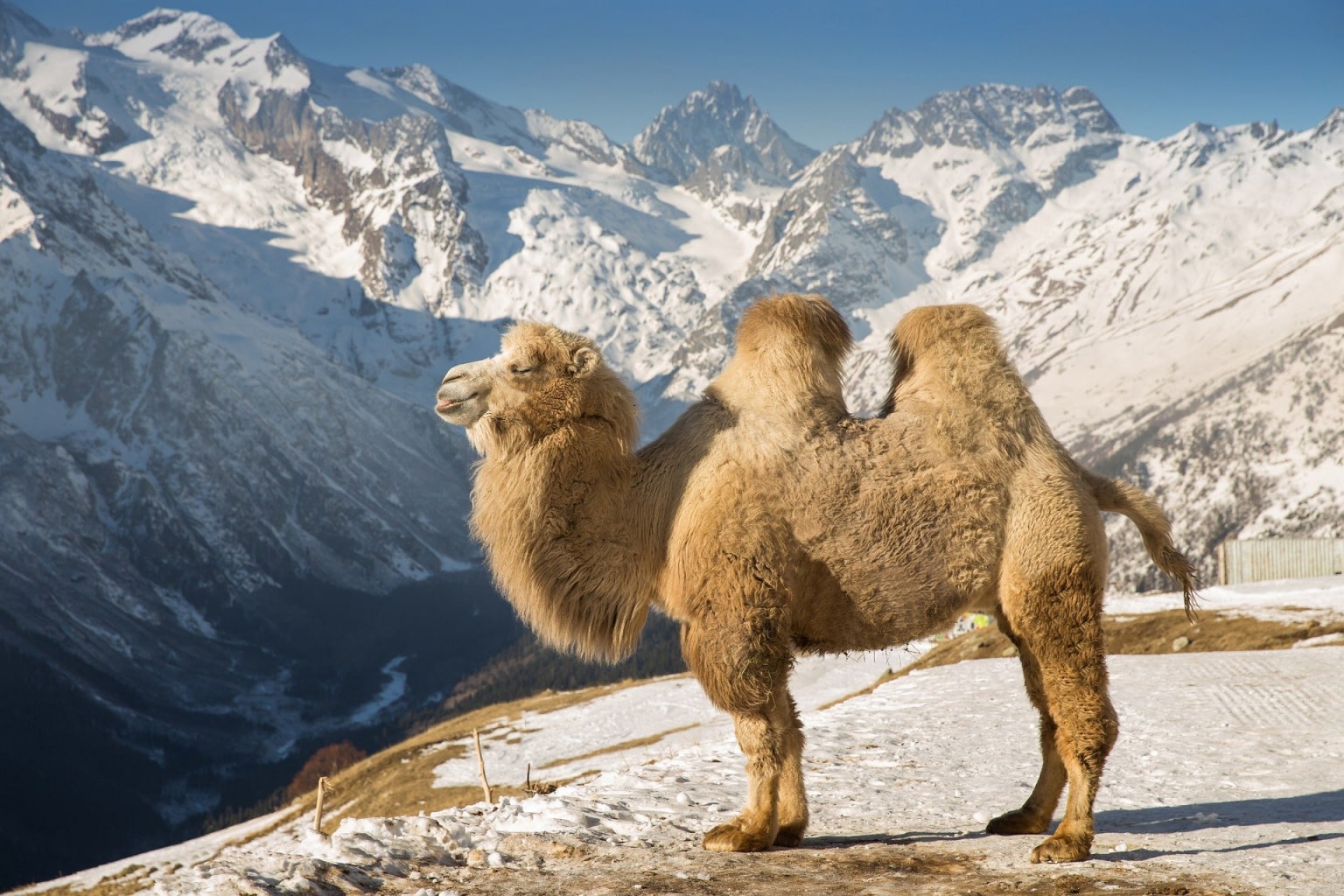
Camelus knoblochi, a species of giant two-humped camel, survived in Mongolia alongside modern humans—and perhaps Neanderthals and Denisovans—until about 27,000 years ago.
Camelus knoblochi, is known to have lived for approximately a quarter of a million years in Central Asia. C. knoblochi’s last refuge was in Mongolia until approximately 27,000 years ago.
Giant 10ft-tall Mongolian camels were killed and eaten by archaic humans before going extinct 27,000 years ago, a study shows.
A new study in Frontiers in Earth Science believes that humans hunting the 2,200-pound camel significantly contributed to their extinction aside from the widely accepted climate change as its cause of demise.
