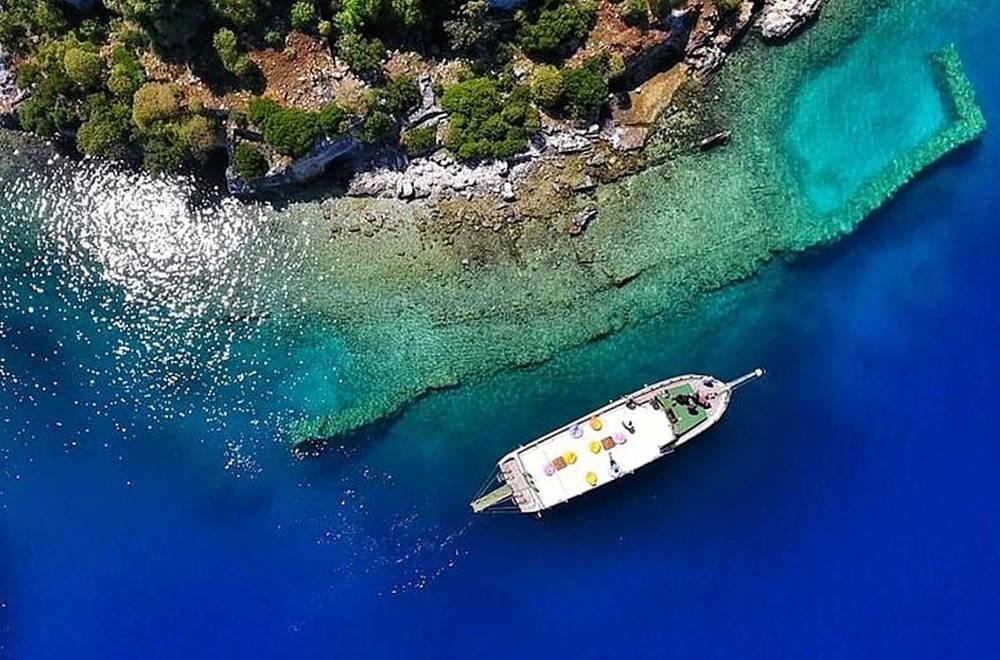
The Kekova region, or Sunken City, which has remained under the sea after two major earthquakes in the sixth century in the Mediterranean, is an archaeological gem located along the Turquoise Coast of Türkiye.
With its submerged ruins, crystal-clear waters, and fascinating history, it has become a must-visit destination for travelers seeking a unique and immersive experience.
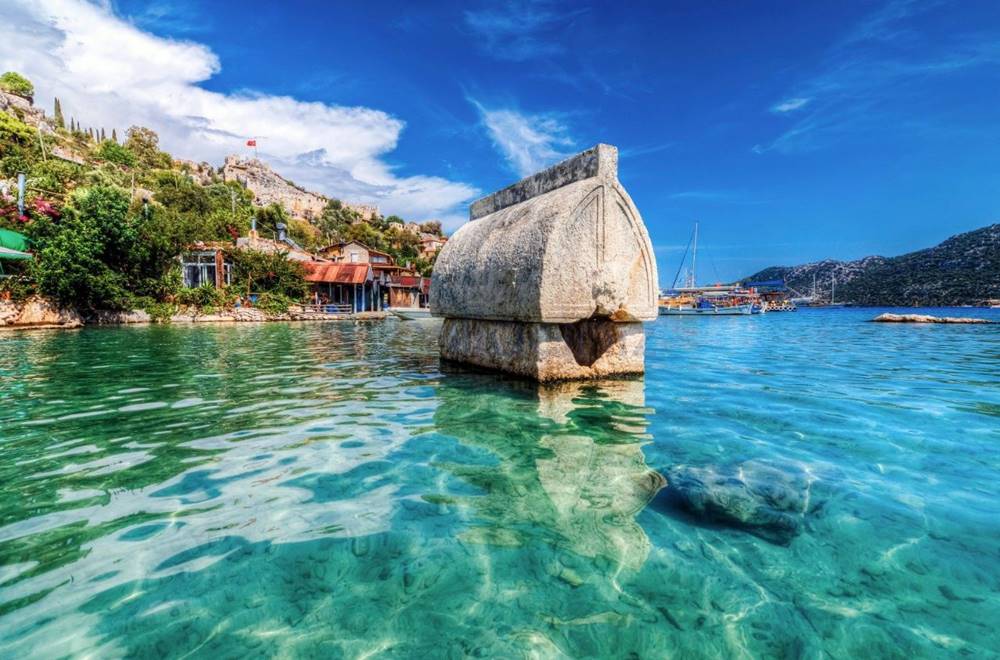
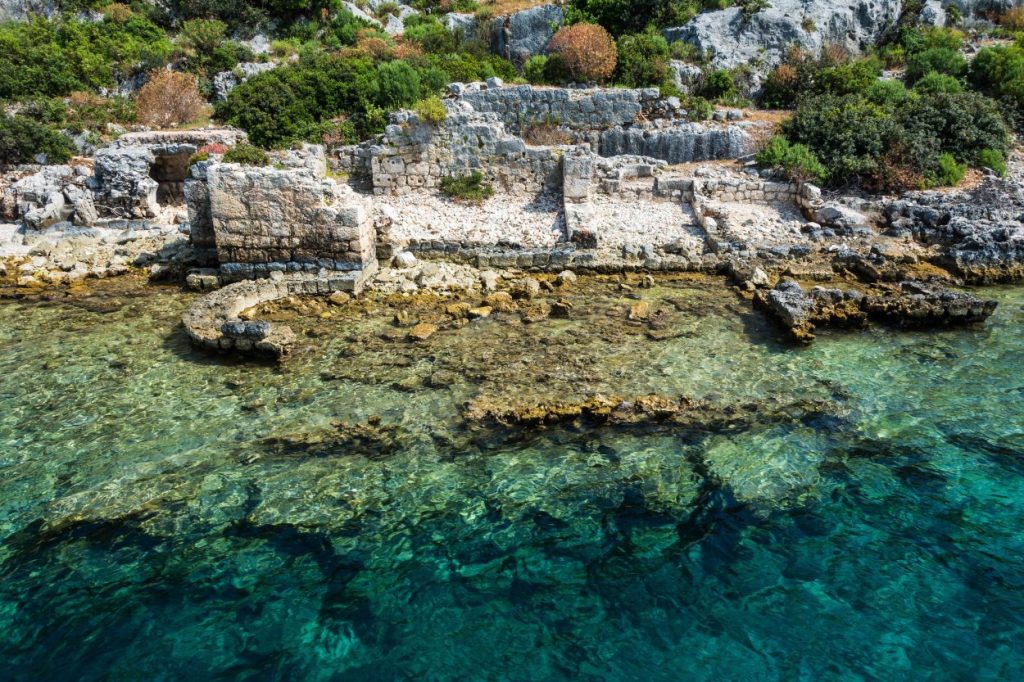
Kekova Port, one of the important trade centers of Lycia, was also flooded after the great earthquakes. Today, it is called the Sunken City because of these ancient ruins.
Although there were major earthquakes like the one in 141, it is known that after the cities were revived, life continued. However, as a result of the major earthquakes in 529 and 540, a large area in Central Lycia, including the Kekova Peninsula of the Demre district, was flooded.
Tours are organized to the region where there is no land transportation. Boats can approach these ancient underwater ruins up to a certain distance. Since they are under protection, you can only visit these ruins from a distance. However, the water is so clear that it is possible to see the remains easily with the naked eye.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
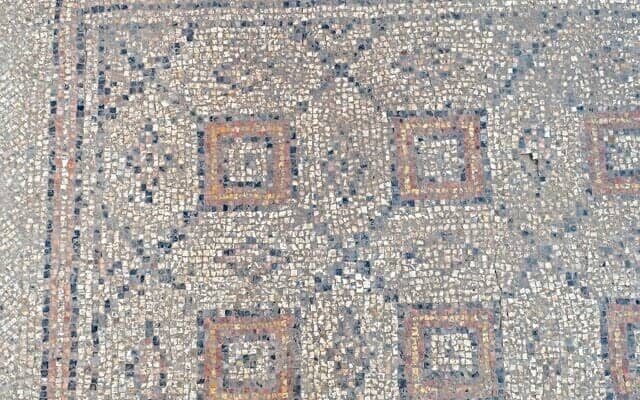
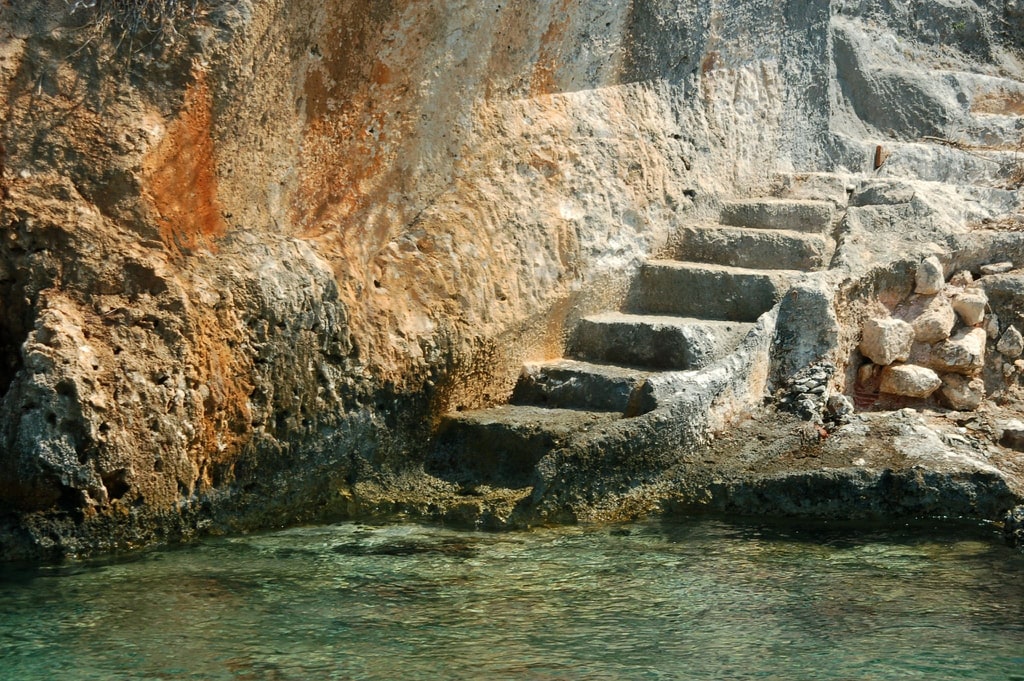
