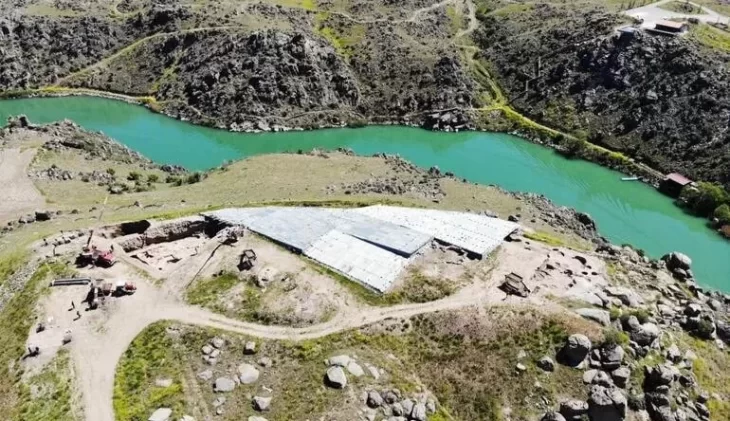
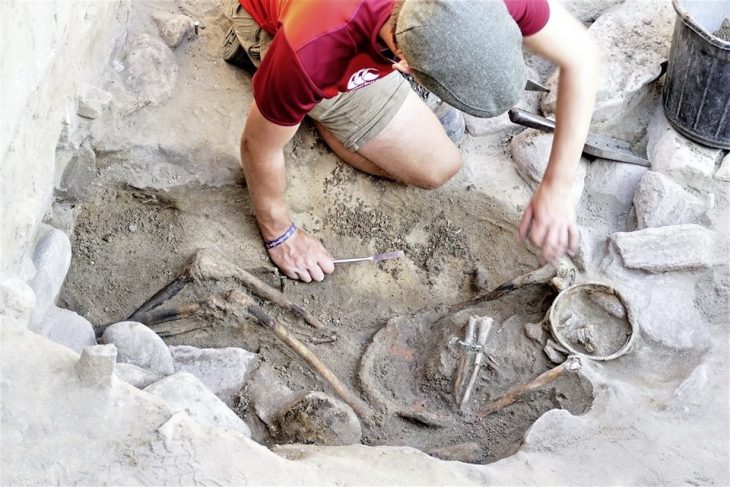
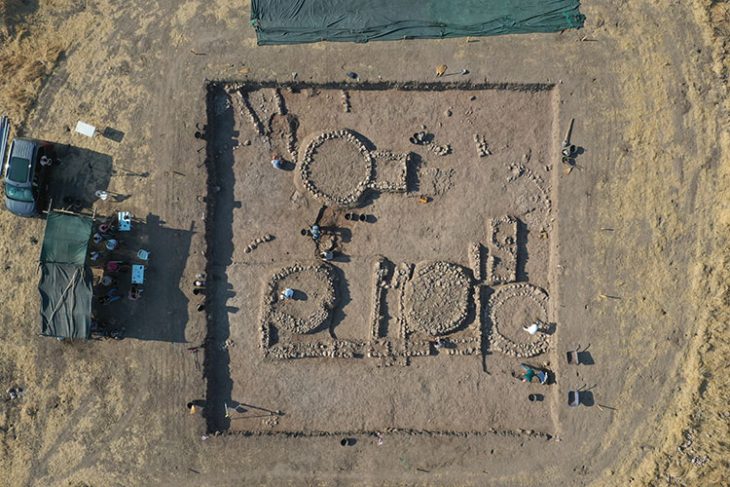Archaeologists in Spain uncovered a previously overlooked tomb while investigating the formation of La Peña de los Enamorados, also known as the sleeping giant.
