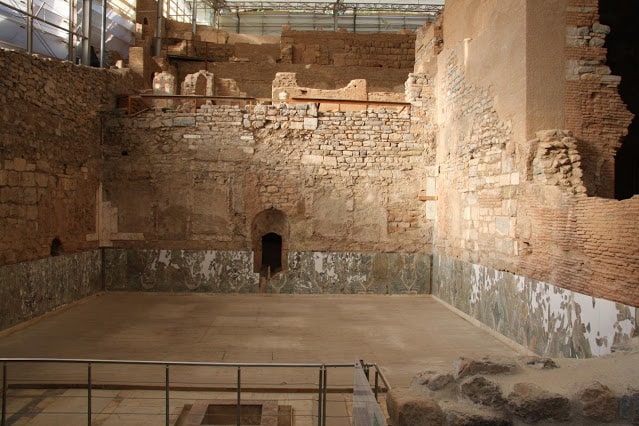
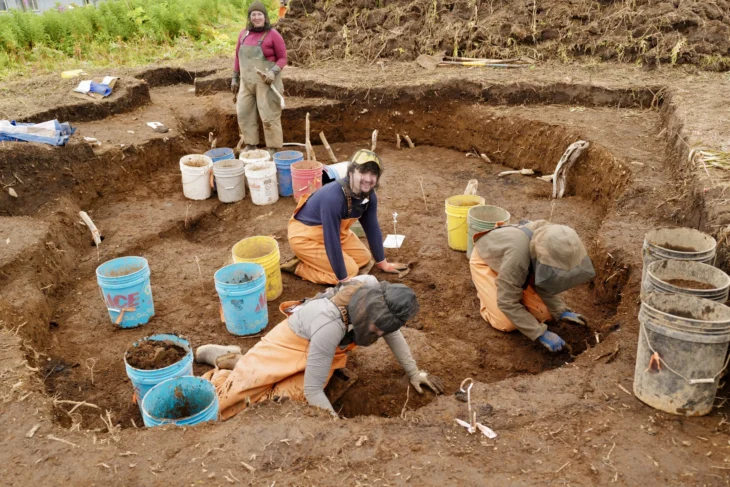
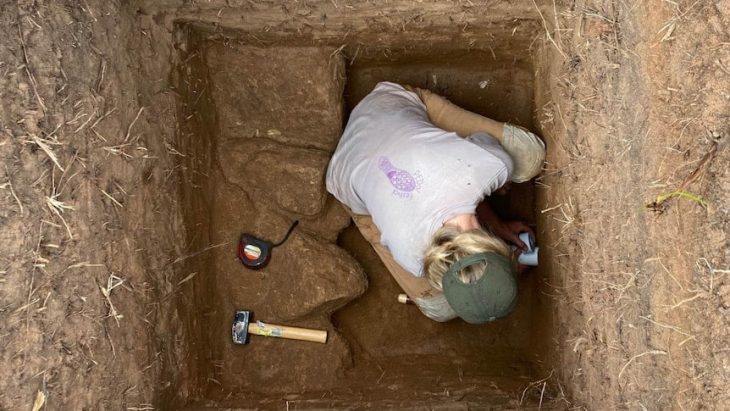
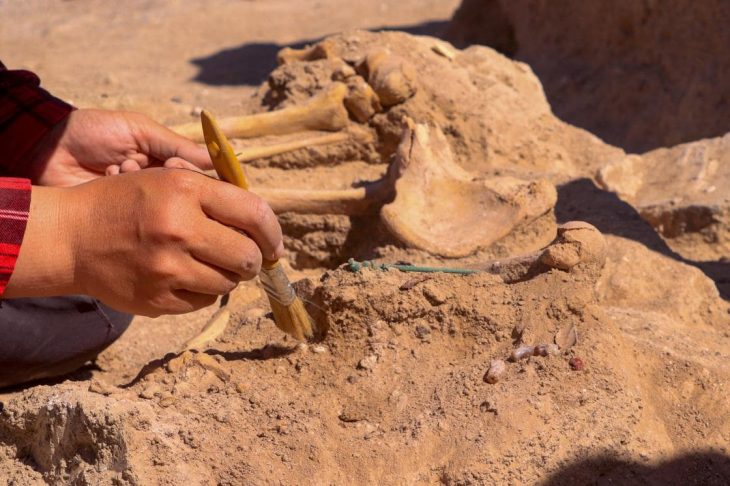
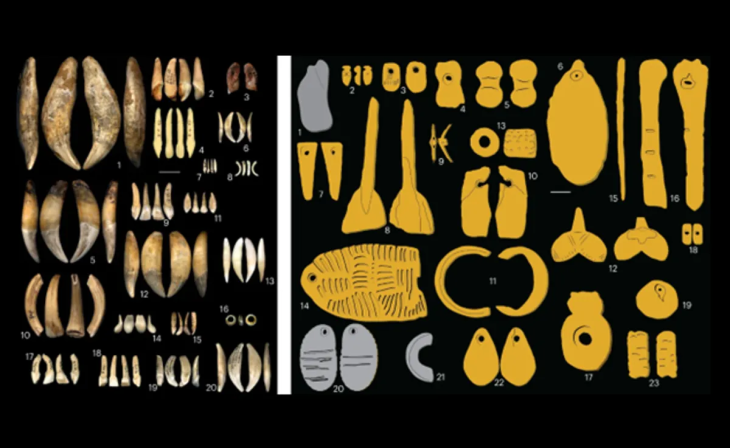
Researchers examined 29 tombs from Szigetszentmiklós-Ürgehegy, one of Hungary’s largest Middle Bronze Age cemeteries, and one of them, a high-status woman’s tomb was quite remarkable.
In the grave numbered 241, the cremated bones of an adult woman and two 7-8-month-old fetuses found in the urn, as well as highly prestigious items.
The site is located in the northern part of Csepel Island (a few kilometers south of Budapest), and c. They are dated to 2150 and 1500 BC.
