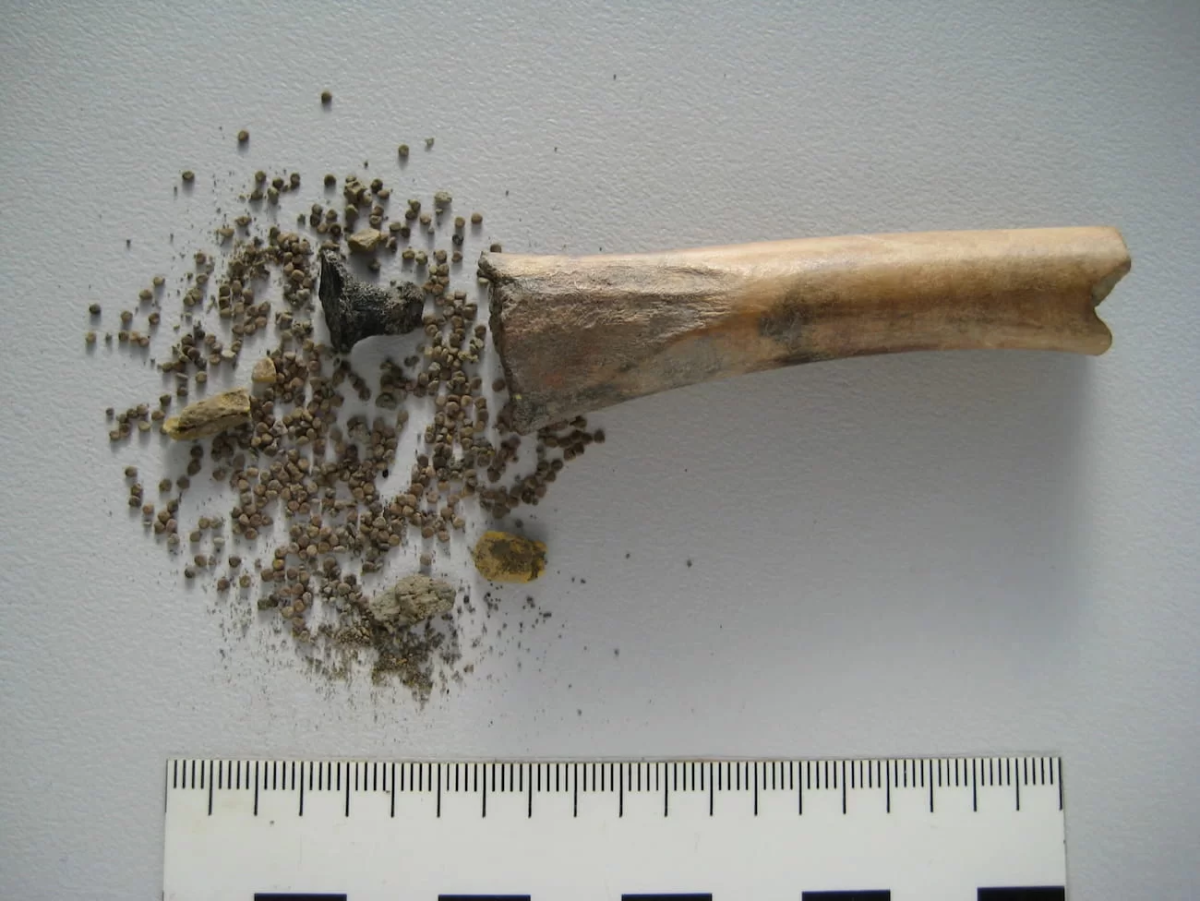
Archaeologists have discovered the first conclusive evidence of the existence of a hallucinogenic and poisonous plant thought to have been used in the Roman world, in a hollowed-out bone at a rural Roman settlement in modern-day Netherlands.
