Archaeologists at Tel Shiloh Claim Structure Matches Biblical Tabernacle Where the Ark of the Covenant Was Housed
In a monumental discovery that could rewrite biblical archaeology, a team of researchers at the ancient site of Tel Shiloh in Israel claims to have unearthed the very location where the Ark of the Covenant was once stored — a find that aligns with scriptural descriptions in the Old Testament.
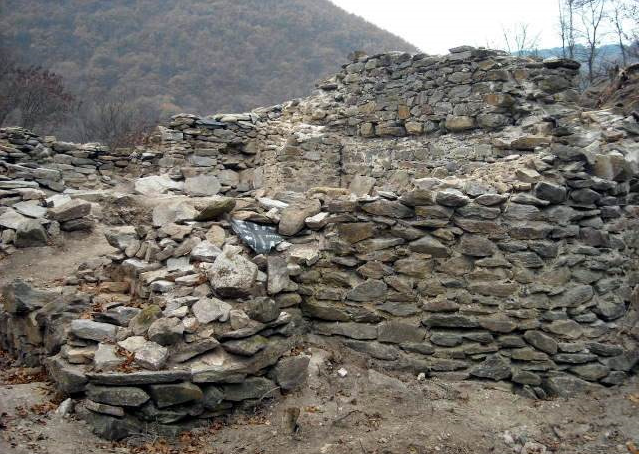
Led by Dr. Scott Stripling, Director of Excavations at Shiloh, the team has uncovered what they describe as a monumental Iron Age I structure that matches the biblical specifications of the Tabernacle — the portable earthly dwelling place of God described in Exodus. The site is located in the hill country of Ephraim, a region noted in the Bible as Israel’s first central worship center.
“We have identified a monumental building from the Iron Age I period that perfectly matches the biblical specifications,” said Dr. Stripling in an interview with The Christian Broadcasting Network (CBN). “It is oriented east-west and has an internal ratio of 2 to 1 — just as described in the book of Exodus.”
Evidence of Sacrificial Rituals Matches Biblical Practices
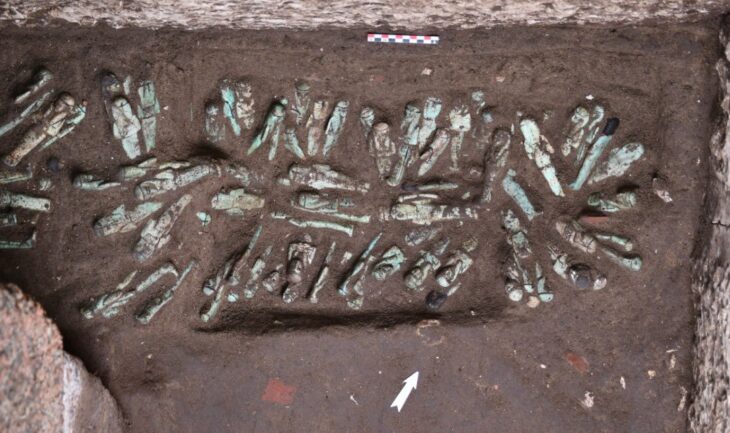
In addition to architectural features, over 100,000 animal bones were found at the site, mainly from sheep, goats, and oxen — the same animals listed in Levitical sacrificial laws. The bones predominantly came from the right side of the animals, which directly correlates with Leviticus 7, where the right side is reserved for priestly offerings.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The evidence of sacrificial rituals here is overwhelming,” Stripling told CBN. “These findings cannot be considered a coincidence. They match the biblical account to a degree that’s hard to ignore.”
Pottery fragments discovered in the same layer date back to the period in which the Ark would have been housed at Shiloh, around the 15th to 11th centuries BC, before it was moved to Jerusalem during King David’s time.

Shiloh and the Biblical Ark: A Powerful Connection
According to the Bible, the Ark of the Covenant — a gold-covered wooden chest containing the Ten Commandments — was kept in the Tabernacle at Shiloh for nearly 400 years. In 1 Samuel 4, it is described how the Israelites brought the Ark into battle, only for it to be captured by the Philistines. The event led to the death of Eli the High Priest, who fell and died upon hearing the news.
Stripling’s team may have even identified the city gate where Eli was sitting when he received the fateful report — a discovery that adds yet another layer of depth to the excavation.
