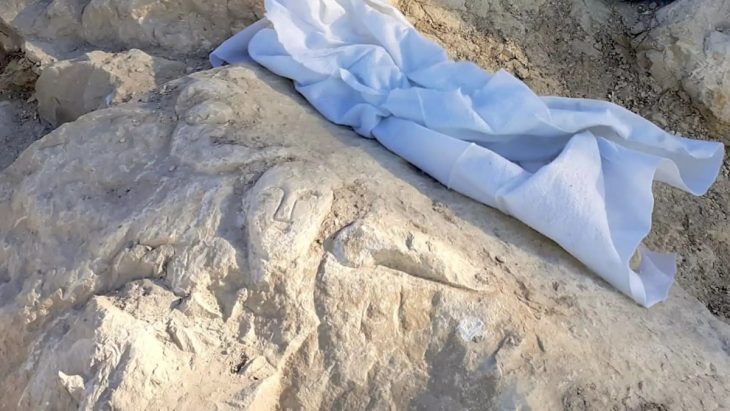
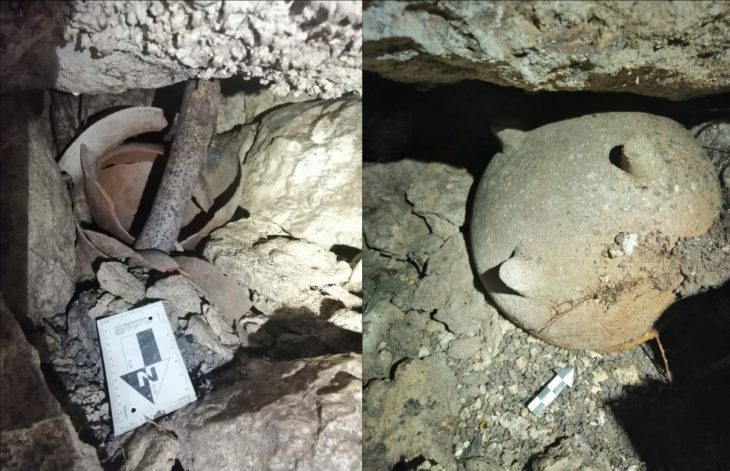
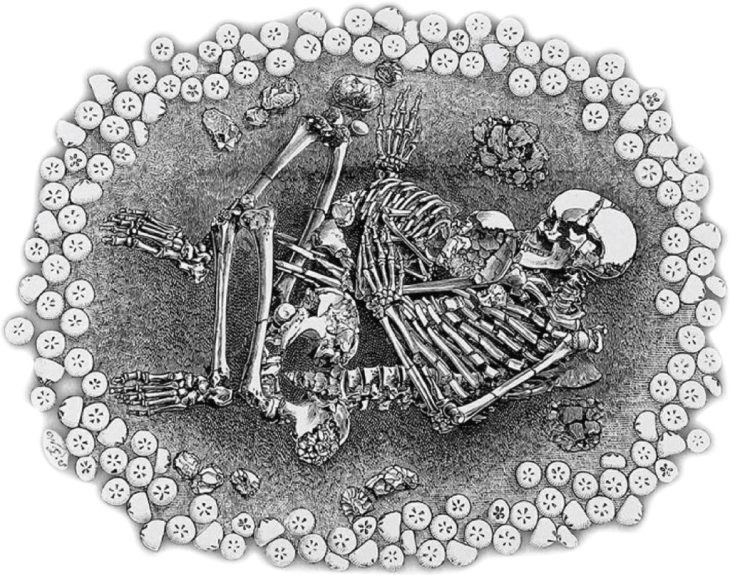
A bone discovered in the Grotte du Renne cave in France may represent the existence of a previously unknown lineage of Homo sapiens. The bone, specifically a hip bone called an ilium, was excavated from the cave several decades ago.