Apart from the underwater ruins, you will also see some ancient ruins from the city on the island. Stairs above and below the water, royal tombs, boathouse, and remnants of walls take you deep into history.
Speaking about the region, the head of the Myra – Andriake Excavations in the Demre district of Antalya, Professor Nevzat Çevik of Akdeniz University said that the settlements in Kekova were a densely populated area before they sank, and that the region became silent for almost 200 years due to the major earthquakes in 529-540 and the tsunami that followed, as well as epidemics.

“Not only Kekova but also the whole region around Andriake, Finike and Kaş sank. We have some ideas about when this area sank at the earliest. The sarcophagus or the other structures underwater in Andriake Harbor show us that the area remained underwater completely. During the great earthquakes in the sixth century, the plate structures slipped more than two meters towards the sea, causing the cities in the entire region to remain underwater. We understand that life in the coastal areas of those cities ended, especially given the fact that other structures such as residences related to the port or civilian settlements near the sea were submerged in the water. We see that life continued in the upper parts of the region during the Christian period, but the coastal part of those cities were used in the classical and Hellenistic ages and the structures near the coast were completely flooded especially in Simena, Teimiussa, Aperlai and Kekova Island. The half-submerged steps and structures seen by boat travelers today are the result of this sinking,” said Çevik.

Çevik stated that after the disaster, Andriake, the largest ancient port of the Mediterranean, lost its function, and continued:
“This is why the excavations in Andriake did not bring any finds after the seventh century. There are many ports and shelters in Kekova. There was heavy sea traffic especially during the Hellenistic, Roman and Byzantine periods. Since Andriake was one of the largest ports in the ancient Mediterranean, there was a great deal of international ship traffic there. When the port lost its function, this function decreased a lot. The main reason for this is earthquakes. Thousands of earthquakes happen due to a main line especially in the Fethiye – Burdur area. Major earthquakes on that line also affected Lycia. Major earthquakes in the Mediterranean also affected all these cities. Factors such as tsunamis and epidemics after earthquakes also deeply affected the civilization, culture and settlement population there and changed life. After that period, we can see from archaeological data that life almost ended, civilization did not progress and settlements were abandoned.”
Stating that these formations had been transformed into picturesque landscapes, Çevik said that for this reason, Kekova creates an incredible visuality not only with its clearest sea and Dalmatian-type impressive nature but also with its underwater ruins.
In order to join this wonderful boat tour, you need to go to Kekova’s Üçağız or Kaş Harbor in Kaş.