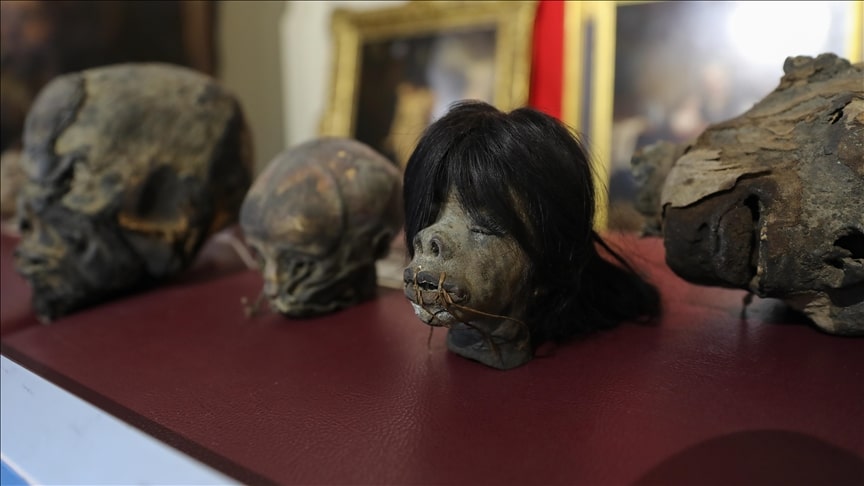
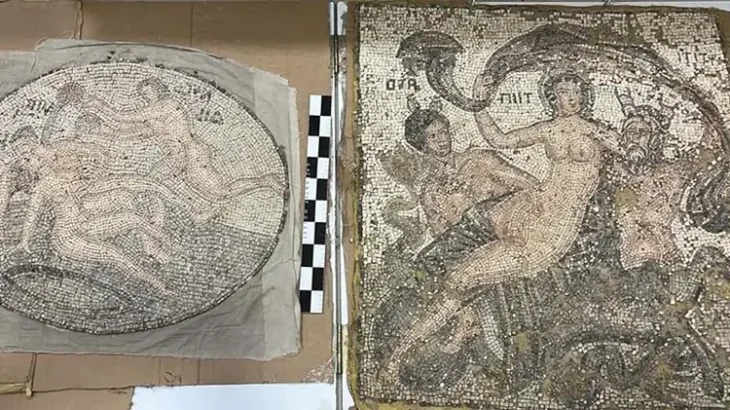
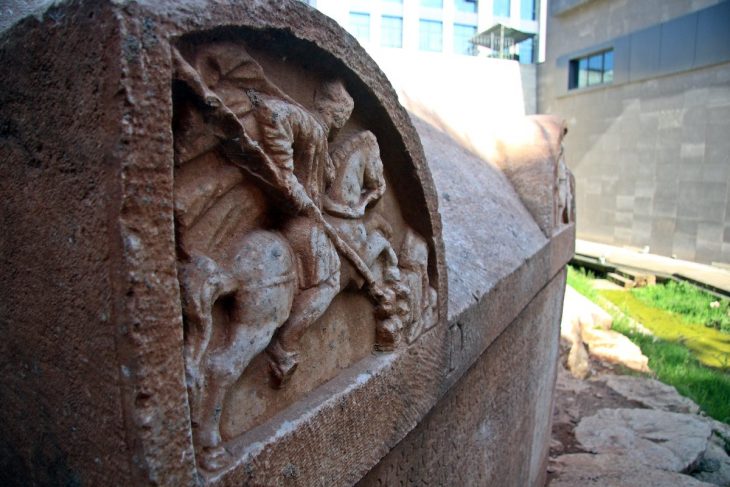
In the operation held in the Aliağa district of İzmir, 400 historical artifacts belonging to various periods were seized, including 4 skulls, which are considered to be from the Jivaro tribe of South American origin.
Evaluating a notice, the Ministry of Commerce Customs Enforcement Smuggling and Intelligence Directorate teams conducted an operation to 2 addresses determined in the Aliağa district.