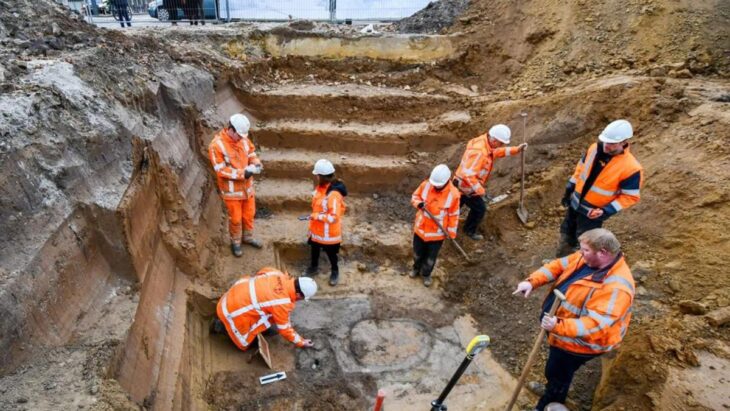
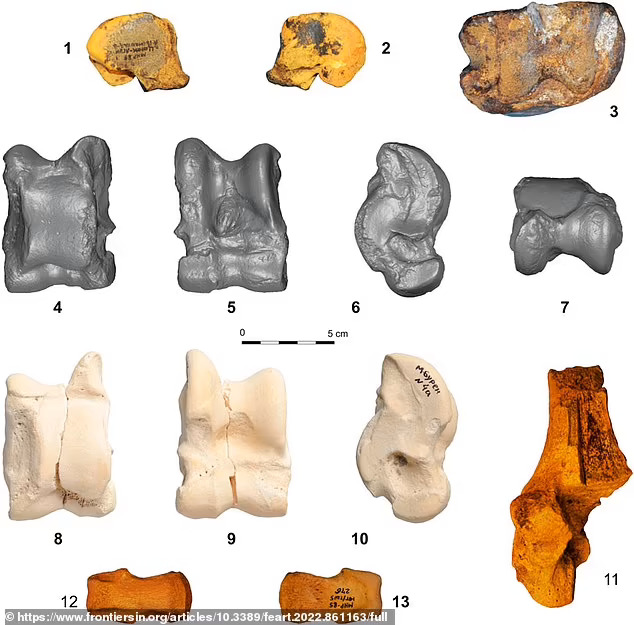
Scientists have studied fossilized remains of the giant camel that have been found in Tsagaan Agui Cave in the Gobi Altai Mountains alongside artifacts left behind by Paleolithic people.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
One metacarpal bone, dated to between 59,000 and 44,000 years ago, bears butchery marks and marks made by gnawing hyenas, said Arina M. Khatsenovich of the Russian Academy of Sciences./

One of the bones shows signs of both butchery by humans, likely to extract protein-rich marrow, and ‘hyenas gnawing on it’.
‘Here we show that the extinct camel, Camelus knoblochi persisted in Mongolia until climatic and environmental changes nudged it into extinction about 27,000 years ago,’ said study author Dr. John W Olsen at the School of Anthropology, University of Arizona.
‘C. knoblochi fossil remains from Tsagaan Agui Cave, which also contains a rich, stratified sequence of human Paleolithic cultural material, suggest that archaic people coexisted and interacted there with C. knoblochi.
Paradoxically, today, southwestern Mongolia hosts one of the last two wild populations of the critically endangered wild Bactrian camel, C. ferus. The new results suggest that C. knoblochi coexisted with C. ferus during the late Pleistocene in Mongolia, so that between-species competition may have been a third cause of C. knoblochi’s extinction. Standing nearly three meters tall and weighing more than a ton, C. knoblochi would have dwarfed C. ferus. The precise taxonomic relationships between these two species, other extinct Camelus, and the ancient Paracamelus aren’t yet resolved.
Olsen said, “C. knoblochi fossil remains from Tsagaan Agui Cave [in the Gobi Altai Mountains of southwestern Mongolia], which also contains a rich, stratified sequence of human Paleolithic cultural material, suggest that archaic people coexisted and interacted there with C. knoblochi and elsewhere, contemporaneously, with the wild Bactrian camel.”
The authors conclude that C. knoblochi finally went extinct primarily because it was less tolerant of desertification than today’s camels, C. ferus, the domestic Bactrian camel C. bactrianus, and the domestic Arabian camel C. dromedarius.
In the late Pleistocene, much of Mongolia’s environment became drier and changed from steppe to dry steppe and finally desert.
First author Dr. Alexey Klementiev, a paleobiologist with the Russian Academy of Sciences’ Siberian Branch, said, “We conclude that C. knoblochi became extinct in Mongolia and in Asia, generally, by the end of Marine Isotope Stage 3 (roughly 27,000 years ago) as a result of climate changes that provoked degradation of the steppe ecosystem and intensified the process of aridification.”
















