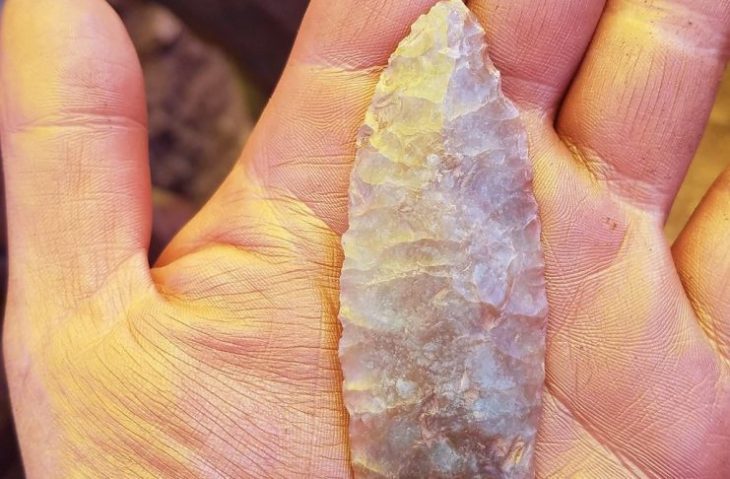
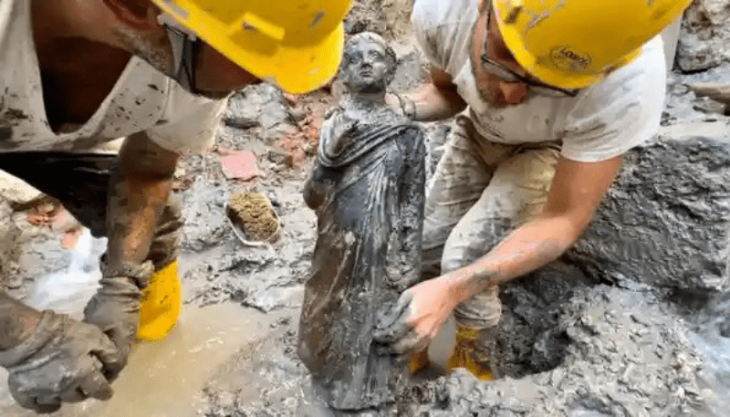
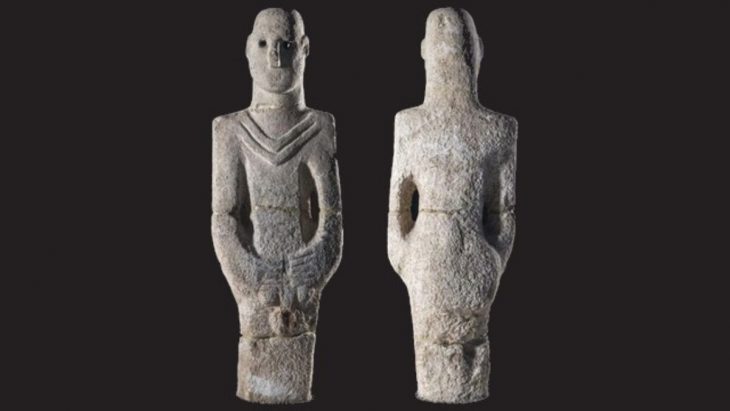
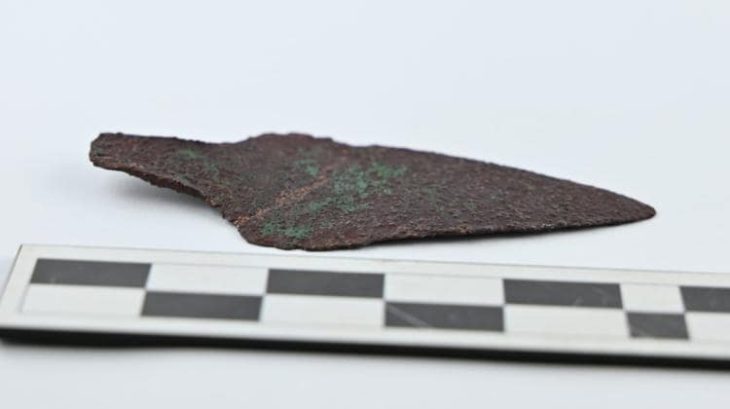
Cyprus was a surprisingly busy trading hub during the early period of international trade in the Mediterranean region. Its awe-inspiring status during the Late Bronze Age (1,500 to 1,150 BC) was made possible by abundant supplies of pure Cyprus copper mined near the ancient Cypriot village of Hala Sultan Tekke.
