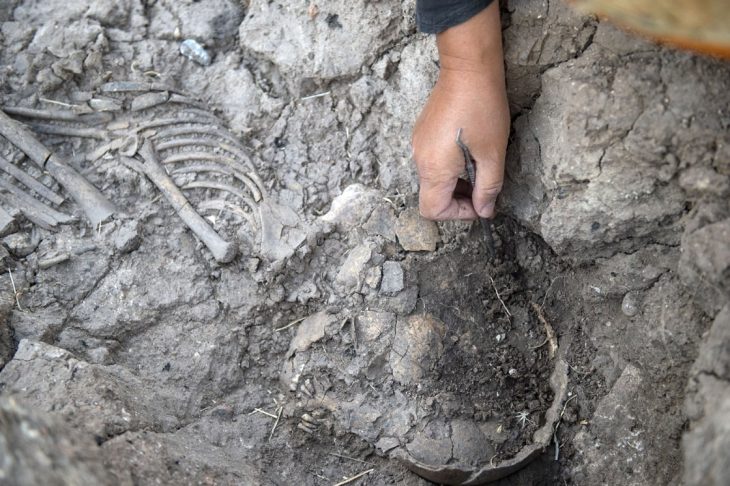
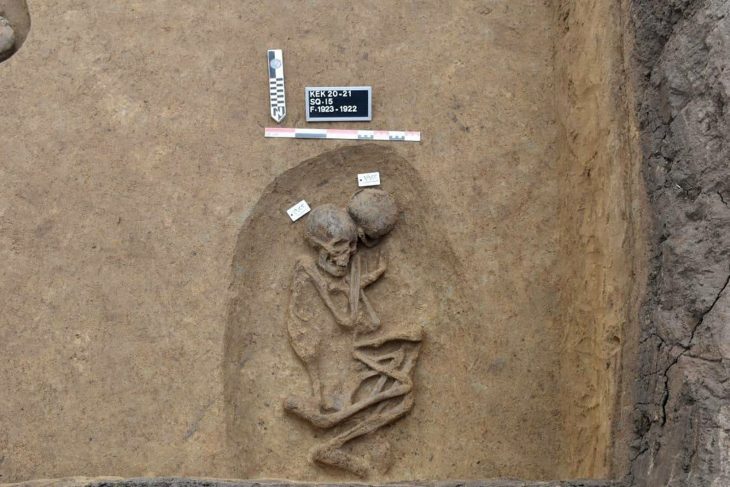
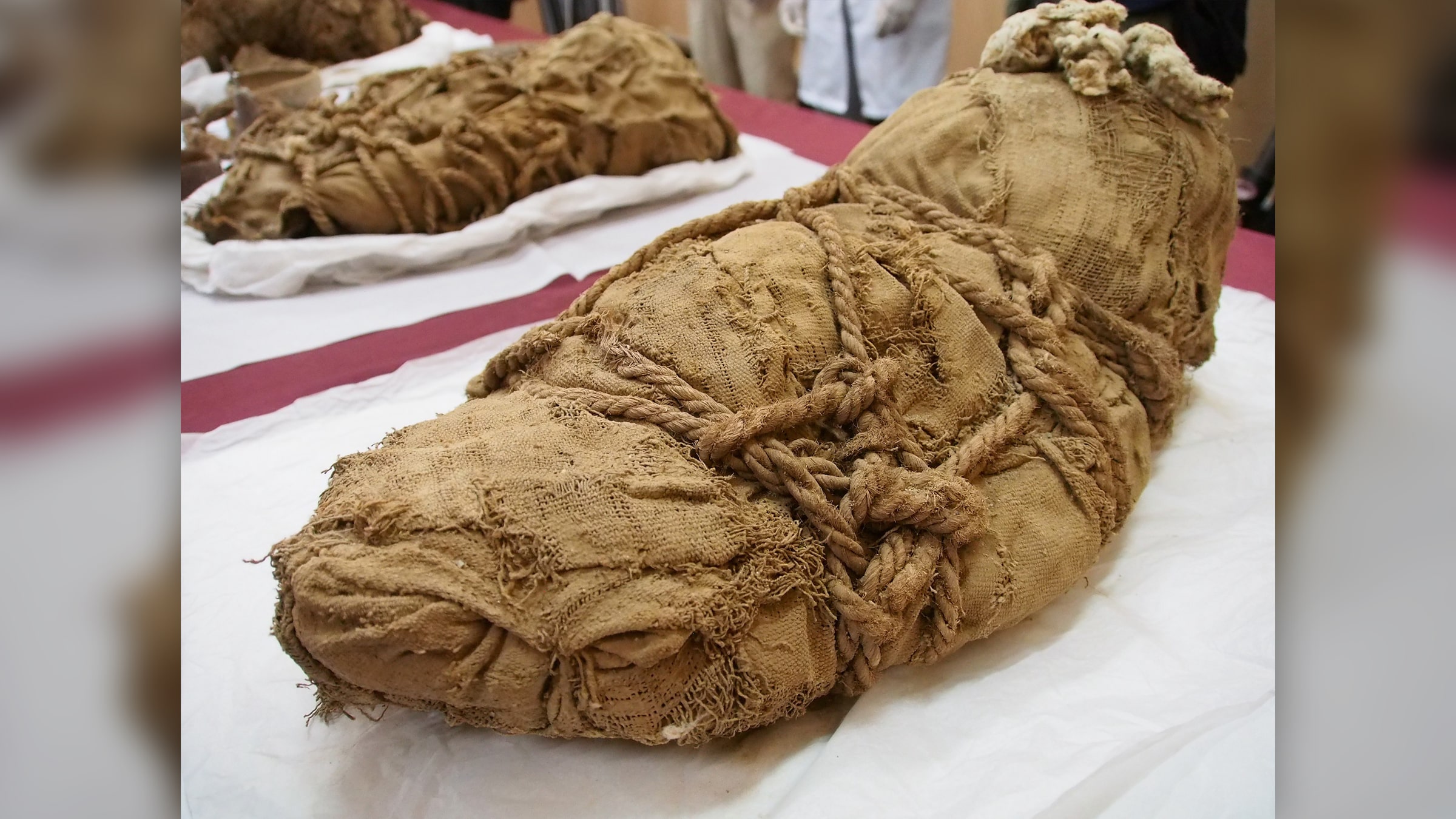
The mummified burials of 22 people, mostly young children and newborn babies, were found in the Peruvian town of Barranca by a team of Polish-Peruvian scientists. In addition to the fabrics used to wrap the bodies of the dead, pottery, tools, and food remains were also found.