People of the Vatya culture-in the early and mid-Bronze Age of Hungary used to cremate their dead. Although this often makes studying their remains challenging, researchers from the University of Bologna in Italy turned to new bone sampling strategies.
The researchers wrote that the aim of the study was to identify variation in mobility patterns among individuals of different gender/ages/social statuses and individuals treated with different burial rites using strontium isotope analysis.
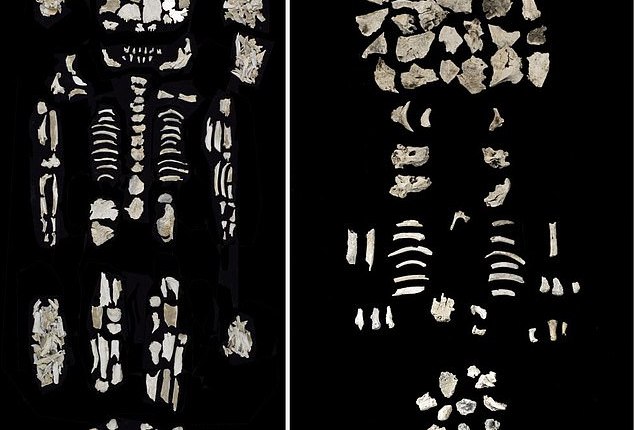
Claudio Cavazzuti of the University of Bologna and his colleagues examined 26 urns of cremated ashes as well as three complete graves, utilizing isotope analysis.
While the majority of tombs contained just the bones of a single person and modest burial goods made of pottery or metal, one was discovered to be unique.