“We believe we have uncovered the very gate mentioned in the story of Eli’s death,” Dr. Stripling told CBN.
The Tabernacle’s Inner Room — A Holy of Holies Found?
One of the most striking architectural features is a massive interior dividing wall, which researchers believe may have once separated the Holy of Holies — the most sacred part of the Tabernacle where the Ark was kept. According to Exodus 26 and Leviticus 16, only the high priest could enter this space once a year, under strict conditions, due to the believed physical presence of God dwelling between the cherubim atop the Ark.
Could This Be the Final Clue in the Ark of the Covenant Mystery?
While the Ark itself remains lost to history — vanishing from records around 586 BC — this latest discovery at Tel Shiloh offers perhaps the strongest archaeological evidence to date of its original resting place. Combined with historical, biblical, and material evidence, researchers say the site aligns too closely with scripture to dismiss.
“If you believe the Bible is rooted in historical truth,” said Stripling, “then this site could very well be where the Ark once stood.”
The excavation continues, and the world watches with anticipation. Whether this discovery finally unlocks the mystery of the Ark of the Covenant remains to be seen — but one thing is clear: Shiloh may be more than just an ancient ruin. It could be the heartbeat of a biblical legend.
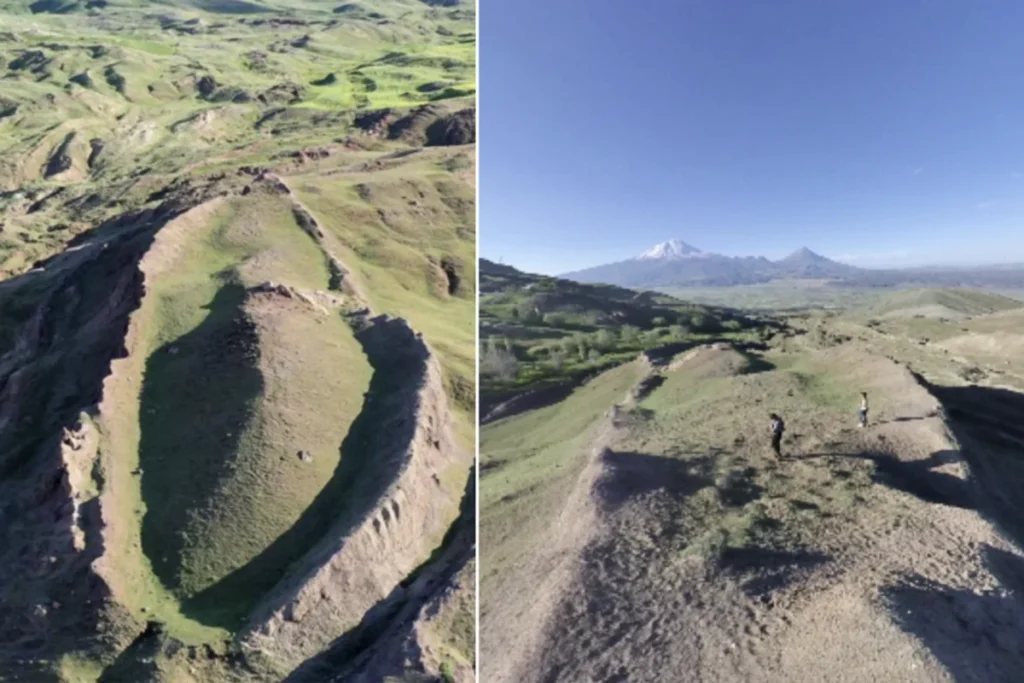

Related Development: Possible Site of Noah’s Ark Being Excavated in Türkiye
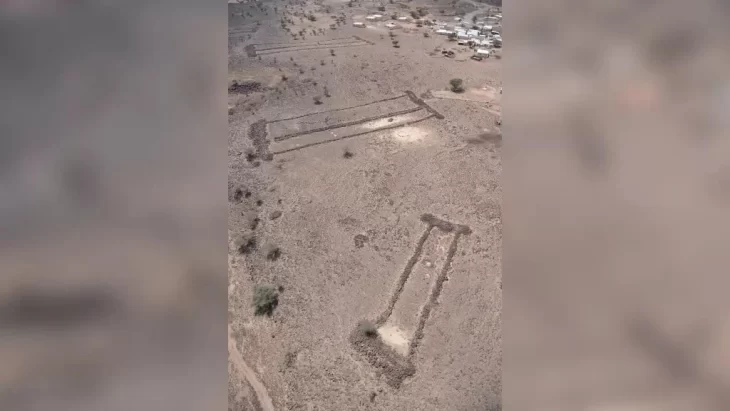
While interest in the Ark of the Covenant intensifies in Israel, another biblical mystery is being explored in Türkiye, where archaeologists have begun excavating the Durupınar formation — a site believed by some to be the resting place of Noah’s Ark. Located approximately 18 miles south of Mount Ararat’s summit, the boat-shaped, 538-foot-long geological formation closely matches the dimensions described in the Book of Genesis.
