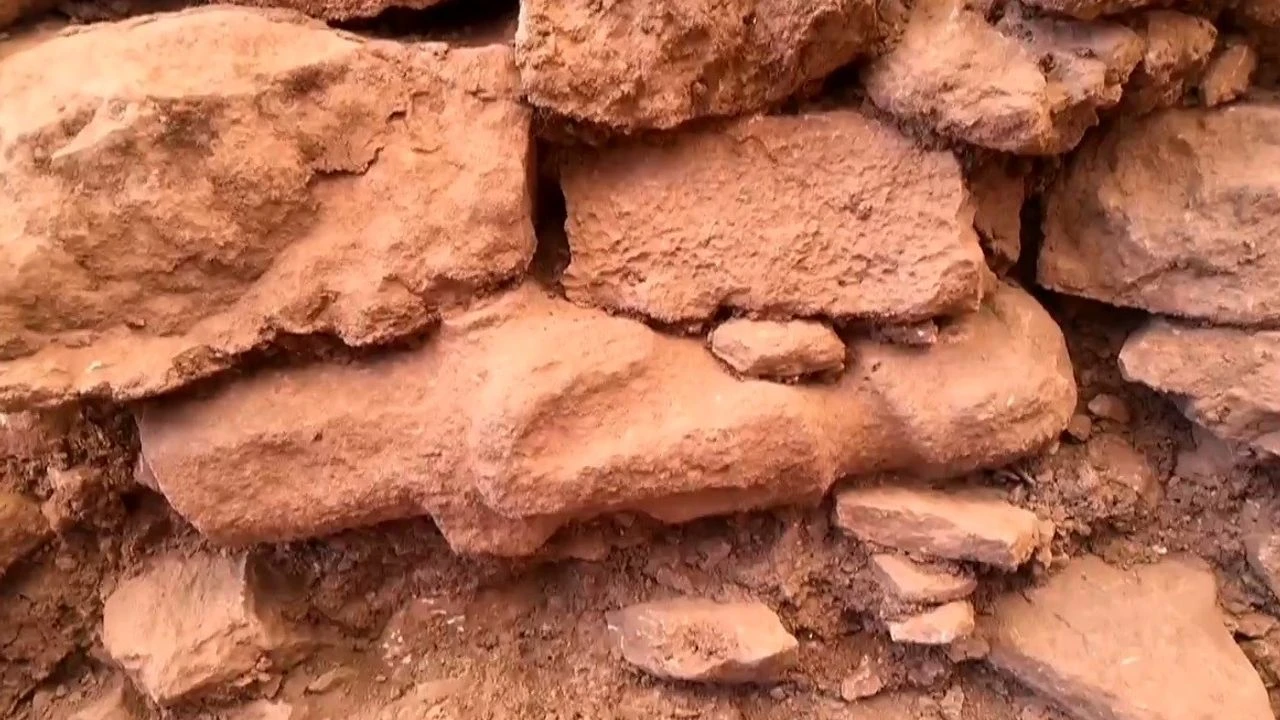
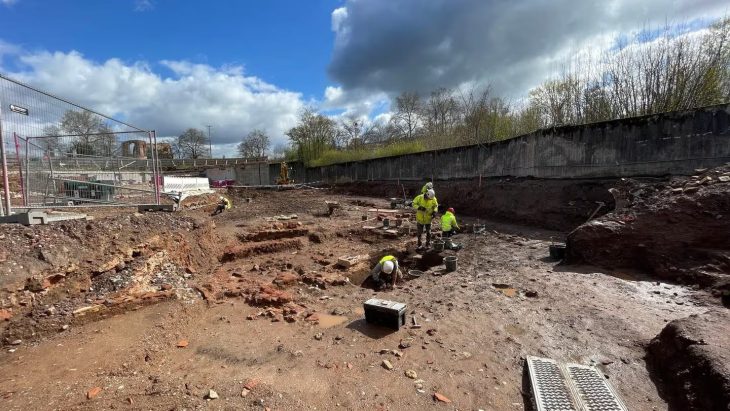
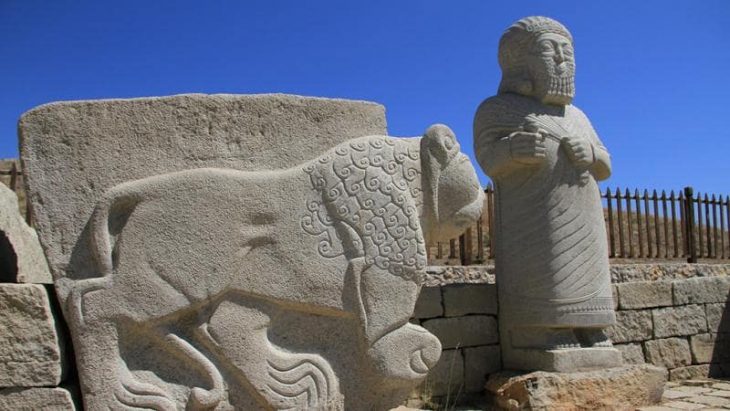
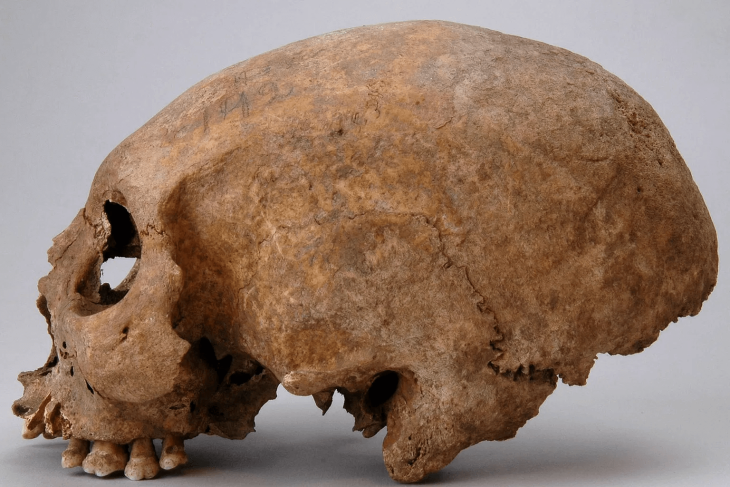
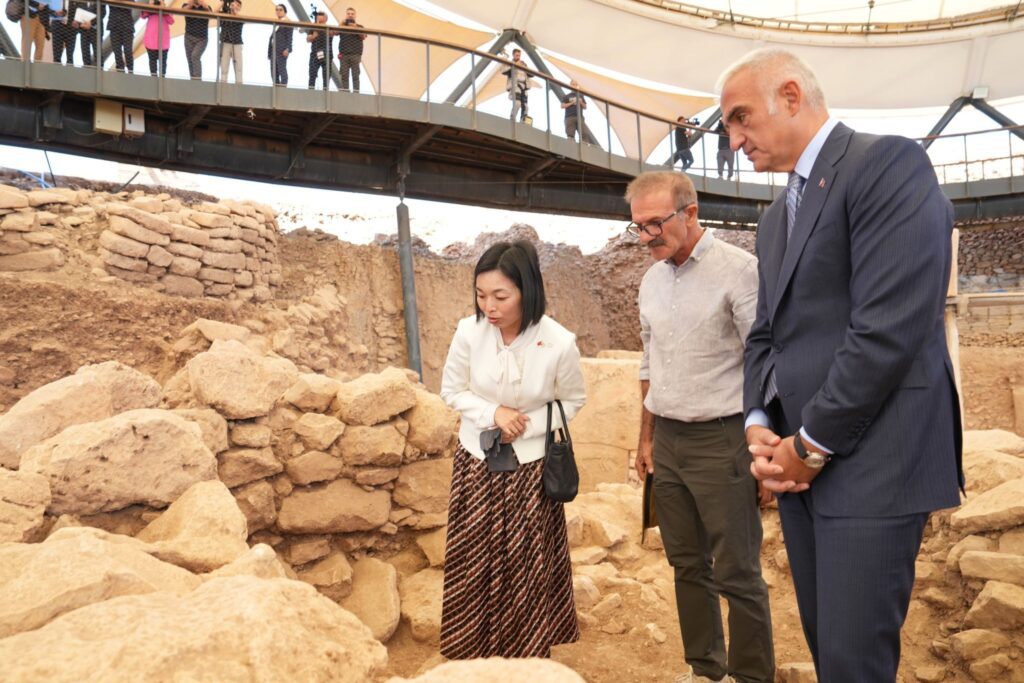
Türkiye’s Minister of Culture and Tourism Mehmet Nuri Ersoy has announced a groundbreaking archaeological discovery at Göbeklitepe, the world-renowned UNESCO World Heritage site often described as the “zero point of history.” Archaeologists have uncovered a human statue carefully mounted inside a wall, believed to have been placed there as an offering more than 12,000 years ago.
“We have seen similar examples at Karahantepe, another major Neolithic site in the region, but this newly uncovered piece from Göbeklitepe is a highly valuable discovery,” Minister Ersoy said. “It provides a deeper understanding of Neolithic rituals and the symbolic world of early human communities.”
The discovery was revealed during Minister Ersoy’s visit to the site alongside Japan’s Princess Akiko of Mikasa, who toured the excavation areas and received a briefing from excavation director Professor Necmi Karul.