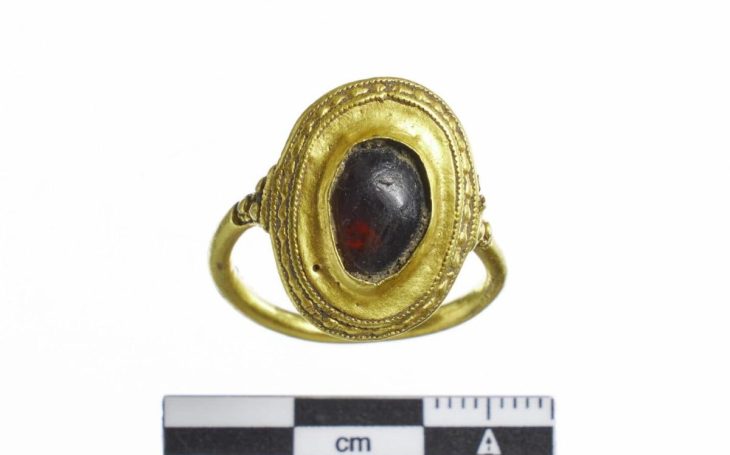
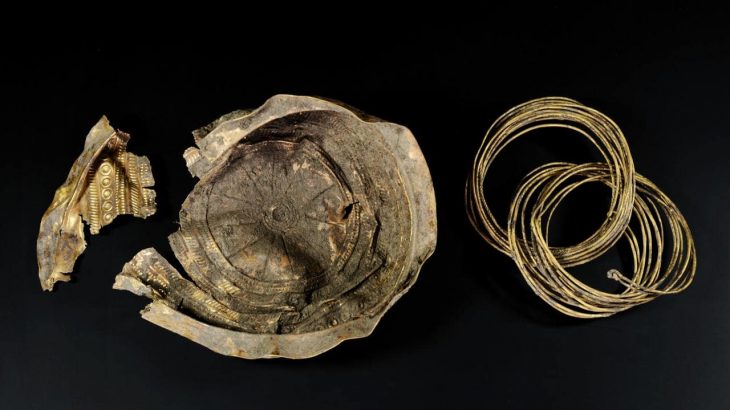
An urn holding the ashes of an adult lady and two 7-8-month-old fetuses may be found at Cemetery No. 241. A golden hairband, a bronze neck ring, and two bone hairpin decorations were among the buried items. And the presence of these ornaments indicates the high status of women.
The researchers think that the lady at gravesite 241 — who, based on her bones, was between the ages of 25 and 35 — died as a result of difficulties while carrying or giving birth to the two twins with whom she was buried.
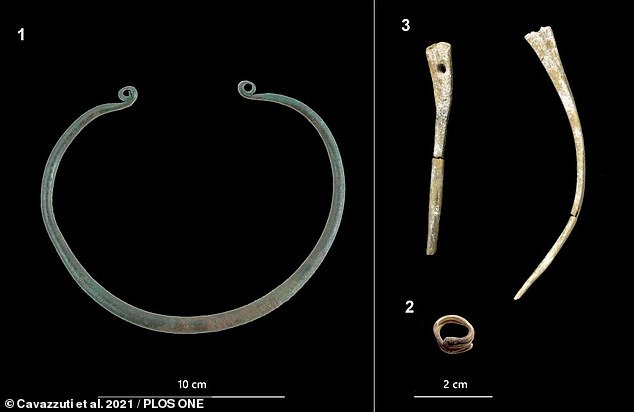

Also, the bone weight of her ashes, which was 50% greater than the average of the 26 ashes examined, shows that her remains were meticulously gathered after her cremation.
‘Thanks to a wide spectrum of new bioarchaeological methods, techniques, and sampling strategies, it is now possible to reconstruct the life-histories of cremated people of the Bronze Age,’ Professor Cavazzuti and his team Dailymail said.
Also, Professor Cavazzuti said ‘In this case, [we] investigated the movements and the tragic events of a high-status woman’s life, settled along the Danube 4,000 years ago, in the territory of modern-day Hungary,’.
Woman’s Strontium isotope research revealed that she was born elsewhere, and relocated to Szigetszentmiklós, between the ages of 8 and 13.
According to the researchers, the results of the study indicate that women in Central Europe during the Bronze Age—especially those of higher status—were often married outside of their immediate social groups.
You can read the full study at PLOS ONE.