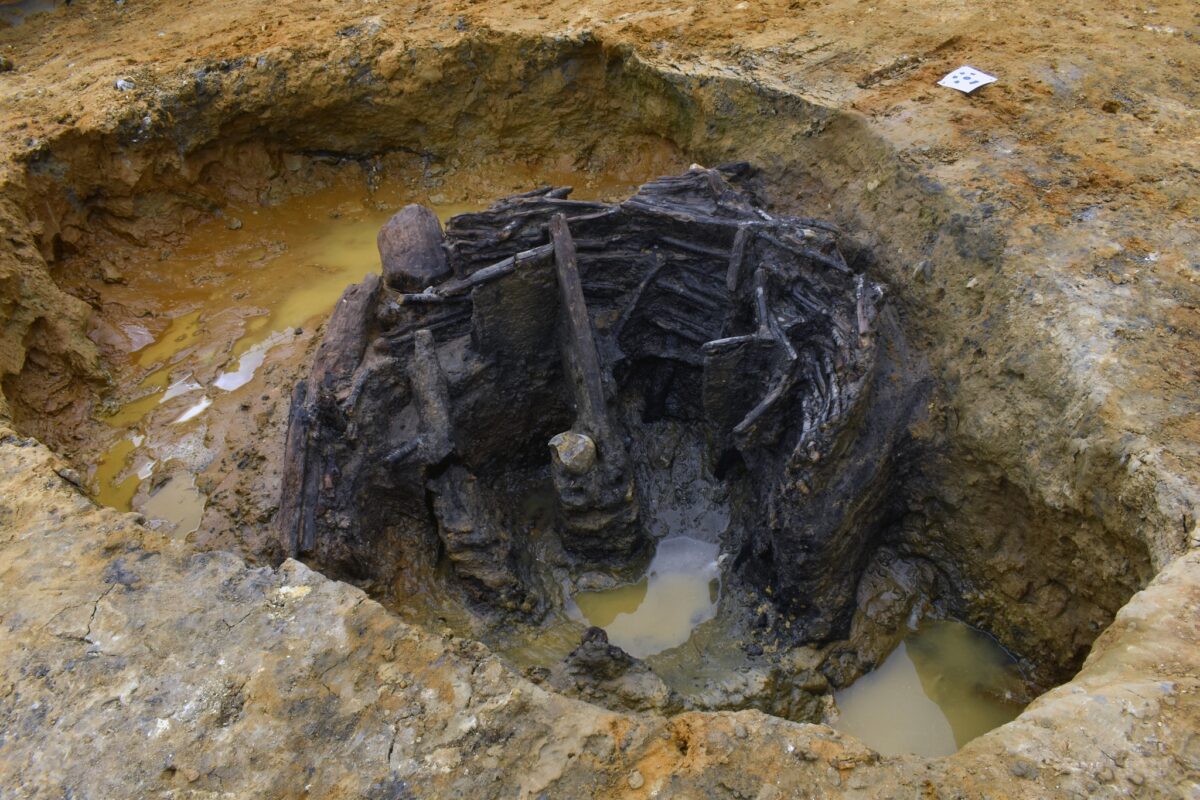
A team of archaeologists from Oxford Archaeology has uncovered a remarkably intact Roman-era well in Norfolk, England, revealing new insights into rural life during the Roman occupation of Britain. What sets this find apart is its unique construction: the well is lined with meticulously woven wicker, an unusual and rarely preserved material from the ancient world.
The well is part of a larger Roman agrarian settlement currently under excavation. While several wells have already been identified at the site, this one stands out due to its impressive state of preservation. Experts attribute this to the waterlogged, oxygen-free conditions underground that have kept the organic materials from decaying over the centuries.
Constructed by digging a vertical shaft down to the groundwater and lining it with woven wicker, the structure resembles a giant basket anchored with vertical wooden supports. Archaeologists believe the space between the cut earth and the wicker wall was padded with large timber offcuts, likely discarded wood repurposed for stability.
Inside the well, the excavation team found remnants of what may have once been a wooden ladder. Although only one rail and a single rung remain, the positioning suggests it was part of a functional climbing structure used to access the water. Without additional rungs or a second rail, however, its exact purpose remains a subject of interpretation.

The discovery is generating excitement not only for its rarity but for the potential it holds. Historically, wells at Roman sites have yielded a variety of significant items, from lost domestic objects to ritual deposits. Similar sites across Europe have revealed contents such as burned bones, pottery shards, glassware, and even marble fragments.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
To document the fragile structure, researchers have already completed a detailed 3D scan of the exposed section. This interactive model offers the public a chance to closely examine the craftsmanship of Roman wickerwork without disturbing the delicate site.
Experts consider the find an extraordinary glimpse into Roman engineering and daily life in Britain nearly 2,000 years ago. As excavation continues, hopes remain high for additional discoveries at the bottom of the well — possibly artifacts that shed further light on the people who once lived and worked in this ancient rural community.
Cover Image Credit: Oxford Archaeology