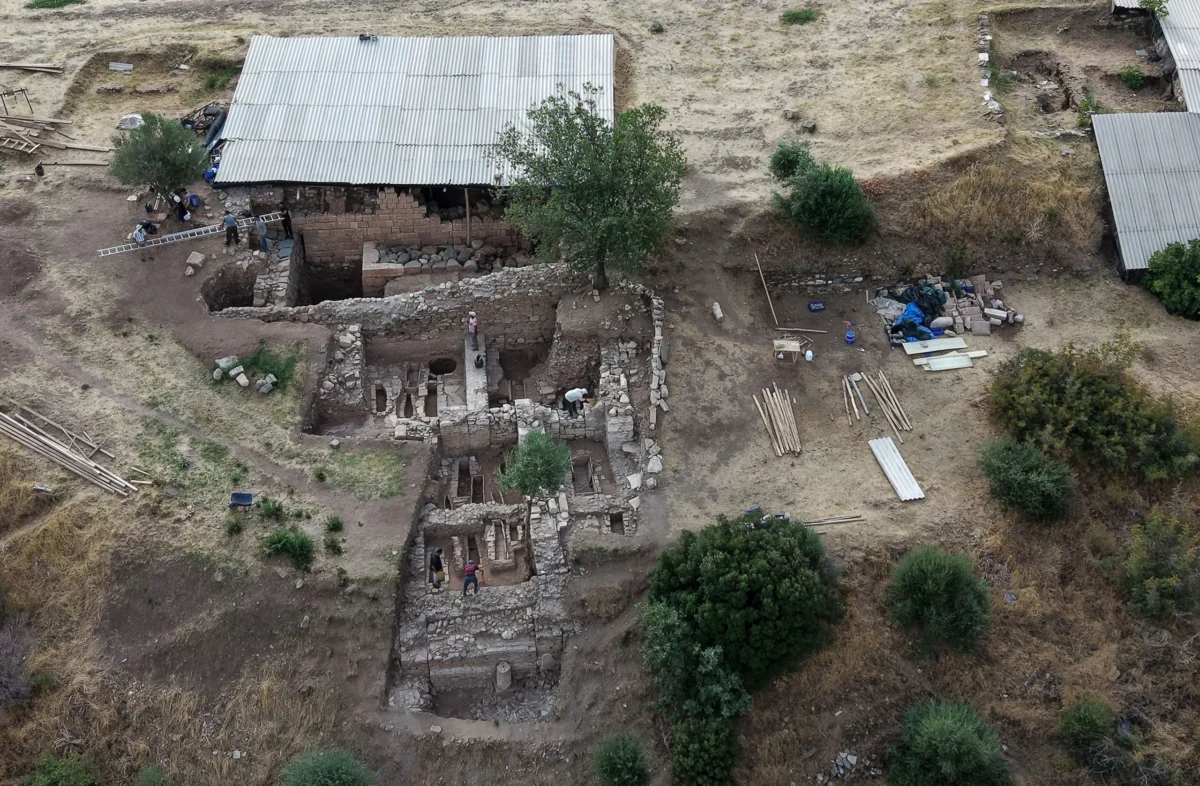
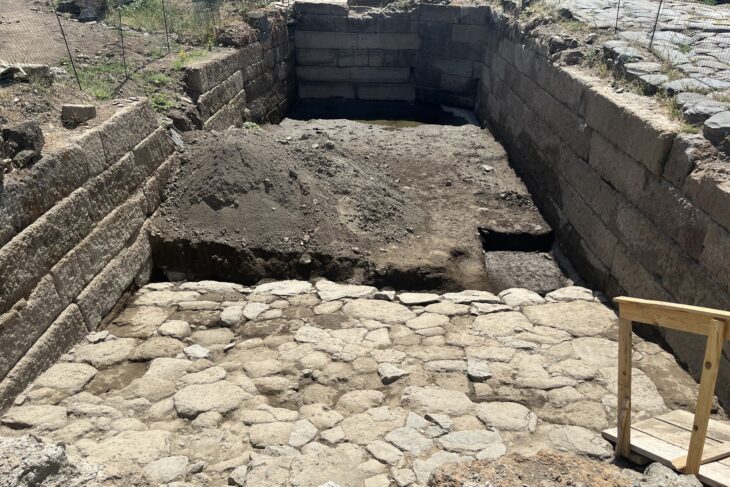
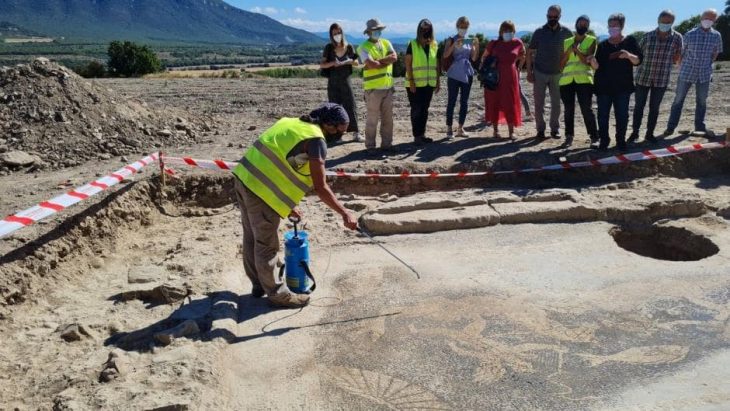
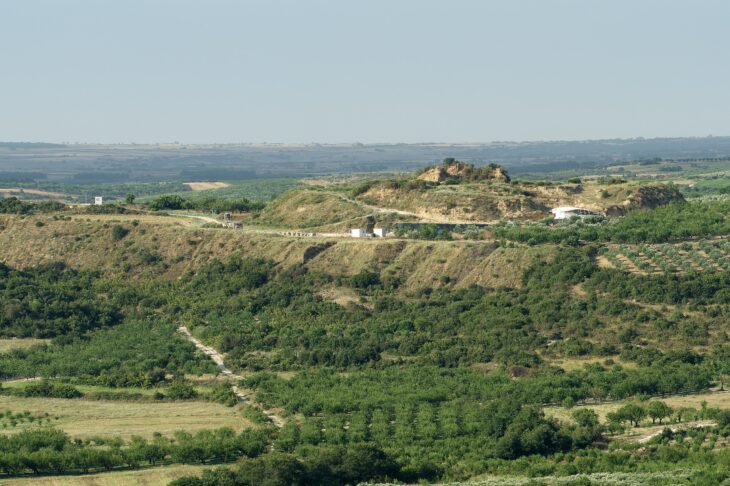
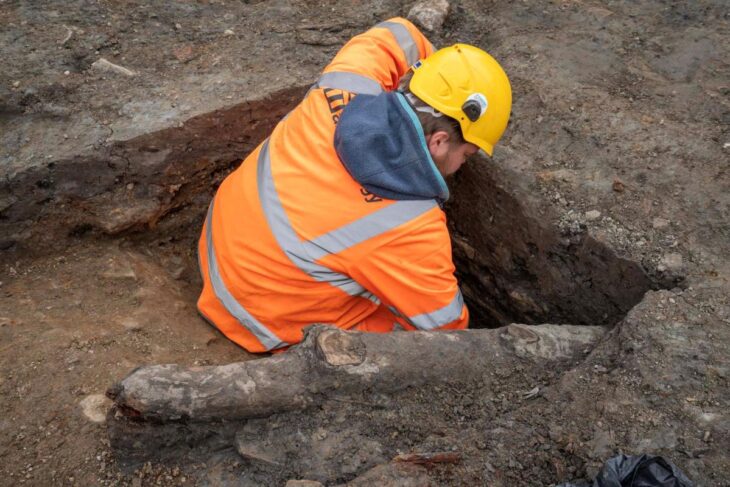
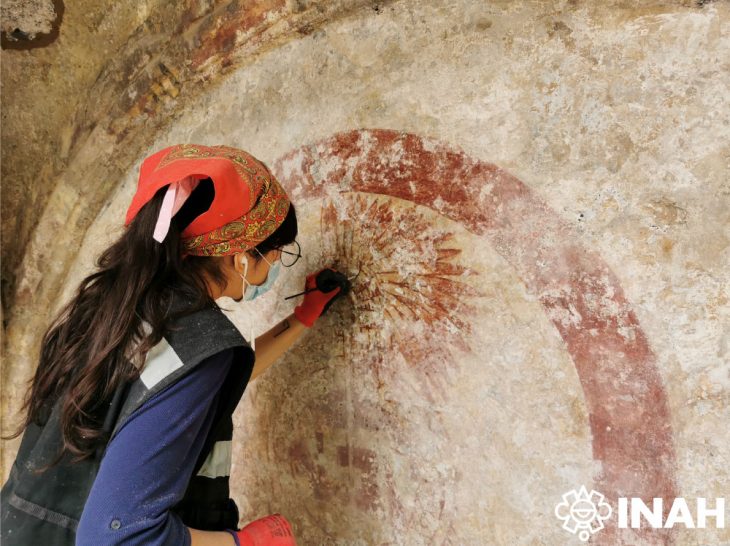
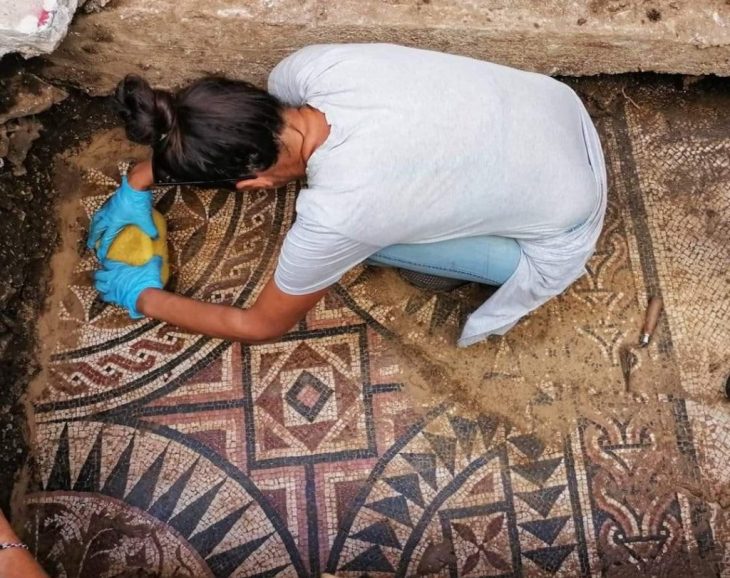
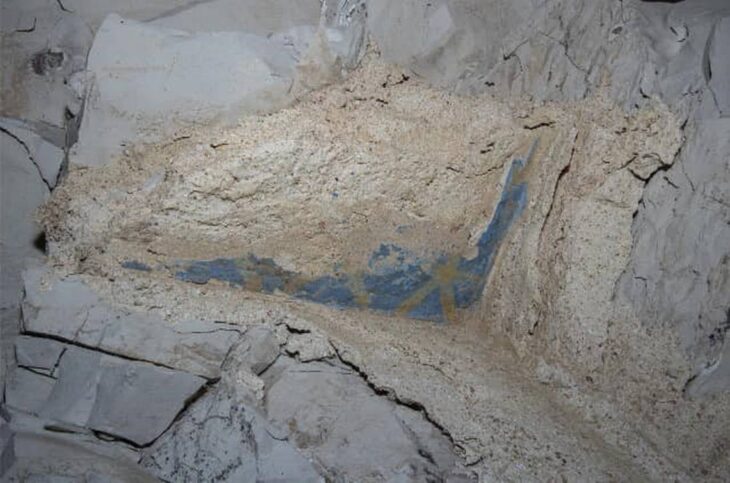
Archaeologists excavating the UNESCO World Heritage site of Sardis, located in the Salihli district of Manisa, Türkiye, have uncovered the remains of a monumental Lydian palace dating back to the 8th century BCE. The find not only pushes back the known timeline of Lydian urbanization but also challenges long-standing assumptions about the civilization’s origins and architectural prowess.
Led by Professor Nicholas Cahill of the University of Wisconsin–Madison, the excavation team reached the palace after digging nearly eight meters below the surface. Over centuries, the site had been buried under layers belonging to the Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods. In addition to the palace, archaeologists discovered luxury houses, terraced structures, around 30 bronze arrowheads, human skeletal fragments, and nine silver coins—some of the earliest known silver currency in the world.
A Game-Changer for Lydian History
For decades, historians believed that the Lydians began forming urban settlements around the 7th century BCE, heavily influenced by Greek culture. The new findings, however, tell a different story. The monumental stone walls of the palace, more than six meters high and up to two meters thick, demonstrate that the Lydians were constructing complex, large-scale urban centers much earlier than previously thought.
“This is important because in the 8th century BCE, Greek cities were still building small houses,” Cahill explained. “The Lydians, on the other hand, were already creating monumental terraces and structures, looking eastward for inspiration. They were not a derivative of Greek culture—they were a distinctly Anatolian civilization.”
