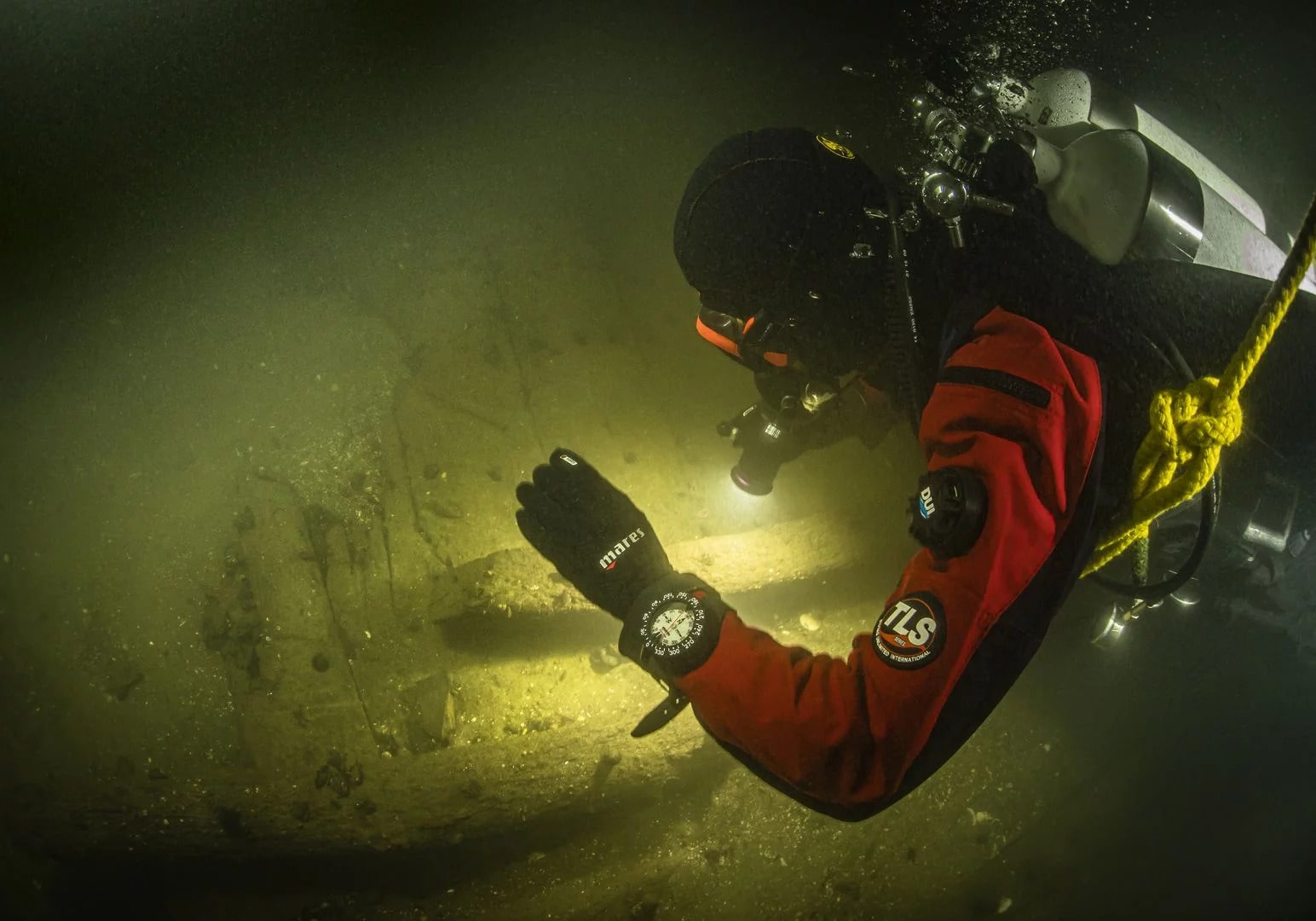
During a routine measurement at Trave, near Lübeck, in the northern part of Germany, Kiel-Holtenau Waterways and Shipping Authority (Wasserstraßen- und Schifffahrtsamt/WSA) discovered a ship at a depth of eleven meters (nearly 36 feet ).
