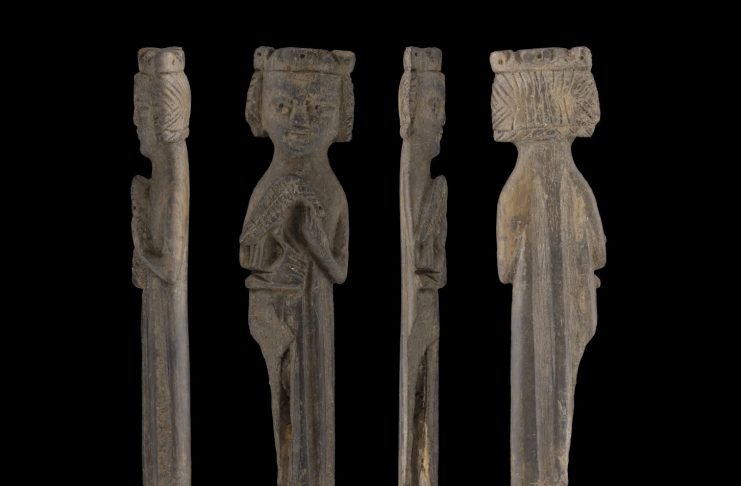
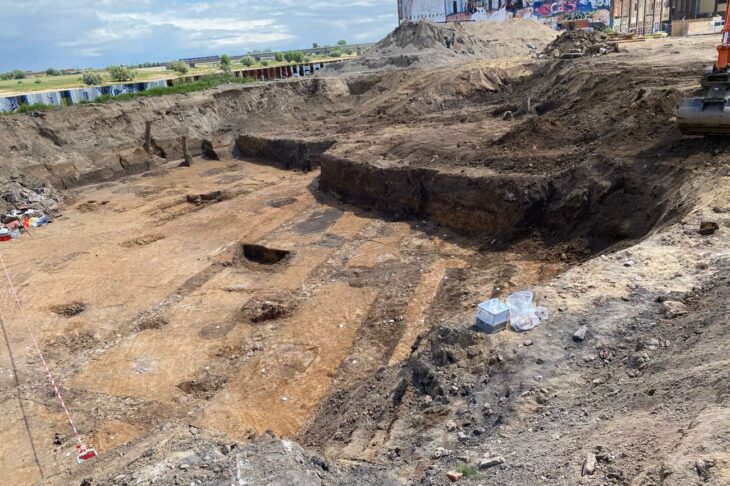
Archaeologist Ann-Ingeborg Floa Grindhaug discovered a three-inch-long figure carved from bone or antler amid the ruins of a fortified royal mansion in Oslo, according to a statement made by the Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU).
NIKU archaeologist Ann-Ingeborg Floa Grindhaug found the figure which she first thought was a big fishbone, but upon further inspection saw the face of a figure with a crown and a kestrel on its arm.
The figure is 7.5 cm long and is formed of organic material with a fairly flat oval cross shape. It is adorned on both sides. The attire and hairstyles indicate that it dates from the middle of the 13th century and was most likely created in an Oslo workshop.
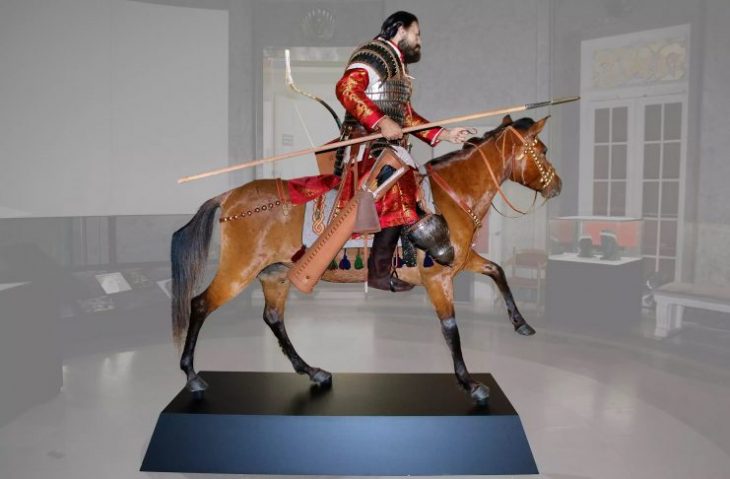
Researchers with Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research say the artifact depicts the earliest Scandinavian representation of the aristocratic activity of falconry.

The smiling, curly-haired figure wears a crown and carries a falcon on a gloved arm, and may therefore depict a king or queen, explained NIKU art historian Kjartan Hauglid.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The falcon itself is not an indicator for gender. Women were also falconers in the medieval period.
“The design of clothing shows that it is from the middle of the 13th century. The hair or head linen also fits the data. Head linen was fashionable for married women at this time”, the researcher elaborates
The style of the clothing and the headpiece suggest that the figure dates to the early thirteenth century, making it one of the earliest-known depictions of falconry in northern Europe, he added.
The lower half of the figure is hollow and may have been placed on a shaft for use by a noble or king. Håkon Håkonsson, who was king of Norway from 1217 to 1263, is known to have practiced falconry and to have given precious falcons as gifts to other European royal houses in order to build alliances.