Some architectural features may have been influenced by the Phrygians, another powerful Anatolian culture known for monumental stone construction in the 9th and 10th centuries BCE. However, the Sardis palace reflects unique Lydian craftsmanship and urban planning.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
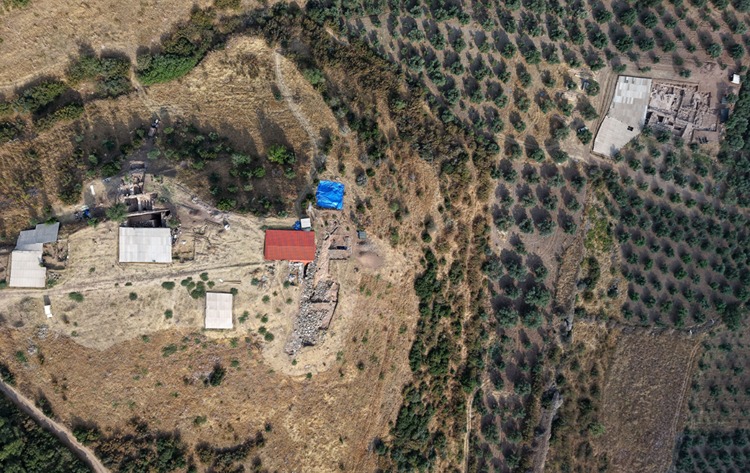

Sardis: Capital of a Kingdom and Birthplace of Coinage
Sardis was the capital of the Lydian Kingdom, a wealthy and powerful state that thrived in western Anatolia between the 7th and 6th centuries BCE. The city held a strategic position at the western end of the Persian Royal Road, linking the Aegean coast to the heart of the Persian Empire.
Perhaps Sardis’s most enduring legacy is its role as the birthplace of coinage. The Lydians were the first to mint coins from a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver called electrum, introducing a revolutionary economic system that spread across the ancient world. The discovery of early silver coins within the palace site further cements Sardis’s reputation as a center of innovation and wealth.
A City of Many Layers
Today, Sardis offers a unique window into over a millennium of history, with remains from multiple civilizations visible in its ruins. Visitors can explore the massive Temple of Artemis, the largest known synagogue from antiquity, a gymnasium-bath complex from the Roman period, and a Christian basilica mentioned in the Book of Revelation. Burial mounds known as tumuli dot the surrounding landscape, marking the resting places of Lydian royalty.
The newly discovered palace stands about one kilometer east of the ancient gymnasium. The monumental scale of the building suggests it may have been not only a royal residence but also a political and ceremonial center, symbolizing the power and sophistication of early Lydian society.
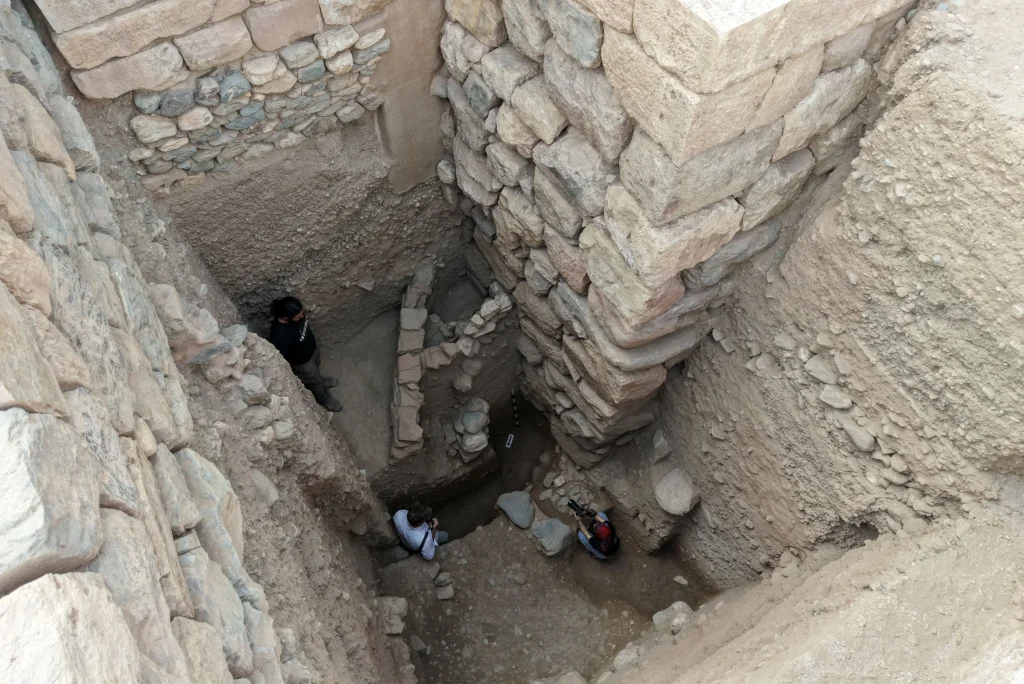

Preserving the Past for the Future
This season’s excavations have now concluded, with the palace remains carefully covered to protect them from winter rains. Further investigations are planned for the next excavation season, as archaeologists continue to piece together the story of Sardis and its role in shaping the cultural and economic history of the ancient world.
The discovery underscores Sardis’s status as more than just an archaeological site—it is a testament to the creativity, resilience, and influence of the civilizations that once flourished in Anatolia. As researchers delve deeper, Sardis promises to reveal even more secrets buried beneath its layered past.
Cover Image Credit: AA