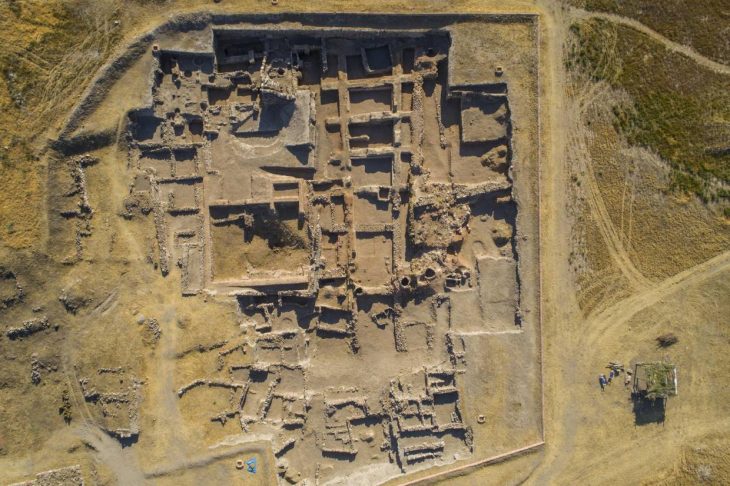
The archaeological site where the discovery is located in Peru, on the outskirts of the city of Barranca on the Cerro Colorado hill in the Pativilca Valley. This place has been known to researchers for several decades. It currently consists of four mounds that cover pre-Columbian buildings. However, the time of their creation and functions remained unknown.