Researchers from the University of Gothenburg confirm the importance of the Bronze Age city in the early period of international trade in the Mediterranean, with their study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
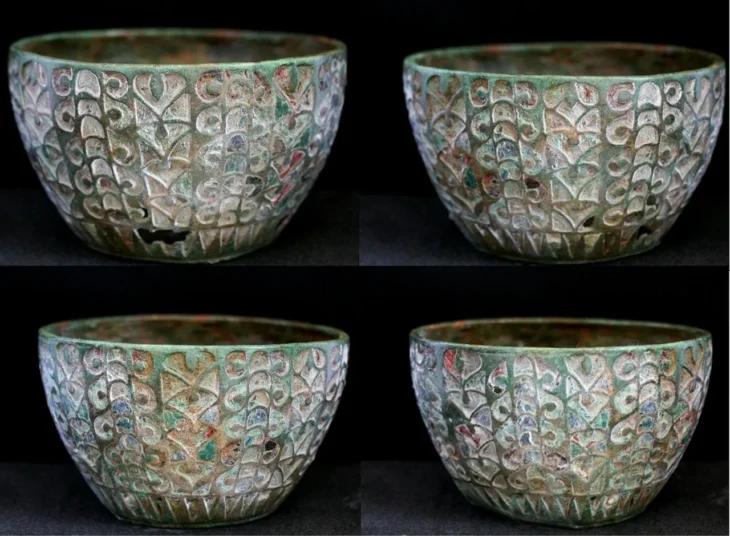
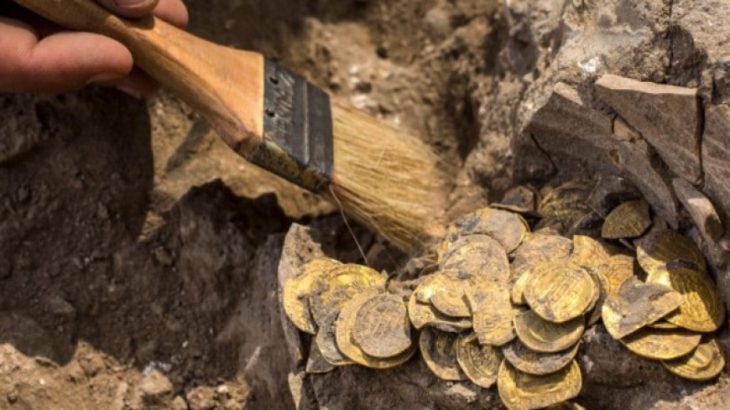
“We have found huge quantities of imported pottery in Hala Sultan Tekke, but also luxury goods made of gold, silver, ivory and semi-precious gemstones which show that the city’s production of copper was a trading commodity in high demand,” says Peter Fischer, emeritus professor at the Department of Historical Studies at the University of Gothenburg and the leader of the excavations.
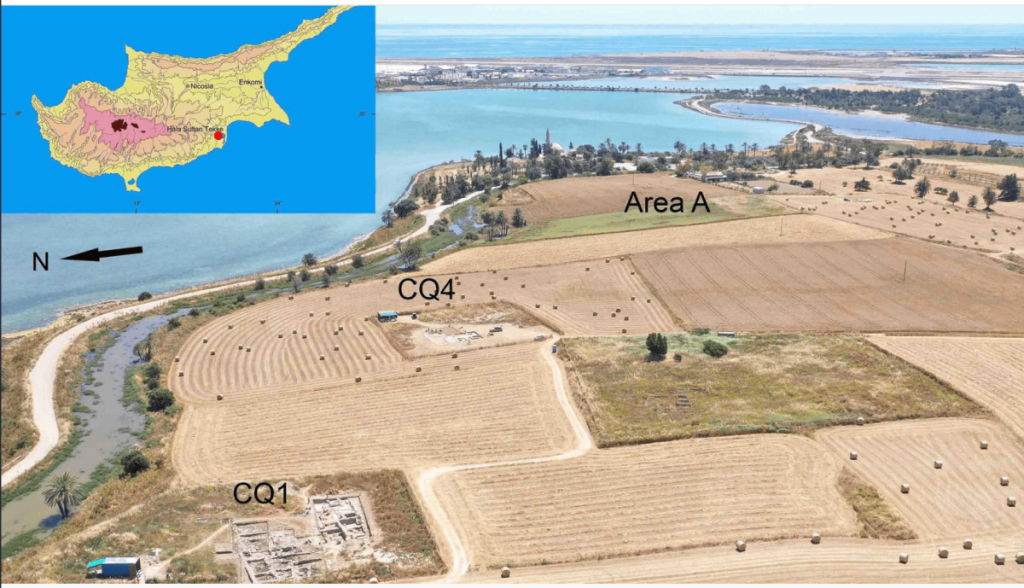
The Swedish Cyprus Expedition is a research project that began in 1927 to map the island’s archaeological history. The most recent expedition led by Peter Fischer at Hala Sultan Tekke, near the modern-day city of Larnaca on the south coast of Cyprus, started in 2010 and has continued for 13 seasons. The excavations have shown that the city covered at least 25 hectares, 14 of which comprised its centre, surrounded by a city wall. The Expedition has also found objects from this period scattered over an even larger area.
“Our investigations and excavations show that Hala Sultan Tekke was larger than was previously thought, covering an area of some 25 to 50 hectares, which is a big city by that period’s standards. Usually, settlements at this time and in this area covered only a few hectares,” says Peter Fischer.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Largest copper producer
During the Bronze Age, Cyprus was the largest copper producer around the Mediterranean. This metal alloyed with tin formed the basis for making bronze which was then used for casting tools, weapons and jewellery before iron started being used.