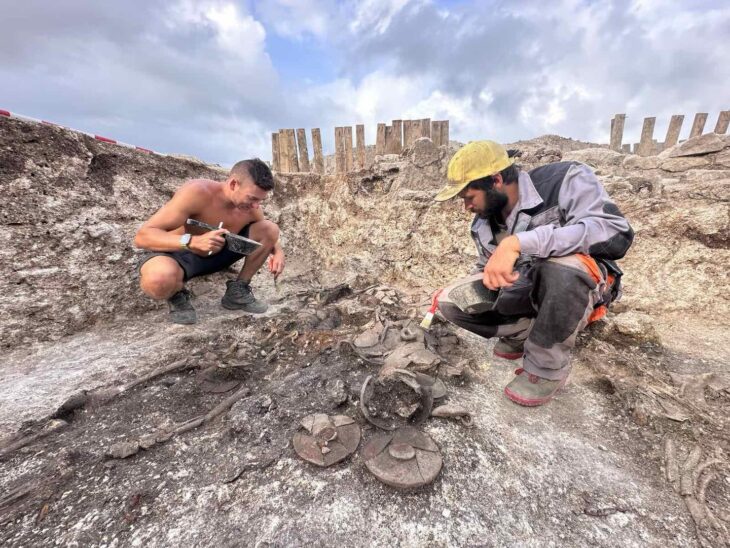
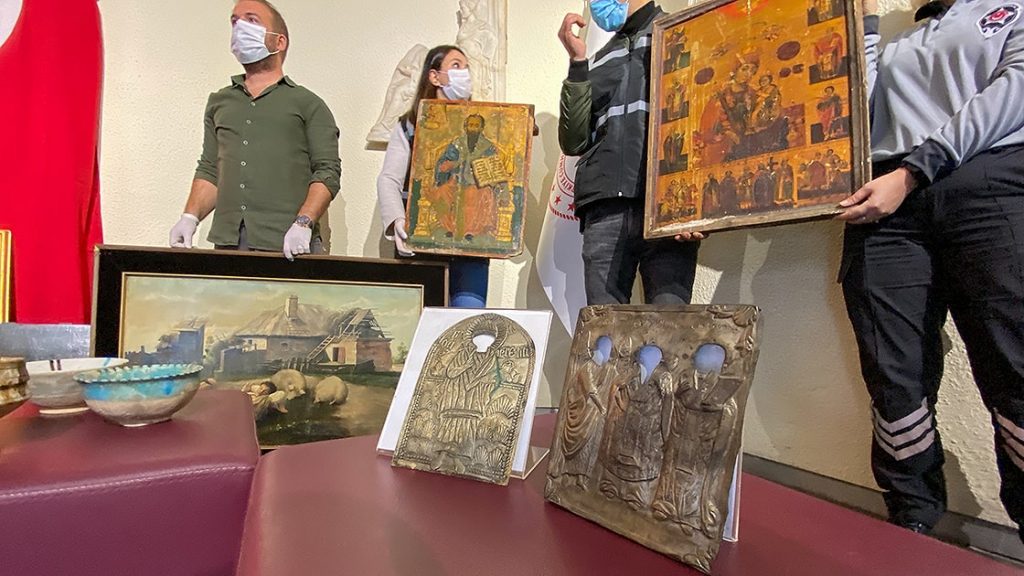
During the searches in the first house, coins from the Byzantine period, 4 bone hairpins, 19 Ottoman manuscripts, as well as 59 historical artifacts from different periods were found.
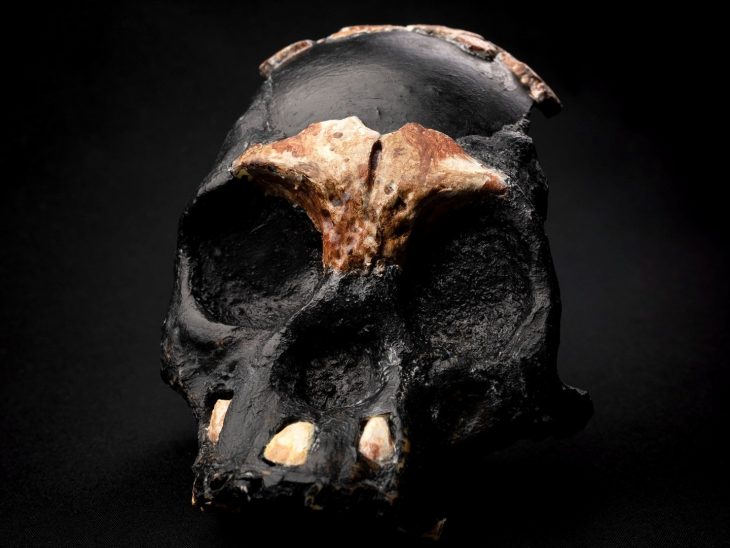
Upon the expansion of the operation, 4 skulls, 3 mummies, 269 historical artifacts, and 27 paintings from the 18th century were found in a warehouse that was searched.