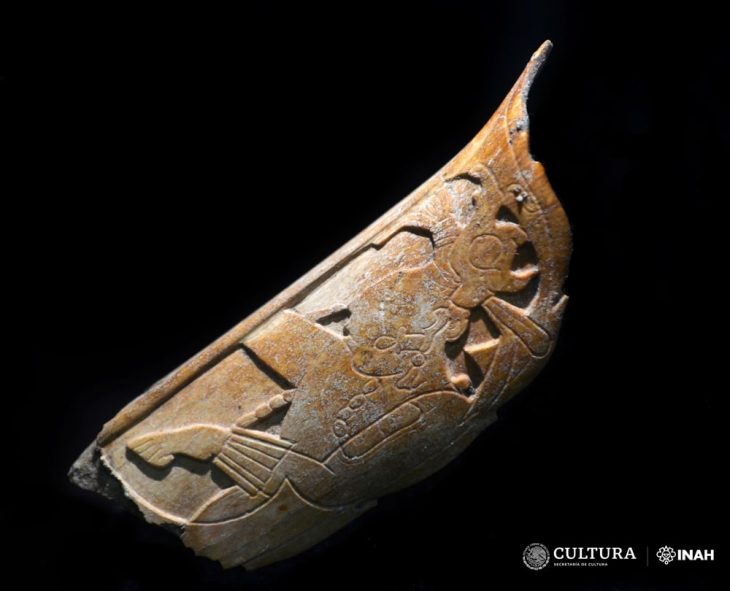
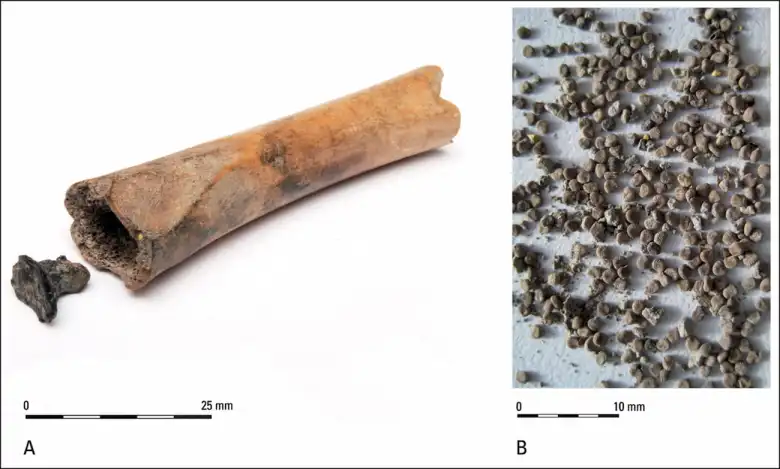
Hundreds of seeds from the plant known as black henbane or mad herb (Hyoscyamus niger) were discovered in a hollowed-out bone at Houten-Castellum, a rural Roman-period settlement in what is now the Netherlands. Because the sheep or goat bone was sealed with a birch-bark tar plug, researchers concluded that the seeds were being used intentionally.
Black henbane is a highly toxic plant with medicinal and psychoactive properties. Its remains are common in archaeological sites in Northwestern Europe because it grows wild near human settlements, making it difficult to determine whether it was intentionally used.
“Since the plant can grow naturally in and around settlements, its seeds can end up in archaeological sites naturally, without intervention by humans,” lead author and Free University of Berlin archeologist Maaike Groot said in a news release. “The find is unique and provides unmistakable proof for the intentional use of black henbane seeds in the Roman Netherlands.”
Archaeologists determined that the seeds were deliberately inserted into the bone, which was 2.8 inches (7.2 centimeters) long. Researchers dated the bone to between A.D. 70 and 100 based on ceramic styles and a wire brooch discovered in the same muddy pit.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
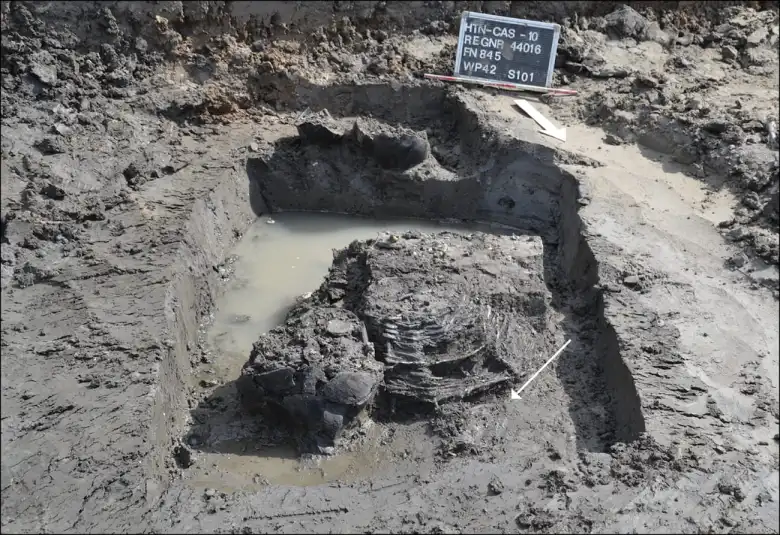

Based on bioarchaeological analysis, it was identified as the hollow shaft of a femur from a sheep or goat, with birch bark tar sealed at one end. The black henbane seeds were identified by the tar’s hyoscyamine content.
This is the first known instance of the seeds being deliberately stored for later use.
Pliny the Elder, a Roman writer, wrote about the plant’s many therapeutic applications almost 2,000 years ago. These included tooth disease, earaches, and insect stings. These sources suggest it was used medicinally and wasn’t considered a recreational drug, according to the study.
The discovery of the seed container in Houten-Castellum, the Netherlands, suggests that henbane use may have been commonplace as the settlement was situated at the rural edge of the Roman Empire.

“Our study contributes to the discussion of how to distinguish between a weed naturally ending up in archaeobotanical assemblages and a plant intentionally used by people,” Groot said. “We argue that future finds of black henbane should be studied by taking into account the context of the find and its relation to other medicinal plants.”
Analysis revealed that black henbane was frequently associated with 13 other species with potential medicinal or symbolic uses at 83 Roman sites in the Netherlands. This implies that they may not have always grown naturally, but rather have been cultivated. Finally, these new findings provide compelling evidence of the deliberate use of black henbane seeds during the Roman period.
The study will appear in the April edition of the peer-reviewed academic journal Antiquity.
Cover Photo: Bone found with black henbane seeds. Maaike Groot et al. / Antiquity