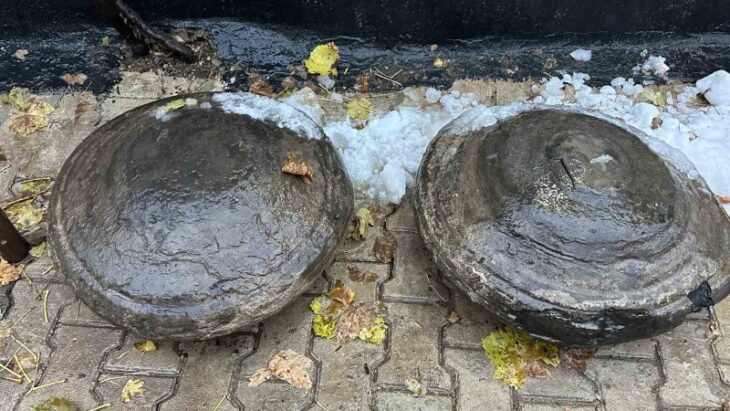
“Remains in the city show extensive copper production in the form of smelting furnaces, cast moulds and slag. The ore from which the copper was extracted was brought into the city from mines in the nearby Troodos Mountains. The workshops produced a lot of soot and were placed in the north of the city so that the winds mainly from the south would blow the soot and the stench away from the city. Today, this type of production would be impossible, since the production process generates waste products such as arsenic, lead and cadmium, but at that time people did not know how dangerous the process was,” says Peter Fischer.
Large quantities of imported goods
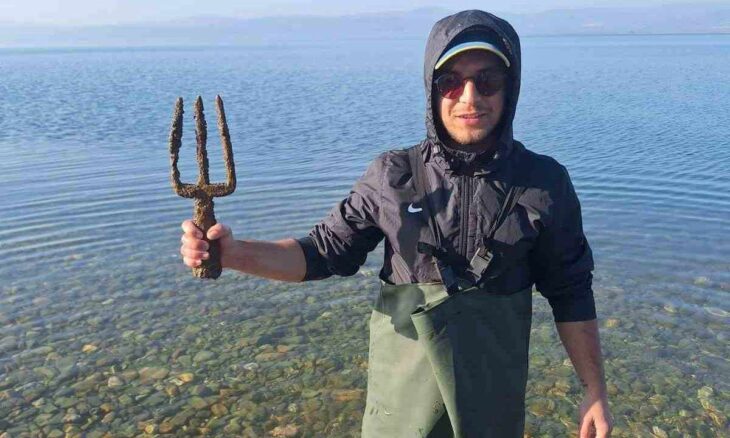
The central location of Cyprus in the eastern Mediterranean and a well-protected harbour created very favourable conditions for lively trade in Hala Sultan Tekke. Large quantities of imported goods in the form of pottery, jewellery and other luxury goods from neighbouring regions such as modern-day Greece, Türkiye, the Middle East and Egypt, as well as longer-distance imports from Sardinia, the Baltic Sea region, Afghanistan and India have been found. These finds show that the city was one of the largest trade hubs in the period 1500–1150 BC and was of great importance during the initial period of international trade in the area.

In addition to copper, highly sought-after purple-dyed textiles were also produced. The dye came from purple dye murex species from which the mucus that produced the purple dye was extracted. The city also produced and exported pottery with characteristic painted motifs of humans, animals and plants. The researchers refer to the artist behind these painted motifs as the ‘Hala Sultan Tekke painter’.
“The great thing about the many pottery finds is that we can assist our colleagues around the Mediterranean and beyond. No pottery has the same spread as the coveted Cypriot pottery during this period. By finding locally made pottery that we can date in the same layer as other imported pottery that was previously difficult to date, we can synchronise these and help colleagues date their finds,” says Peter Fischer.
Trade flourished for 500 years
The name of the Bronze Age city comes from the expedition having initially named the site after the mosque, Hala Sultan Tekke, which now stands close to the excavation site. Trade flourished in the city for almost 500 years, but like several other sophisticated Bronze Age civilisations around the Mediterranean, Hala Sultan Tekke collapsed just after 1200 BC. The prevailing hypothesis was that the ‘Sea Peoples’ invaded the eastern Mediterranean around this time, destroying its cities and bringing the Bronze Age civilisations to an end.
“In the past, it was thought that the ‘Sea Peoples’ were the sole explanation. Our research in recent years has given more nuance to this explanation. For example, there are now new interpretations of written sources from this period in Anatolia (modern-day Türkiye), Syria and Egypt, which tell of epidemics, famine, revolutions and acts of war by invading peoples. In addition, our investigations indicate that a deterioration in the climate was a contributing factor. All of this may have had a domino effect, that people in search of better living conditions moved from the central Mediterranean towards the south-east, thus coming into conflict with the cultures in modern-day Greece, on Cyprus and in Egypt,” concludes Peter Fischer.