They seized 337 historical artifacts were delivered to the İzmir Archeology Museum Directorate, and 27 paintings were delivered to the İzmir Painting, Sculpture Museum and Gallery Directorate.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
It has been reported that the Aliağa Chief Public Prosecutor’s Office continues its investigation into the smuggling of historical artifacts.

Artifacts from the Neolithic period
İzmir Archeology Museum Director Hünkar Keser said that some of the artifacts seized date to the Prehistoric period.
Noting that there are materials from both Anatolian geography and different parts of the world among the artifacts, Keser said, “The examination of these artifacts will take a long time. We need to do some laboratory or DNA analyzes. It will be possible to determine the date and origin of the artifacts at the end of these analyses. The principle of our country and ministry, international agreements. and according to bilateral agreements, it is to send the work to whichever country it belongs to,” he said.
Skull and mummy remains
Keser gave the following information about the artifacts:
“Our oldest artifacts are flints, arrowheads, which we think belong to the Neolithic period. There are also artifacts that we think are from different cultures of the world. There are tiny skulls the size of oranges among them. We think that they are at least 500 years old, made of real human skulls. These tribes lived before America was discovered.” “When they met the modern world, these skulls started to be smuggled to Europe. Today, it is forbidden to move them to another region.”
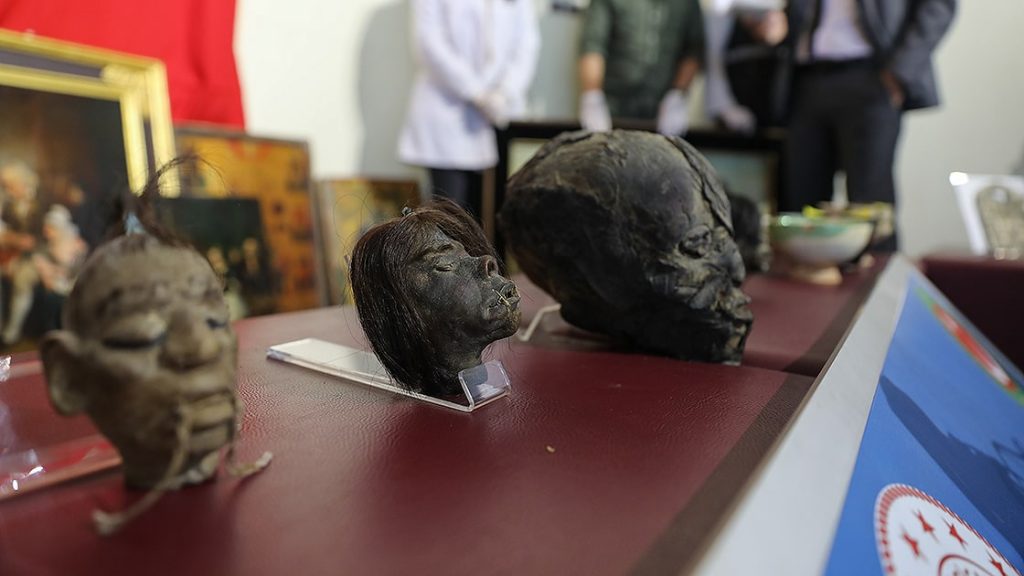

Tsantsas, or shrunken heads, is an ancient traditional technique of the Jivaro Indians from northern Peru and southern Ecuador, forensic researchers say.
“Tsantsas, or shrunken heads, is an ancient traditional technique of the Jivaro Indians from Northern Peru and Southern Ecuador. Tsantsas were made from enemies’ heads cut on the battlefield. Then, during spiritual ceremonies, enemies’ heads were carefully reduced through boiling and heating, in the attempt to lock the enemy’s spirit and protect the killers from spiritual revenge. The presence of sealed eyelids, pierced lips with strings sealing the mouth, shiny black skin, a posterior sewn incision, long glossy black hair, and lateral head compression are characteristic of authentic tsantsas.”
İzmir Archeology Museum Director Hünkar Keser stated that mummy remains were among the seized materials and that they would conduct DNA analysis to determine where the mummies came from.