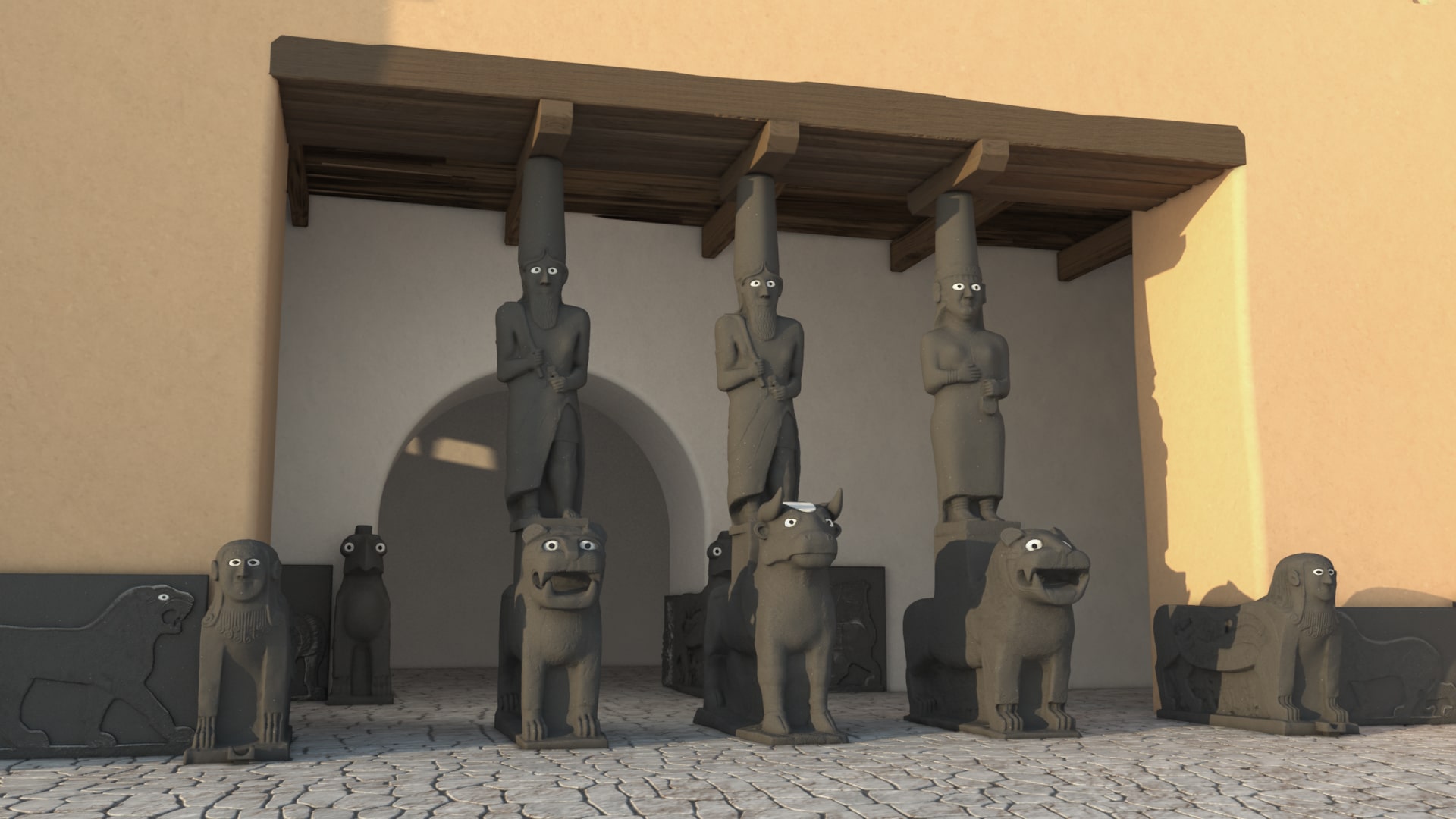
It is thought that the word Bit-Hilani is derived from the Hittite word Hilambar, that is door. It is seen that it was used in everywhere with hot climate in the iron age. It can be thought of as a kind of sun protection system.