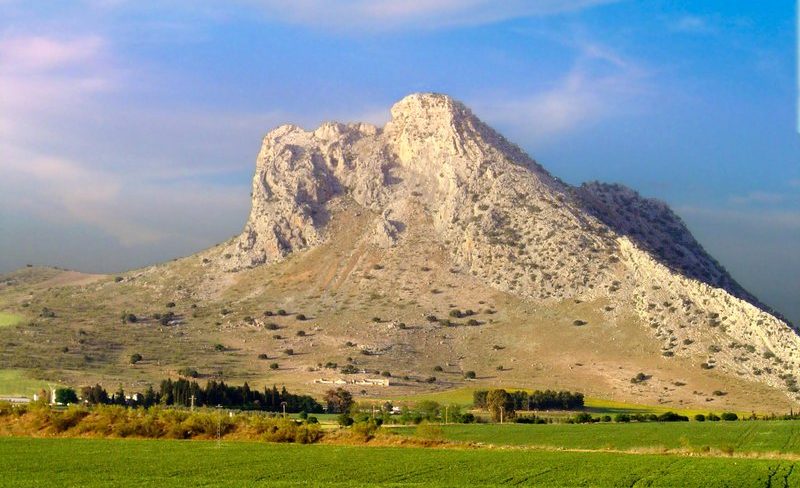
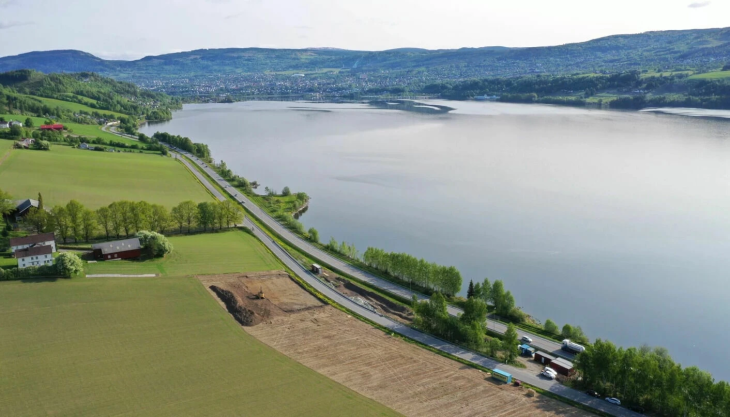
The Antequera archaeological site in southern Spain is home to a number of ancient structures dating back to the third and fourth millennia BC, including the Menga, Viera, and El Romeral megaliths.
According to a study that was published on April 15 in the journal Antiquity, the Antequera site contains both man-made and “natural monuments,” but is best known for its prehistoric megaliths.
The “natural monuments” at the site include La Peña de los Enamorados, a stone “sleeping giant” that towers about 2,900 feet above the ground, researchers said.
The Sleeping Giant had a 5000-year-old secret hidden in his chest: Piedras Blancas megalithic grave.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
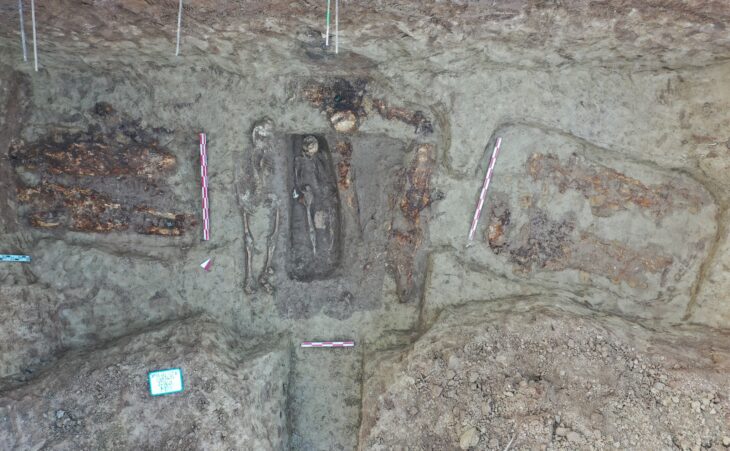
The rectangular stone structure was built at least 5,000 years ago, according to the study. It was used for millennia in three distinct phases before being abandoned between 1950 and 1180 B.C.
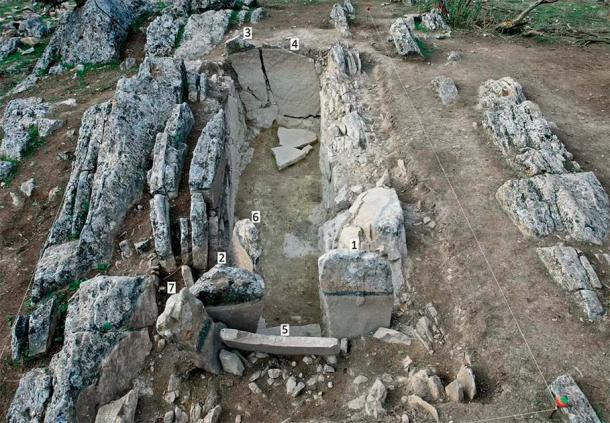

Lead author of the new paper, Leonardo García Sanjuán, a Professor in Prehistory at the University of Seville (Spain), said the location of the Piedras Blancas tomb was “carefully chosen.”
The tomb’s stone slabs were carefully arranged to coincide “with the summer solstice sunrise,” researchers said. Some of the “heavily engraved” slabs “appear to have been precisely placed to ‘funnel’ the light from the rising sun towards the back of the chamber at the summer solstice.”
