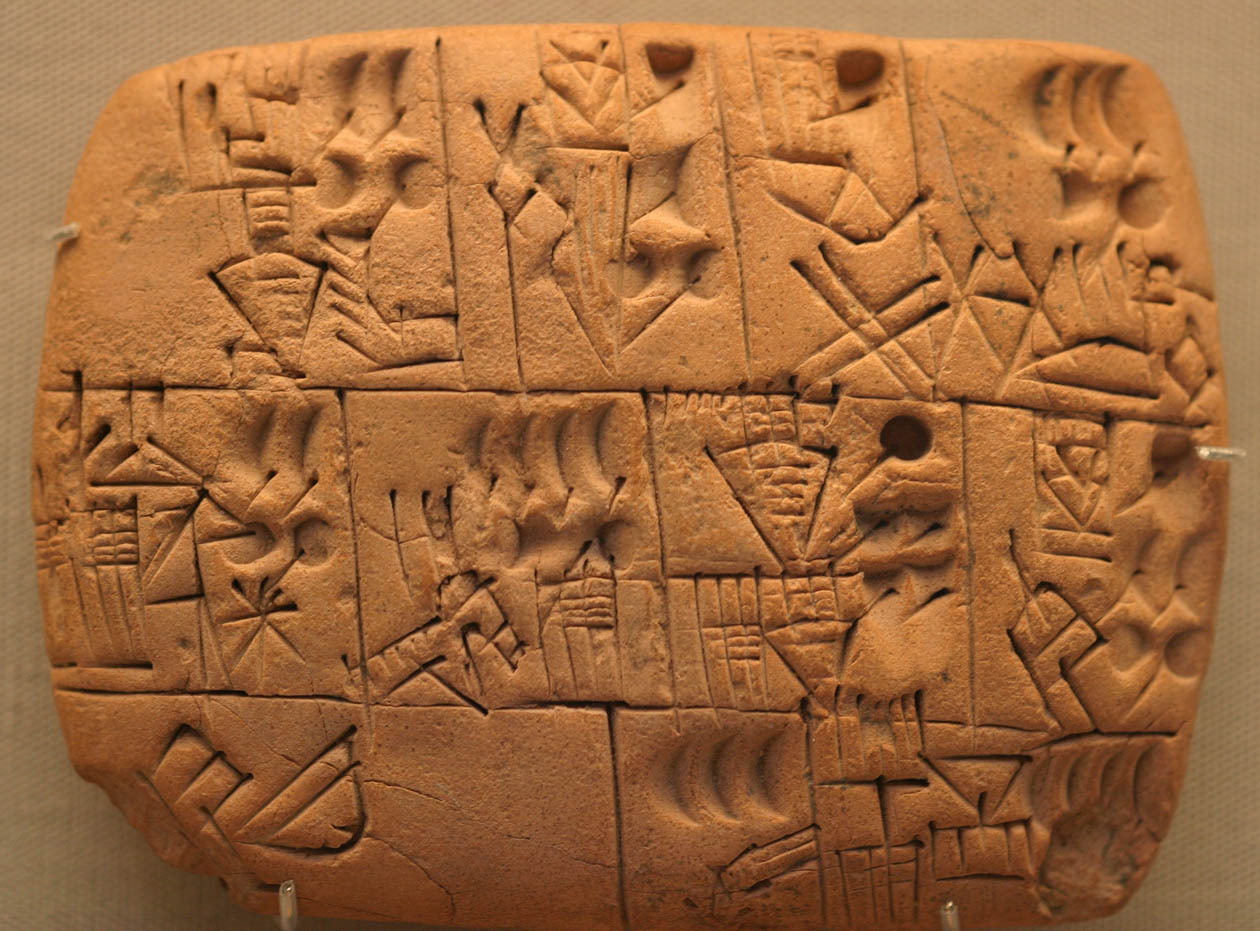
Researchers successfully deciphered 4,000-year-old cuneiform tablets discovered over a century ago in what is now Iraq. The tablets, housed at the British Museum, were discovered in Iraq more than a century ago and contain some of the earliest records of omens associated with lunar eclipses.
All of the writing on the four clay tablets that were found in Iraq was readable and in excellent condition. But because they were written in an antiquated Babylonian language, it was very challenging to translate them completely. However, two scholars who specialize in ancient languages and cultures have recently cracked the code completely, providing the first explanation of the cuneiform messages’ actual meaning.
The ancient Babylonians regarded lunar eclipses as prophetic signs of impending disaster, so they were more than just a source of entertainment. Deciphering the clues concealed in the darkness that engulfed the Moon was, thus, a significant field of study that led to the creation of numerous manuscripts detailing the diverse portents associated with an eclipse.
In a paper just published in the Journal of Cuneiform Studies, Andrew George, an emeritus professor of Babylonian at the University of London, and Junko Taniguchi, an independent researcher, introduce the results of their intensive study of these tablets.
In a recent study, the researchers present their translations and discuss how different eclipse features could be used as predictive tools for future events.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“As products of the middle and late Old Babylonian periods they represent the oldest examples of compendia of lunar-eclipse omens yet discovered and thus provide important new information about celestial divination among the peoples of southern Mesopotamia in the early second millennium BCE,” they wrote. “They are all found to bear witness to a single text, which organizes the omens of lunar eclipse by time of night, movement of shadow, duration, and date.”

The recently deciphered omens, which foretell impending doom and gloom for specific areas, people, or states, provide some fascinating insights into the anxieties and concerns that plagued ancient Mesopotamian cultures.
Royal advisors could foresee terrible misfortunes that fate had in store for a king by keeping an eye on the time and date of a lunar eclipse as well as the path of the Earth’s shadow across the moon. For instance, the tablets reveal that “an eclipse in the morning watch” signaled “the end of a dynasty” in the Mesopotamian city of Akkad.
In Babylonia and other parts of Mesopotamia, it was believed that events in the sky could predict the future. Rulers would seek the advice of astrologers who monitored the night sky and compared their observations with omen texts. If the prediction was dire, such as “the king will die,” additional rituals would be performed, including divination from animal entrails, to determine whether the king was in danger.
Fortunately, however, kings didn’t have to accept their fate lying down, as protective rituals could be employed to counteract unfavorable omens. If the divination results indicated danger, appropriate rituals were believed to nullify the bad omen and counteract the evil forces behind them. Therefore, despite the bad omens, it was believed that the predicted future could be changed.
The texts analyzed by the study authors are believed to have originated in the ancient Babylonian city of Sippar, located in modern-day Iraq.
The study is published in the Journal of Cuneiform Studies.
Cover Image: İowa State University