If we look at the Bit-Hilani plan: it has a building plan that consists by entering a horizontal-axis room through an entrance with a portico on the same axis. In Hilani buildings built as a temple, a room is added to these two rooms, which does not spoil the plan. This room is generally used as a warehouse.
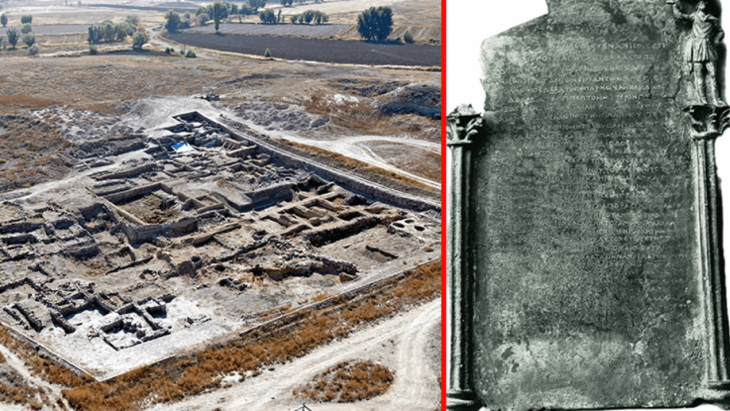
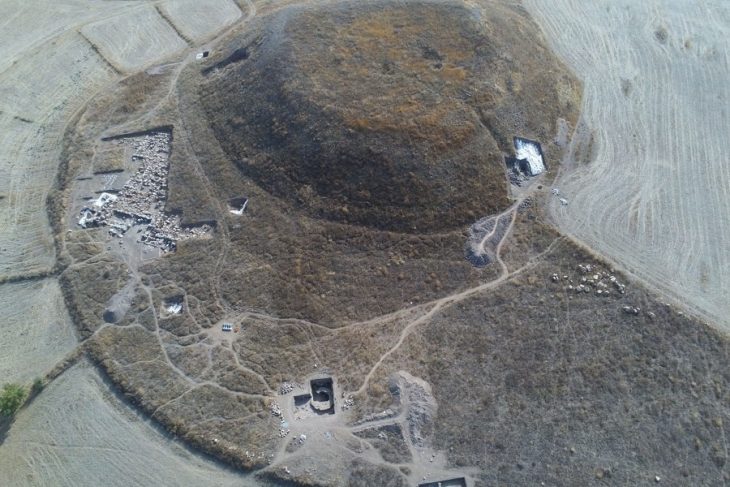
Although the Bit-Hilani type, which is quite common in the Late Hittite settlements, is still a controversial issue in origin, the E structure, which is considered to be the pioneer of Hilani structures in Tilmen Höyük, written by Professor Refik Duru. Likewise, the E structure in Büyükkale, located in the Boğazköy Hattusa, has an entrance with a portico in front and a structure with a room divided into two at the back, with a lateral extension. The relationship of both Tilmen mound and Hattusa palace with the Hilanis is evident. But how did these structures turn into the Iron Age Hilanis?

It is obvious that such structures are popular in Hittite geography. It is also normal that porch entrances are needed in hot climates. In fact, it will not be surprising that these structures are of Anatolian origin.
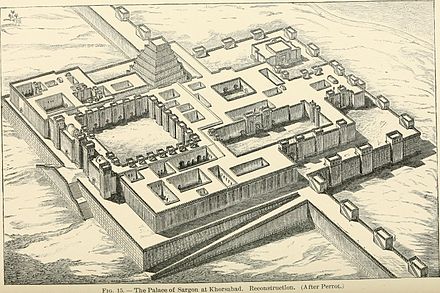
Assyrian King II. Sargon mentions such a building in the Establishment text of Dur-Sharrukin.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“A portico, patterned after the Hittite palace, which in the language of Amurru they call a bit-hilani, I built in front of the palaces’ gates.”
Since the structure in the western corner of the palace terrace is not known exactly, it is possible that it is the structure described with these words. II. Sargon says that these structures are unique to the Hittites.