Researchers from Kiel University spent eight months studying the wreck, determining that 150 barrels of cargo went down with the Hanseatic ship.
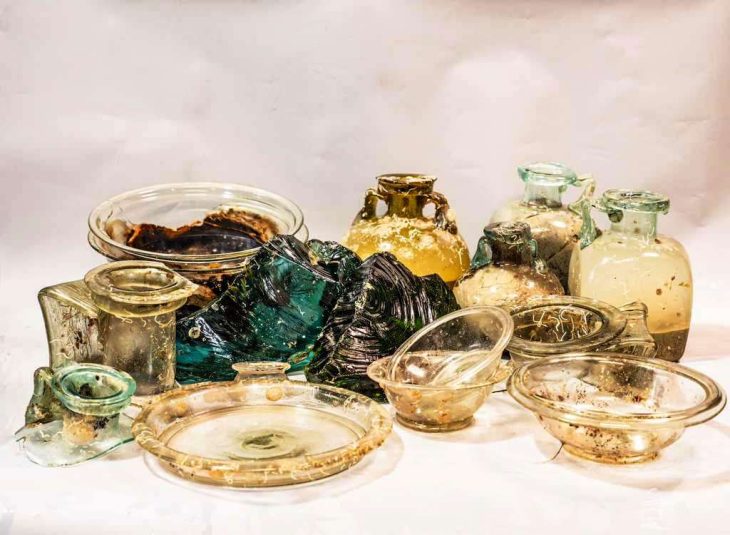
The researchers described the wreck as “a unique discovery in the western Baltic Sea region.” The Hanseatic wreck was about 400 years old and contained 150 barrels of quicklime, a common building material at the time.
Based on images and videos, the researchers created 3D models to calculate the ship’s original length, which was 20-25 meters. As a result, the ship was a medium-sized cargo sailing ship, the workhorse of the Baltic Sea trade.
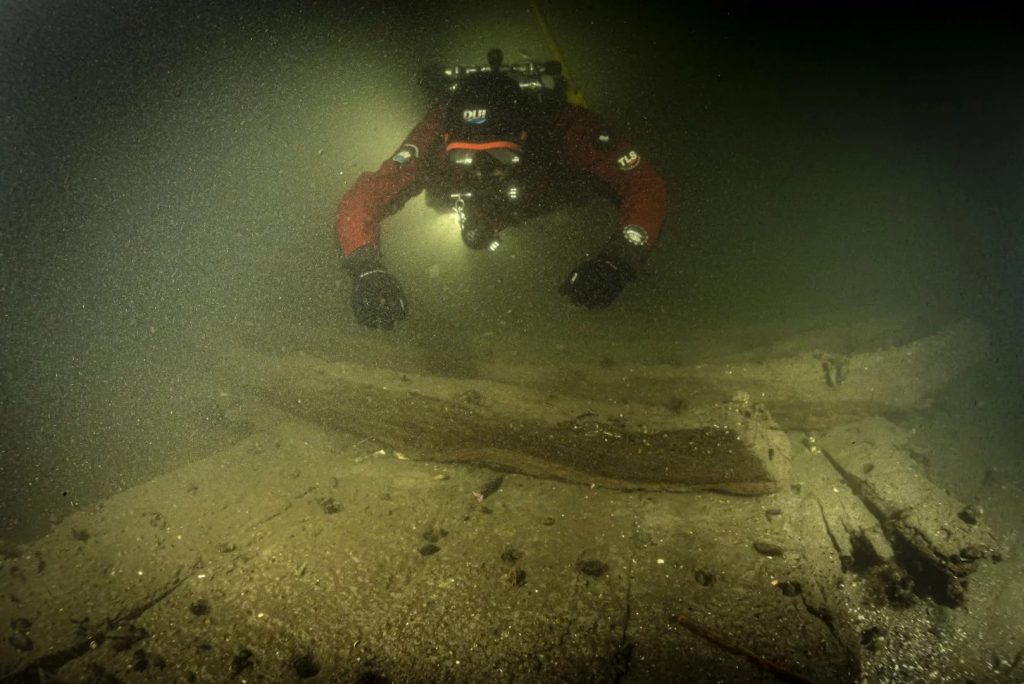

“This find is extraordinary for the western Baltic Sea region,” said Fritz Jürgens, an archaeologist at Kiel University in Germany whose team examined the wreck, in a university release. Until now, similar wrecks dating from different centuries have only been found in the eastern Baltic Sea region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Independent dating of the ship’s timbers in three different laboratories revealed that the ship must have been constructed in the mid-17th century,” added Dr. Fritz Jürgens.
