Israeli archeologists have deciphered an 8th-century BC inscription discovered on a palm-sized stone tablet after a decade of research.
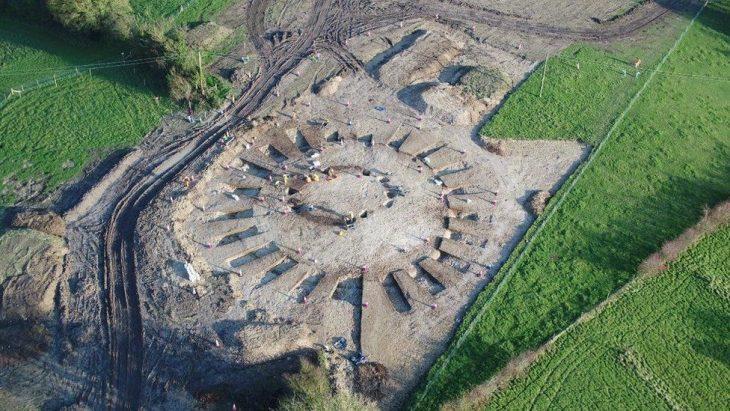
The artifact was discovered during excavations at Jerusalem’s City of David National Park in 2007, but it was only recently that it was deciphered.
It was deciphered after a ten-year research by Prof. Gershon Galil, head of the Institute for Biblical Studies and Ancient History at Haifa University, and Eli Shukron, from the Bible and Ancient History research institute.
The biblical king’s name was found partially written into the inscription, and the fragment could be filled in to read a specific part in the bible referring to Hezekiah.
The inscription references King Hezekiah and his accomplishments, paralleling the biblical passage in 2 Kings 20. Hezekiah is noted several times throughout the Bible in regard to the construction of pools and tunnels and the discovery of the inscribed stone was made at just such a “pool” location in the Gihon Spring area. Hezekiah is also noted as doing “what was right in the eyes of the Lord, according to all that his father David had done” (2 Chron. 29:2).
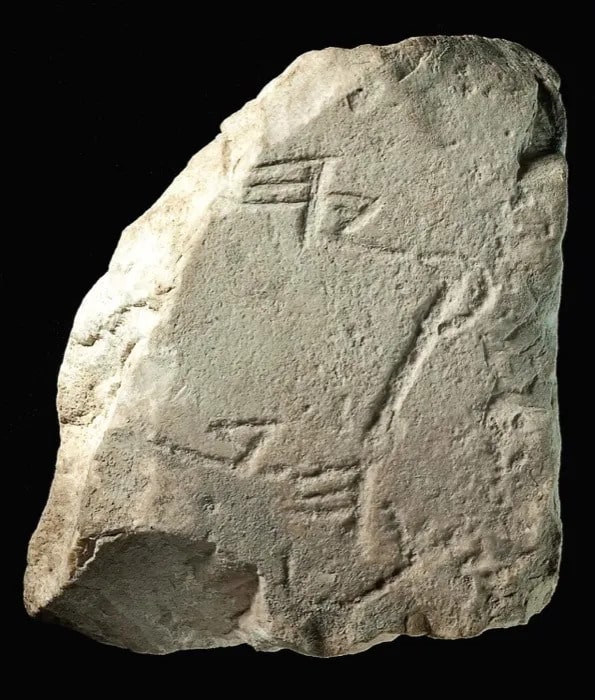

Eli Shukron and Ronny Reich discovered the limestone fragment near a man-made pool in the Siloam tunnel, within a refuse pile containing pottery shards dating from the 8th century BC, as well as dirt and stones.
According to Prof. Gershon Galil, former chairman of the university’s department of Jewish history, the inscriptions mention the name of Hezekiah and summarize his main actions during the first 17 years of his reign, including the water project (the cutting of the Siloam Tunnel and the pool), ritual reform, the conquest of Philistia, and property accumulation.
The small but significant stone fragment measures about 5.3 inches long by 3.8 inches wide. There are two lines of writing containing six letters inscribed in Old Hebrew script.
The three letters of the first line of the inscription, (z)q y h, are part of a single word which has been reconstructed as:
ח]זקיה] / [H]zqyh / [He]zekiah.
The initial letter h/ח is missing. Note that Hebrew is read from right to left and doesn’t contain vowels.
The first word of the second line includes the two letters kh and is reconstructed as:
ב]רכה] / [br]kh / bricha (berecha) or pool in English.

Prof. Gershon Galil, head of the Institute for Biblical Studies and Ancient History at Haifa University, and Eli Shukron, from the Bible and Ancient History research institute, have concluded the full inscription was: “Hezekiah made the pool in Jerusalem.”
Researchers believe that the broken stone was once a part of a monumental inscription written on a large public building.
Gershon Galil, The University of Haifa Bible scholar, “This is an extremely important discovery that changes [some basic assumptions of] research, since until today it was commonly accepted that the kings of Israel and Judah, unlike the kings of the ancient Middle East, did not make themselves royal inscriptions and monuments… to commemorate their achievements,”
“These are actually the earliest manuscripts of the Bible. They predate the Ketef Hinnom silver amulets by about 100 years and the Dead Sea Scrolls by hundreds of years. They also support the claim that scriptures in the Book of Kings are based on texts originating from chronicles and royal inscriptions and that the Bible reflects historical reality and not imagination,” he added.

Links to Other Inscriptions
This “new” inscription has been linked with a fragment found further south of the Gihon Spring in 1978 by famous archaeologist Yigal Shiloh. This text fragment includes the word “seventeen/seventeenth” which may connect to the “new” inscription and reference Hezekiah’s seventeenth year of reign in 709 BC. Hezekiah reigned for a total of 29 years (2 Kings 18:2). The same type of limestone and lettering are used on both inscriptions.
The letters also closely resemble those of the Siloam Inscription that was found in Hezekiah’s Tunnel in terms of shape. According to the Siloam Inscription, the tunnel was built by excavating from both ends and joining them in the middle. The tunnel was built to carry water into the city so that the attacking Assyrians led by Sennacherib could not cut off Jerusalem’s water supply.
This finding will change the way that we think about a number of other written artifacts from that time period as well as future discoveries.