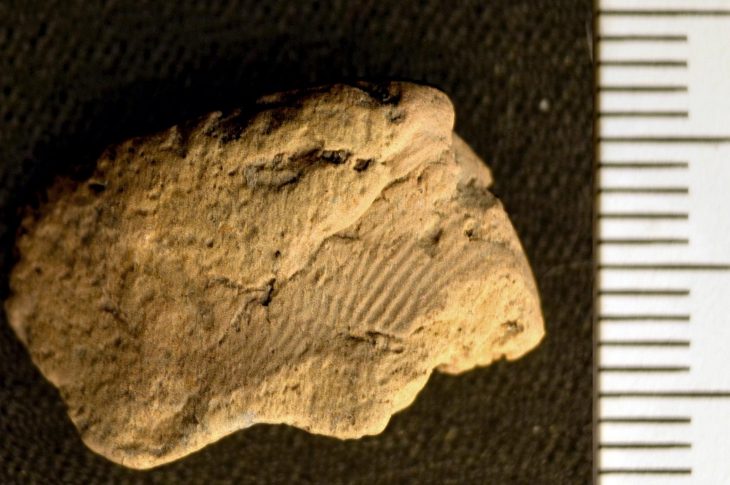
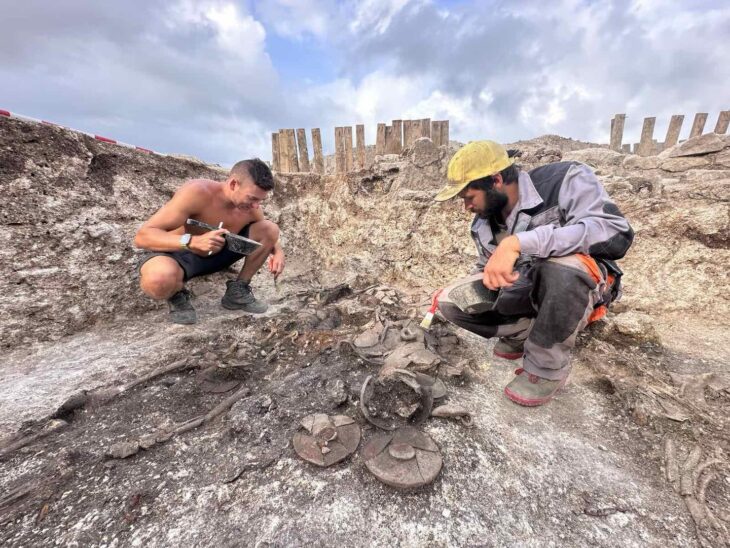
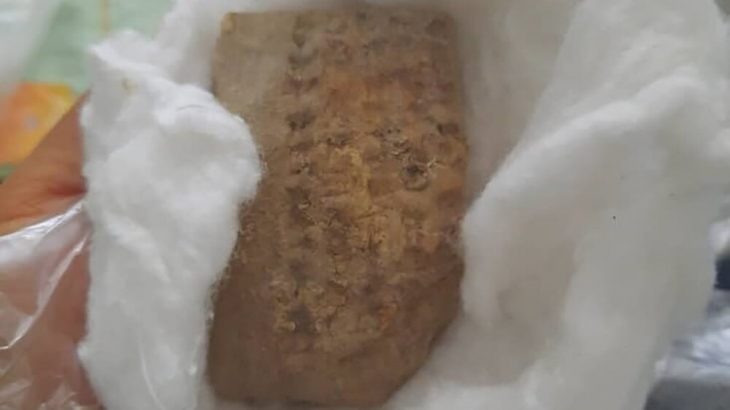
In Antequera, the oldest megaliths date back to 3,000 BC, and this rectangular stone tomb was built at the same time. Researchers believe that bodies were spread out on a sizable flat stone platform at the time ceramic offerings were left in the tomb. Later, the decomposing corpses were pushed off the stone platform and into the surrounding area, where the researchers discovered “40 teeth and 95 bones.”
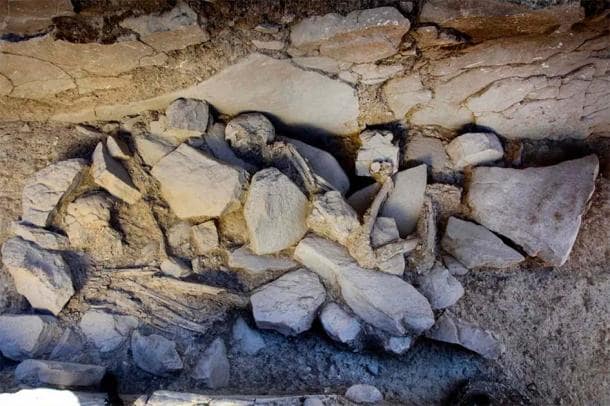

Furthermore, the archaeologists identified a “triangular, arrow-like stone” lodged into the floor, oriented in the direction of the rising sun.
The Piedras Blancas tomb was renovated around 2500 B.C., and niches for two burials were added, according to the study. Researchers believe these were high-status individuals, most likely a man and a woman. It’s unclear whether they were buried simultaneously or over the course of a century.
The tomb later “underwent another significant transformation,” according to researchers. Stones were placed at the entrance “as if to block or seal” it, and the bones of at least two children and three women were interred. According to the study, the tomb was abandoned and has remained untouched ever since.