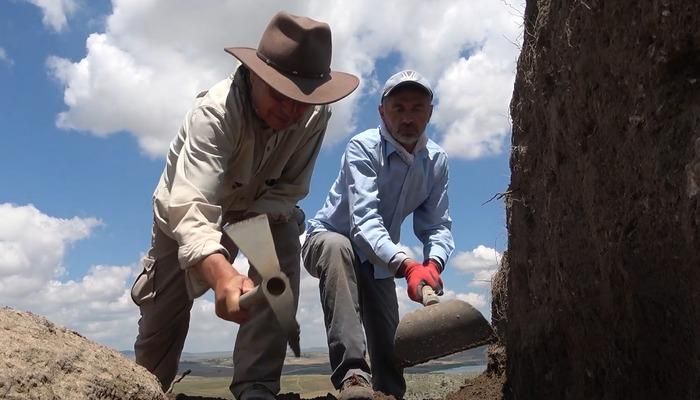
In 2022, a team of archaeologists from Peru and Poland, operating as part of the Programa de investigacion ‘Los valles de Barranca’ group, started a new research project. Its leader is the Peruvian archaeologist Plinio Guillen Alarcón, and its co-founder and member is the Kraków bioarchaeologist Łukasz Majchrzak. Students of the Jagiellonian University and the University of St. Mark in Lima took part in the excavations.
Last year, scientists determined that the origins of the complex date back to the second half of the 19th century. At the top of the highest mound, they discovered destroyed burials 3rd millennium BC.
This year’s work, during which 22 intact burials were discovered, was carried out as part of a research project financed by the National Agency for Academic Exchange. The team’s work is led by Dr. Justyna Marchewka-Długońska from the Cardinal Stefan Wyszyński University.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
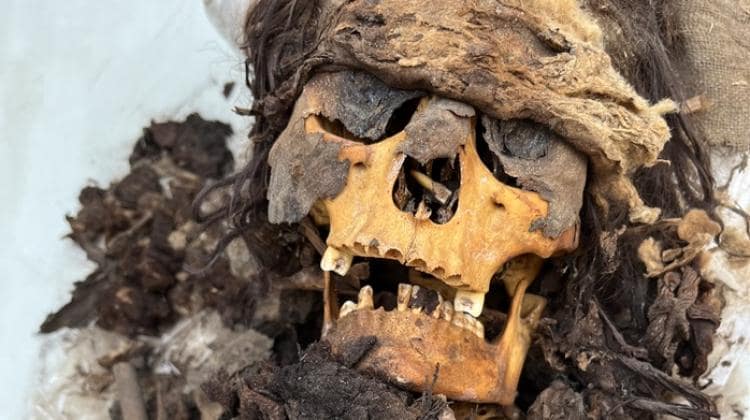

“These are bodies wrapped in fabrics and plant material, which in archeology we call burial bundles. Examination of human remains, between the layers of these fabrics we find ceramics, tools, and cult objects” says bioarchaeologist Łukasz Majchrzak.
Six of the discovered burial bundles belonged to adults, and the remaining 16 – located some distance away – belonged to children, most likely of different ages.
– Until recently, high child mortality was standard, especially when a child was weaned. This is not always reflected in the archaeological material, because children were not always buried on equal terms with adults, but often there are more of them than adults. In the case of Cerro Colorado, what we are wondering is not the number, but the method of making and depositing the children’s bundles – comments Łukasz Majchrzak.