Excavation efforts, now officially underway, aim to determine whether this natural feature may in fact be the remains of the legendary vessel. Though long debated among geologists and theologians alike, renewed interest and fresh data have sparked scientific curiosity once again.
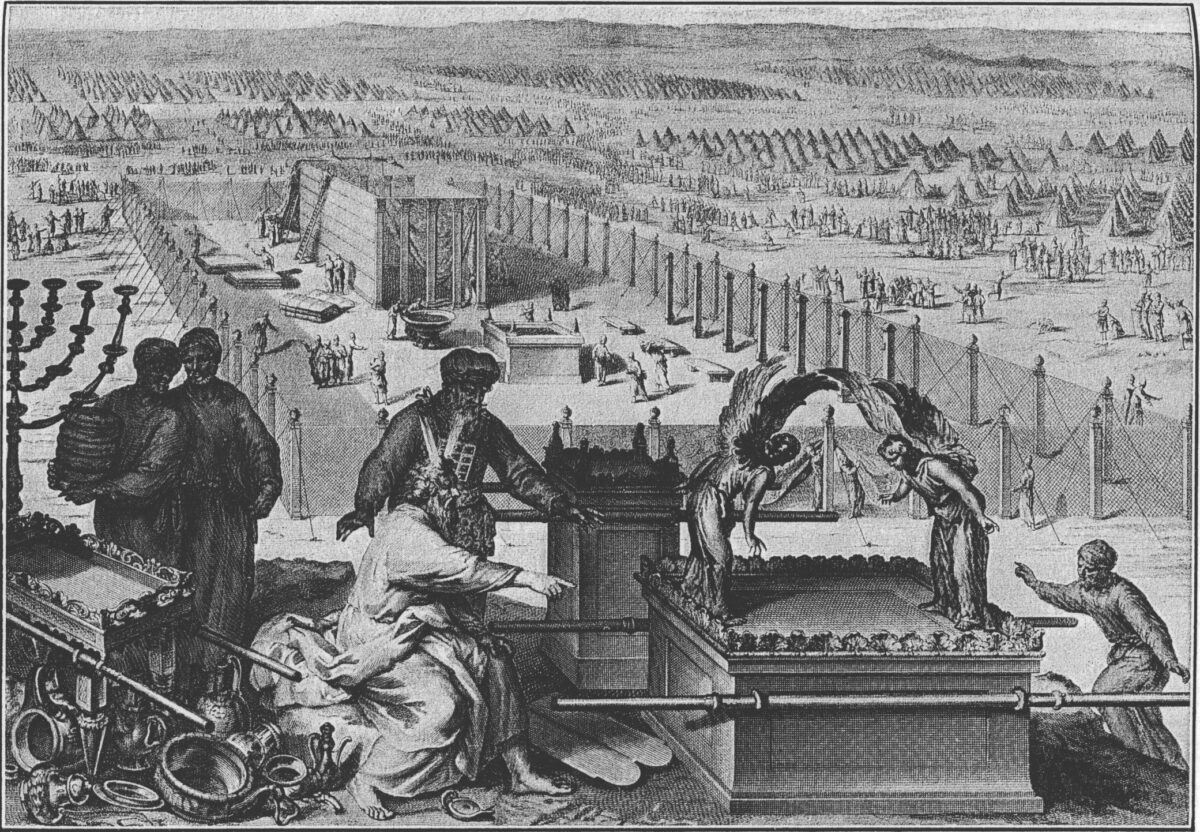
Cover Image Credit: 1728 illustration of the Ark at the erection of the Tabernacle and the sacred vessels, as in Exodus 40:17–19. Public Domain