The dives revealed that the wreck was eroding rapidly and that exposed areas were plagued with shipworm. If no protection measures are adopted, the wreck will be destroyed within a few years, and this relic of the Hanseatic City of Lübeck’s significant marine trade would be gone forever.
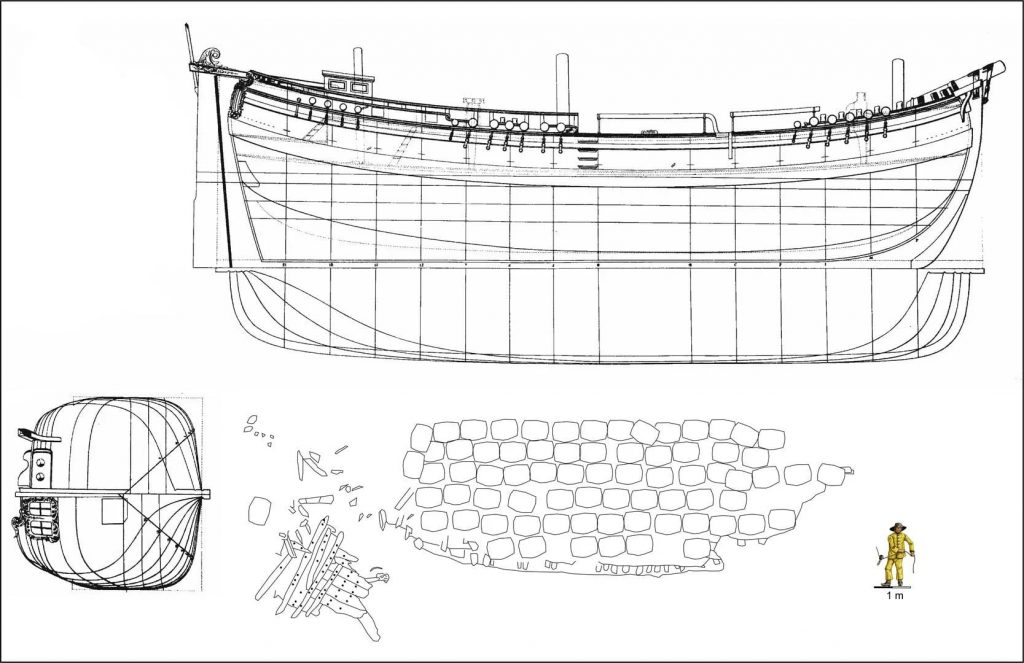
The researchers at Kiel University are developing a plan for the continued care and protection of the wreck in collaboration with the City of Lübeck and other organizations to avoid this from happening. They are considering salvaging and then preserving it.
According to initial findings, the ship was on its way from Scandinavia to Lübeck but never arrived. More research is needed to establish why the Hanseatic ship sunk. Initial indications suggest that the ship could have run aground on a bend in the Trave river, where it was seriously damaged and therefore sank.