As he describes, they are located at a similar depth, at the height of the heads of the deceased adults. They are all in a horizontal position, while the adults’ bodies are in the fetal position with their upper and lower limbs tucked under their chests. The adults’ bodies are arranged vertically, making them appear as if they were sitting. They all have a similar external appearance, are wrapped in thick fabric and entwined with rope.
“At this point, it is difficult to give a single interpretation of this find. It is possible that the entire community simply buried children in this place. What is still puzzling is the fact that these are clearly children no older than 2 years old (judging by the length of the bundles), some of them certainly newborns or infants. It is possible that for some reason older children were buried in other parts of the cemetery,” Łukasz Majchrzak said.
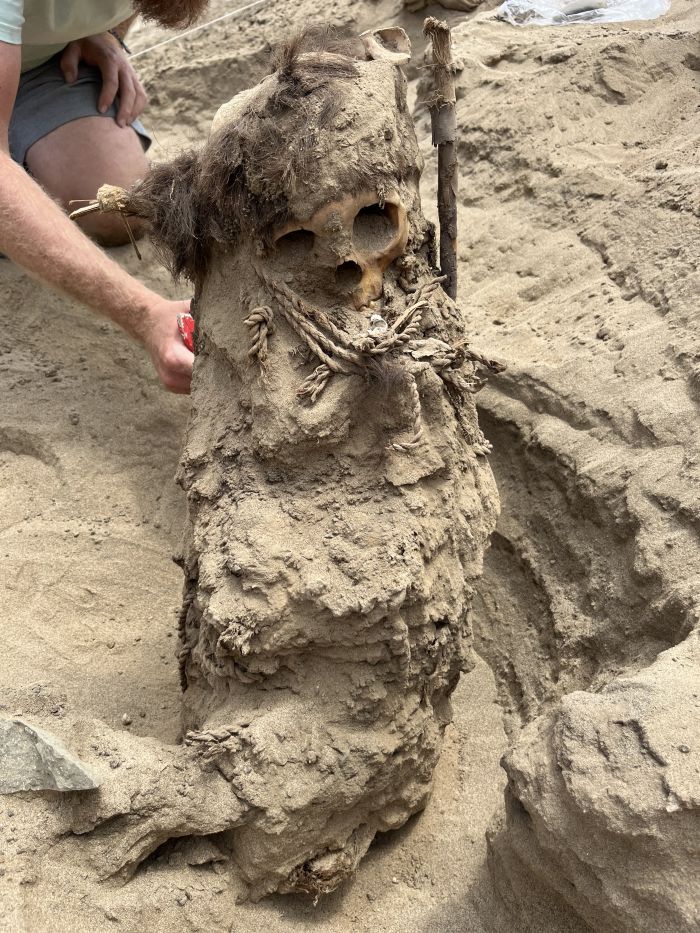

So far, the team has only examined an area of 20 square meters. Scientists unrolled one baby bundle in which a newborn was buried.
– We subjected two more bundles to tomography, so we know that one of the children was slightly older, and the other was also a newborn – describes the bioarchaeologist.
The fabric of one of the already-developed bundles is decorated with geometric patterns. The remaining bundles – as Majchrzak suggests – may contain representations of animals and gods. The materials in which the dead were wrapped were supposed to be useful in the afterlife.
“In the Andean posthumous vision, a man travels for a year until he reaches his destination. So he needs food. We even found corn cobs and other unidentified plant materials in several of the bundles.”
However, as for Andean graves, there were few vessels, 4-5 for each bundle – the researcher describes.
Researchers will analyze subsequent burial bundles, which scientists tentatively date to 1000 – 1100 AD. These preliminary findings will be confirmed by radiocarbon dating.
Scientists will use computed tomography to examine completely preserved burial bundles with no visible damage. It will allow for non-invasive anthropological analysis. In further stages, they plan to carry out chemical analyzes and isotope analysis, including the strontium isotope, which will clarify whether we are dealing with a local population.
Cover image: A bundle with a Peruvian mummy. Photo: Sebastian Castaneda / Reuters / Forum