It is a search for an origin that is not exaggerated that our naming it an Anatolian-origin construction technique within the scope of the plan and explanations. However, Bit-Hilani buildings have developed continuously and the columns at the entrance have begun to be decorated with sculptures. For these columns, cedar wooden pillars are used, the front facade is decorated with reliefs, protom-headed lions and sphinxes.
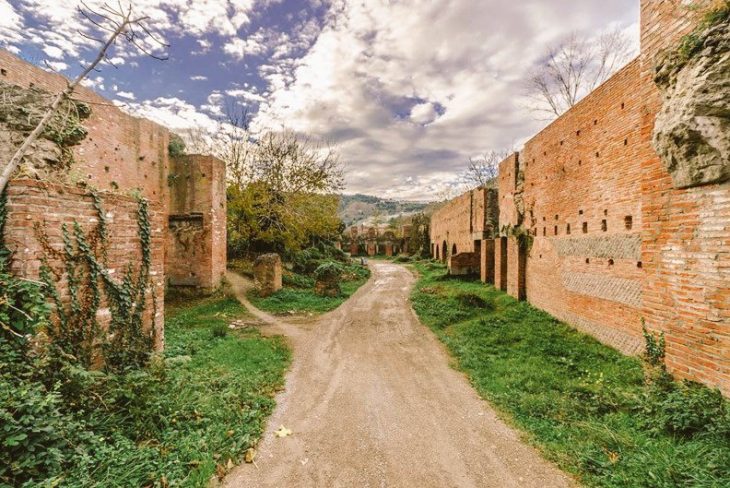
İf when it comes to Tell Halaf, the Hilani façade evolves from pretentious to impressive. Kapara Palace in Tall Halaf stands out with its early Hilani. It is the earliest example of monumental Hilanis.
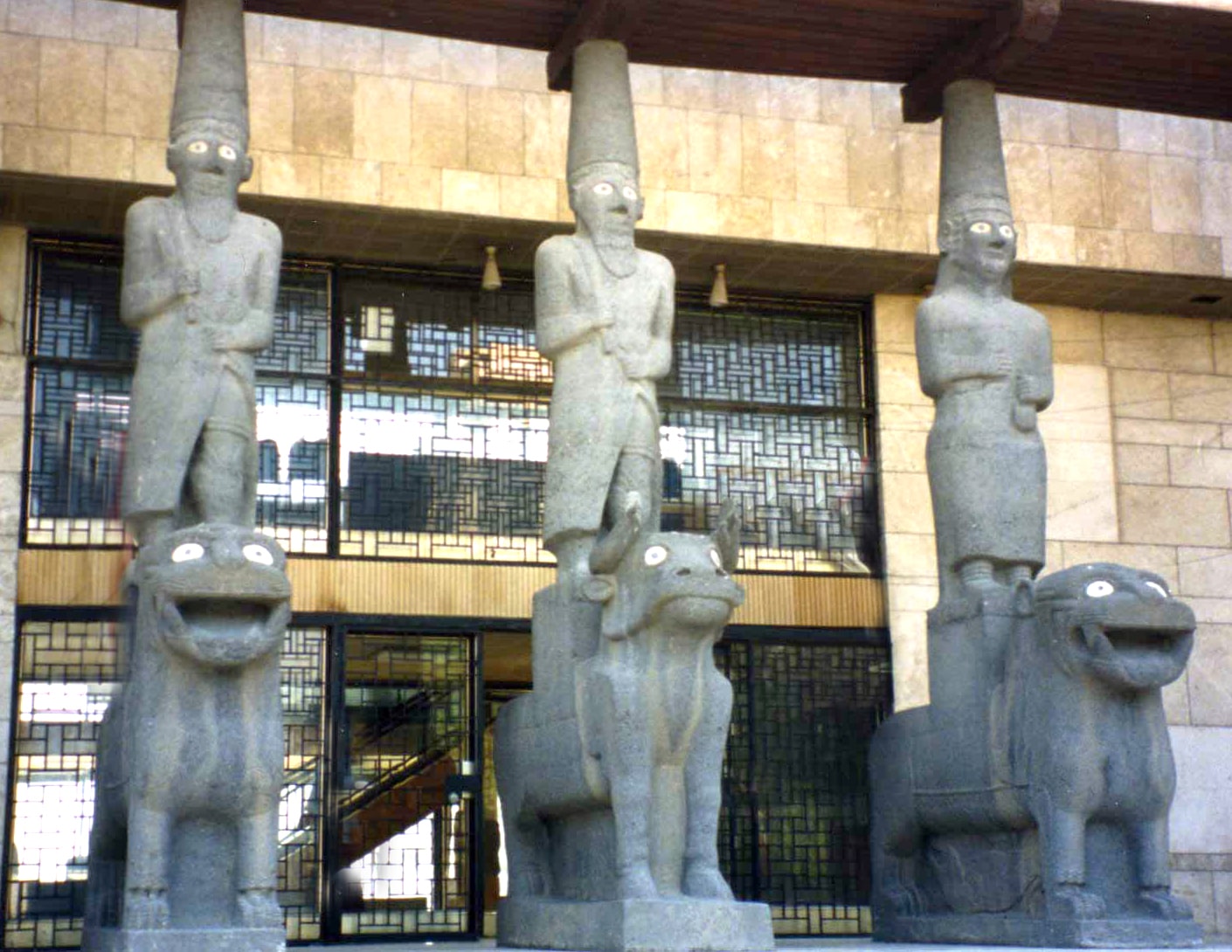

There were god statues on the sacred animals carrying the roof at the Hilani entrance of the Kapara Palace.
-Mother Goddess on the lioness (right)
-Storm God Tesup on the bull (center)
-The son of God Teshup is depicted on the lion (left).
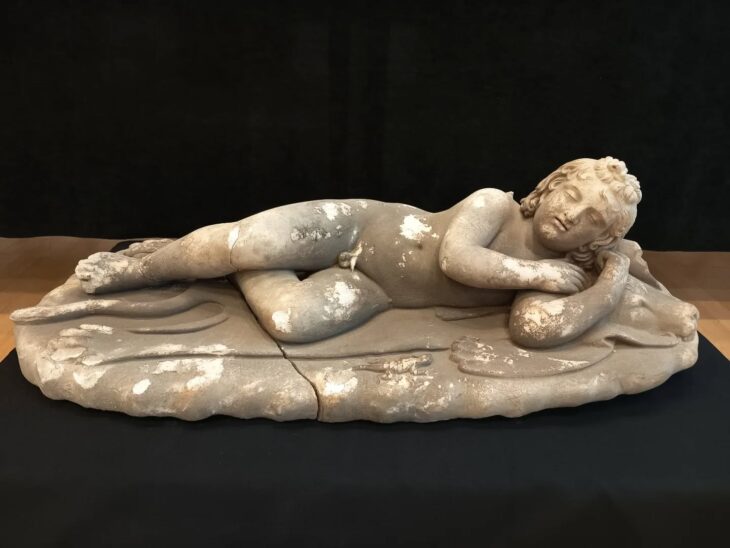
It is the earliest example of using human figures.
Human figures are the oldest example used. It is not surprising to see that a situation ascribed to Greek art has a predecessor as early as 10 century BC. It is not an unknown phenomenon that Europe reached the development of Anatolia and Mesopotamia much later.

The Erechtheion temple in Athens (421-406 BC) was built centuries after this palace, but it is worth comparing with its style similarity. It was a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena and the god Poseidon. The south columns formed by the Karyadit girls can be likened to hilani doorways. There is no doubt that the understanding of art here and the art understanding of those who made the Kapara Palace were at a level that could compete with each other. Although the materials used have changed, it is not difficult to see the same logic and understanding of art for these structures. It is not at all strange for the Ancient Greek artists to develop an architecture they have seen, from the idea that art is formed by a phenomenon of inspiration.
While Bit-Hilani is a structure open to development, can we associate the closed-to-development of the Ancient Greek Megoran structures with open to development face of the east? Who knows, maybe if we were the Teotihucan people who thought that the architectural structures were alive, we could have reached far more conclusions than this inference!