A New Window Into the Neolithic World
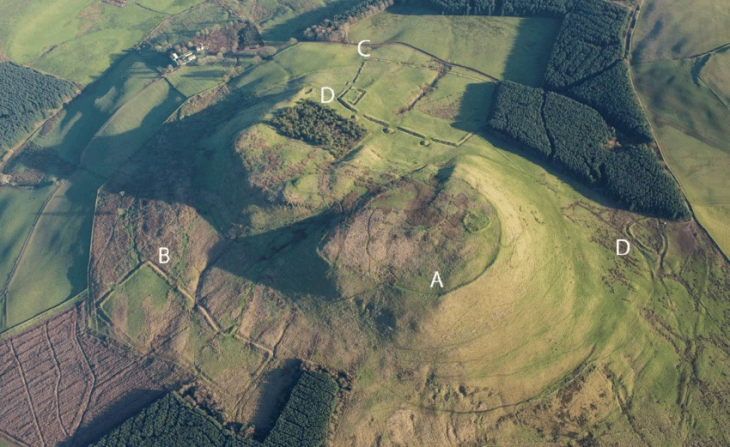
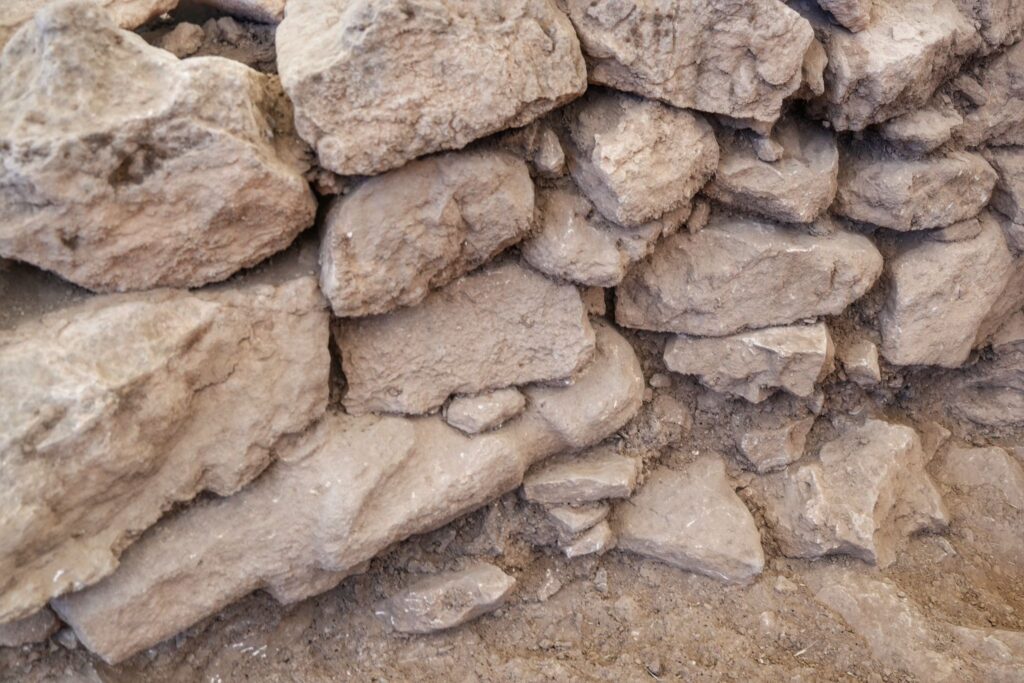
The statue was unearthed between Structures B and D, embedded horizontally within the wall of a chamber. Experts suggest that its placement was deliberate and likely part of ritual or ceremonial practices. Such findings are rare and provide unique insights into the belief systems, spiritual traditions, and social structures of early farming communities in Upper Mesopotamia.
