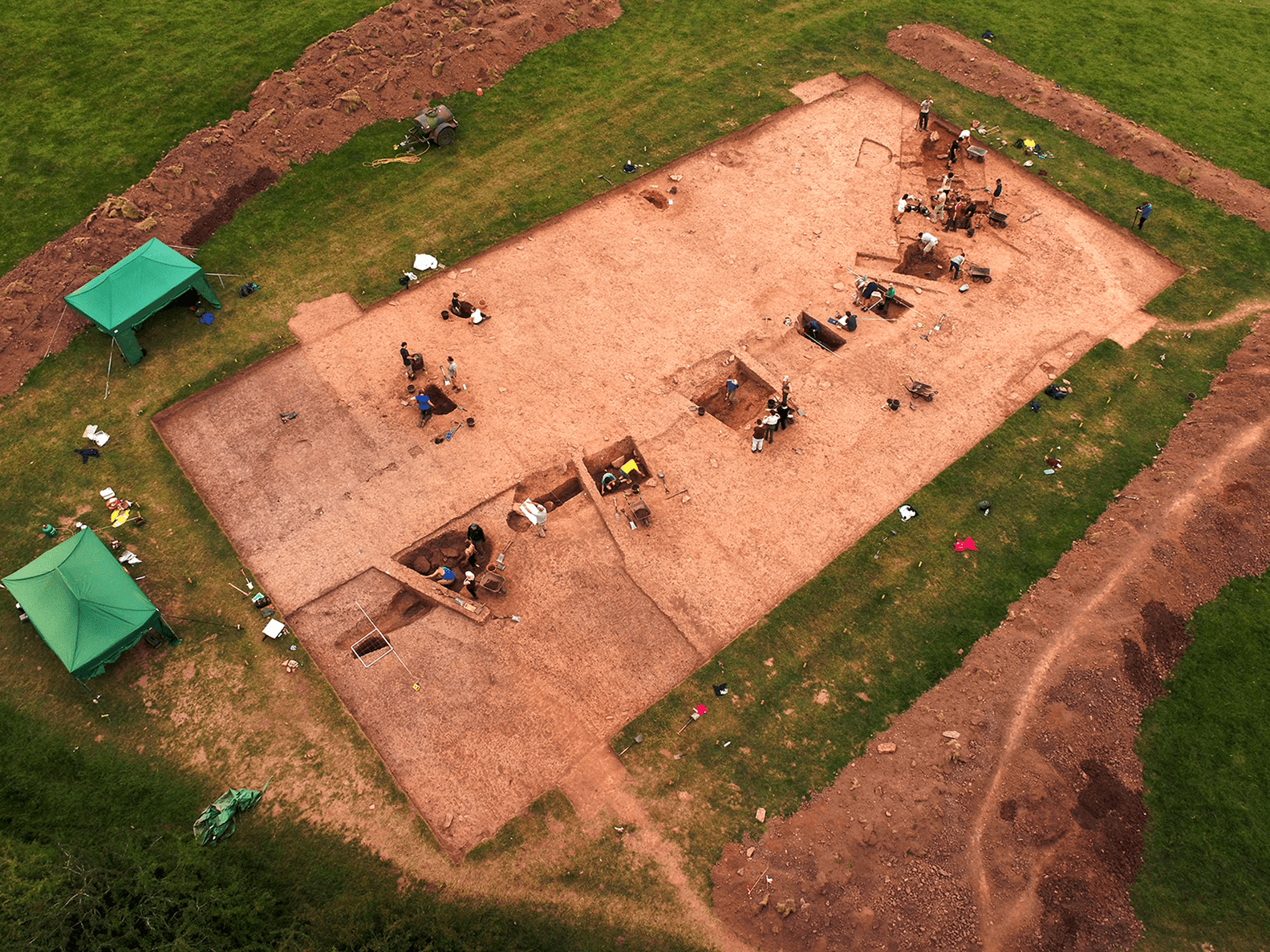
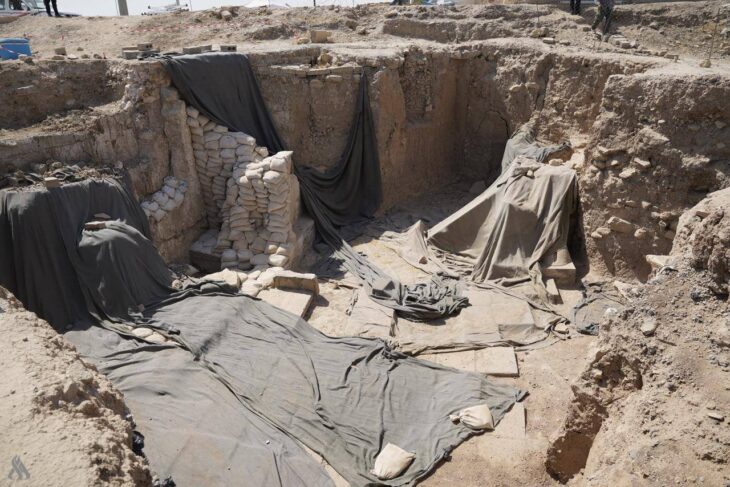
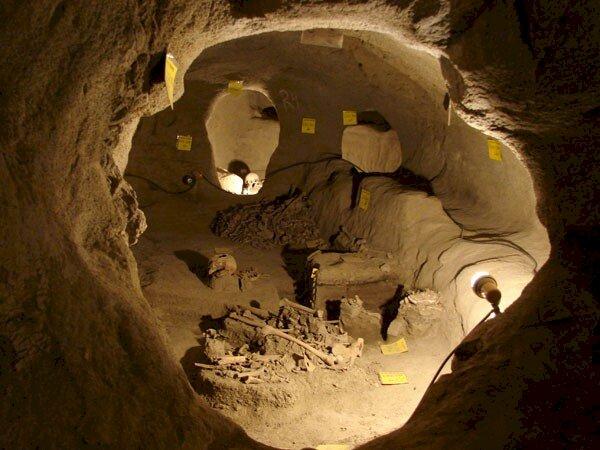
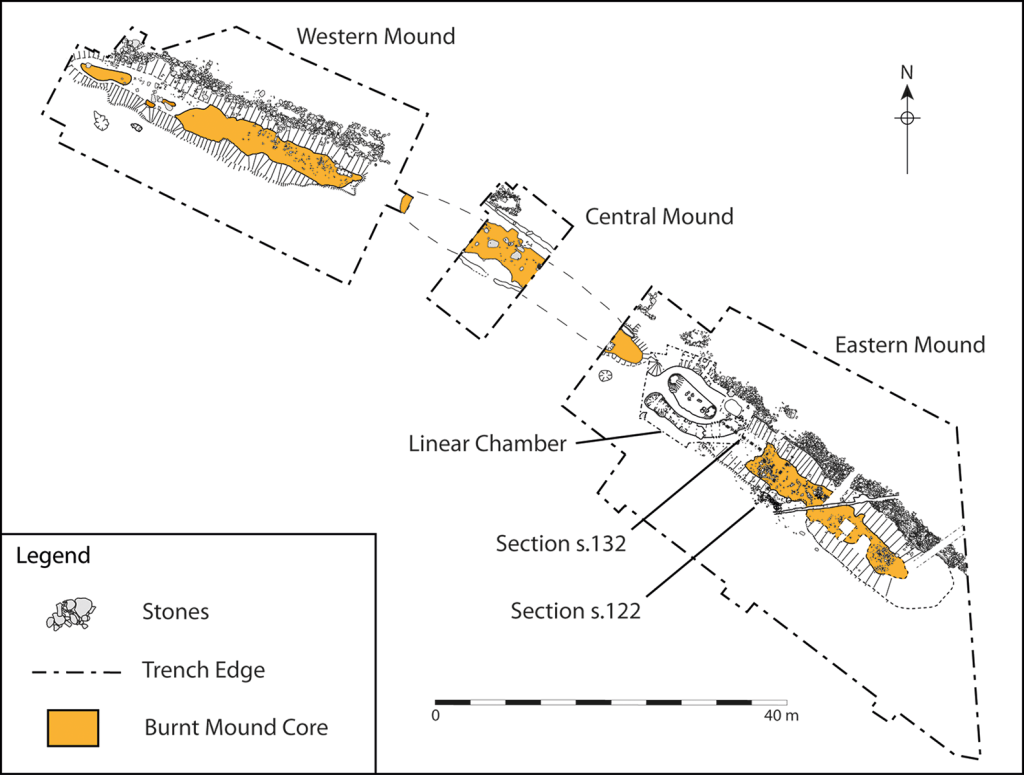
Archaeologists discovered a remarkable complex of early Neolithic monuments while investigating the area around Dorstone Hill in Herefordshire, England. The Early Neolithic monuments complex: consists of three long barrows constructed on the footprints of three timber buildings that had been deliberately burned and plus a nearby causewayed enclosure.
Researchers used advanced radiocarbon dating to investigate the age of Neolithic monuments and the results showed the structures were much older than expected.
The dating shows that at least 5,800 years ago, the area was inhabited by Neolithic people, who engaged in farming and the construction of monuments rather than hunting and gathering. This would make Dorstone Hill the earliest culturally Neolithic site in the west Midlands of England, comparable with early dates from Penywyrlod and Gwernvale in the Black Mountains of Wales.
These early dates, so far inland, suggest that Neolithic practices did not spread evenly from south-east to north-west across Britain, as has sometimes been suggested, but instead moved somewhat irregularly, with pockets of hunter-gatherers and farmers sometimes co-existing for hundreds of years.
Dorstone Hill was excavated between 2011 and 2019, but this is the first time that advanced statistical methods have been used to analyze the radiocarbon dates that resulted. This analysis shows that activity at the site began much earlier than it did elsewhere in the region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Seeking to place the various structures and deposits at Dorstone Hill into a temporal context, Professors Keith Ray and Julian Thomas, with a team of investigators from Cardiff University, the University of Manchester, and Manchester Metropolitan University, carried out a program of radiocarbon dating and chronological modeling for the site. Their results are published in the journal Antiquity.
Bayesian chronological modeling is a mathematical method that allows archaeologists to integrate all the available dating evidence, including radiocarbon dates and stratigraphy, to produce more robust chronological frameworks.
In this case, the team collected 12 new radiocarbon measurements from bone, antler, and short-life carbonized plant material found at the site, then modeled these against stratigraphy and archaeological phases identified during the excavations. This revealed that almost all phases of occupation were earlier than expected, with the earliest occupation probably going back further than 3800 BC.
“Dorstone Hill appears to have been a location in which a series of phenomena seem to have occurred at an unusually early date,” said Professor Julian Thomas. “This marks it out as an important regional center, a place of origins and beginnings, which acquired and retained a particular significance through the earlier fourth millennium BC.”
Importantly, this means that the monuments at the site are among the earliest in Britain, despite being located in a landlocked part of the island, remote from the southeast where Neolithic migrants from the continent were believed to have first arrived.
Cover Photo: Antiquity (2023). DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2023.93