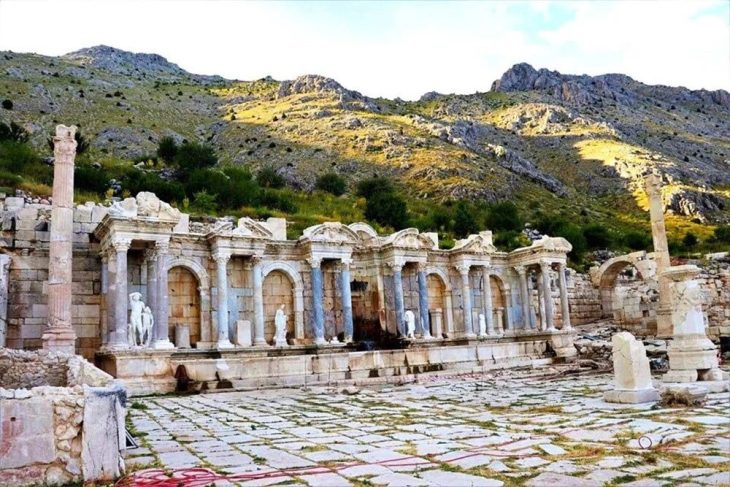
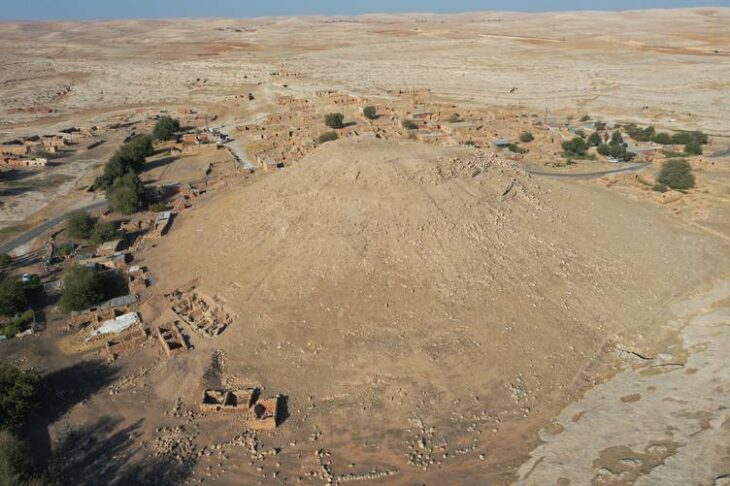
Göbeklitepe, located about 15 kilometers from the city of Şanlıurfa, is widely regarded as the world’s oldest known monumental religious sanctuary, dating back to around 9600 BCE. The site predates Stonehenge by more than 6,000 years and the Egyptian pyramids by about 7,000 years. It consists of massive T-shaped limestone pillars arranged in circular enclosures, many decorated with carvings of animals such as snakes, foxes, boars, and vultures. These symbols are believed to have conveyed cosmological and spiritual meanings to the people who built them.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Excavations, Restoration, and Sustainable Tourism
Since its inclusion on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2018, Göbeklitepe has attracted global attention from archaeologists, historians, and visitors alike. Under the “Legacy for the Future Project,” excavations at the site are complemented by restoration and conservation work.
Minister Ersoy explained that significant progress has been made at Structure C, the largest of the uncovered enclosures. Archaeologists have stabilized walls and re-erected multi-ton standing stones with meticulous care. Traditional building methods and authentic materials, including mortar reinforced with goat hair, were used to preserve historical accuracy.
Looking ahead, Türkiye is investing in infrastructure to manage the growing influx of visitors. A new visitor center, parking facilities, and walking paths are set to open before the end of 2025. “We aim to manage the global interest in Göbeklitepe sustainably, ensuring that the site remains protected while allowing people to experience its unique heritage,” Ersoy noted.

Expanding Global Awareness
In addition to excavation and conservation efforts, the Turkish government is promoting Göbeklitepe on the international stage. Following last year’s successful exhibition at Rome’s Colosseum, which attracted over six million visitors, a new exhibition titled “Myths in Stone: Göbeklitepe and the World of the Last Hunters” will open at Berlin’s James-Simon Gallery of the Near East Museum from February 5 to July 31, 2026. Ninety-six artifacts from the Şanlıurfa Museum collection will be on display, offering European audiences a closer look at the spiritual and artistic achievements of the Neolithic builders.

Göbeklitepe as Humanity’s Shared Legacy
Minister Ersoy emphasized that Göbeklitepe is not only a Turkish treasure but a shared heritage of humanity. “This site does not just illuminate the past—it is a legacy for the future. Protecting it, preserving it, and passing it on to future generations is a responsibility we all share,” he said.
The Minister also thanked Japan for its contributions to archaeological research in Turkey, highlighting how cultural cooperation strengthens diplomatic ties. Princess Akiko expressed her admiration for the site and the efforts being made to safeguard it.
Why Göbeklitepe Matters
Göbeklitepe continues to transform scholarly understanding of human history. Previously, archaeologists believed that large-scale communal structures emerged only after the development of farming and settled village life. The discoveries at Göbeklitepe, however, suggest the reverse: ritual gatherings and shared religious practices may have driven the shift toward agriculture and permanent settlements.
This revolutionary idea positions Göbeklitepe not only as an archaeological marvel but also as a site that reshapes our understanding of human civilization itself.
As excavations continue under the Taş Tepeler Project, involving more than 36 international institutions and 220 experts, Göbeklitepe and the surrounding sites are expected to reveal further secrets about the origins of belief, art, and community life.
Republic of Türkiye, Ministry of Culture and Tourism
Cover Image Credit: Republic of Türkiye, Ministry of Culture and Tourism