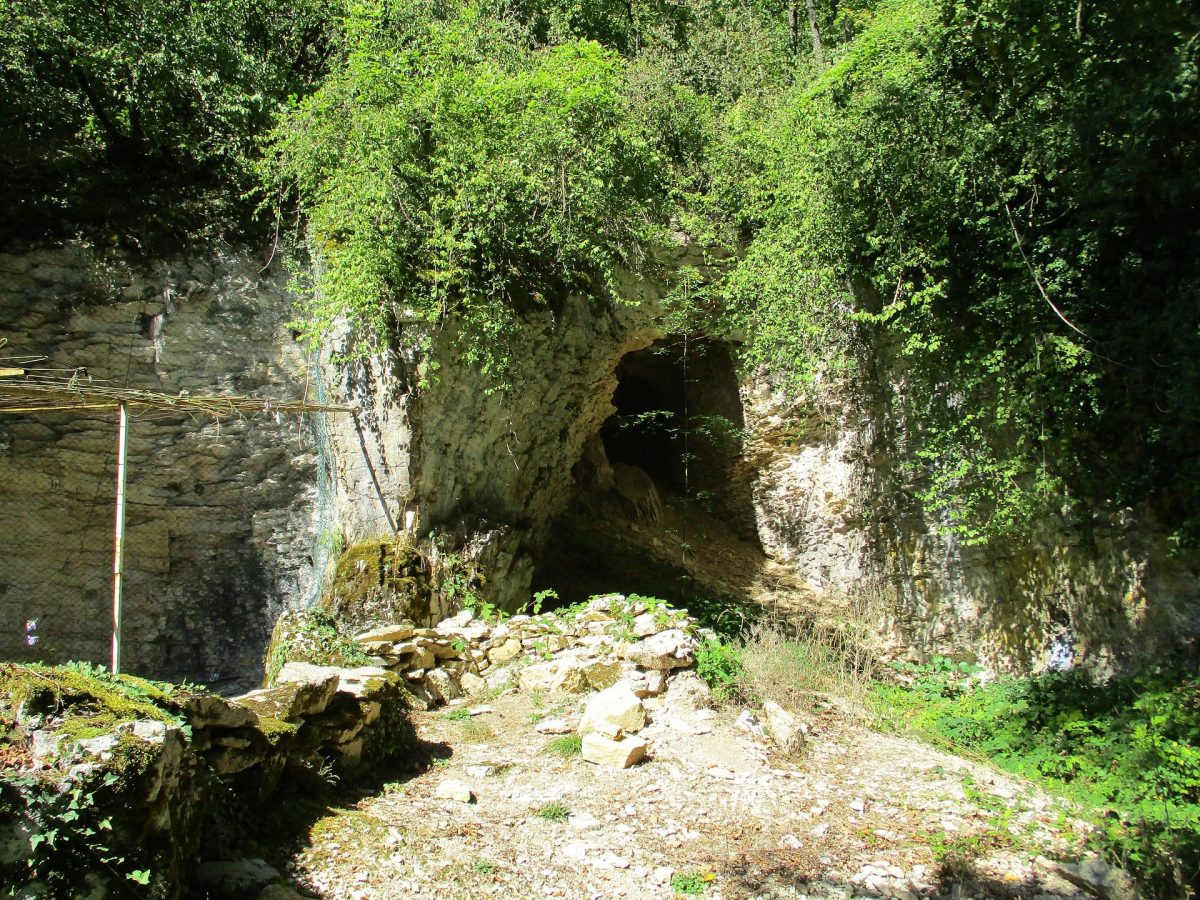
The cave is considered as one of the most fascinating Paleolithic sites in Europe, with Neanderthal remains. The Grotte du Renne cave has been a site of archaeological research for many years, revealing layers of historical significance. The lower layers indicate the time when Neanderthals occupied the cave, while the upper layers represent the period when anatomically modern humans (AMHs) inhabited it. The team discovered an intermediate layer that suggests the co-existence of both hominids.
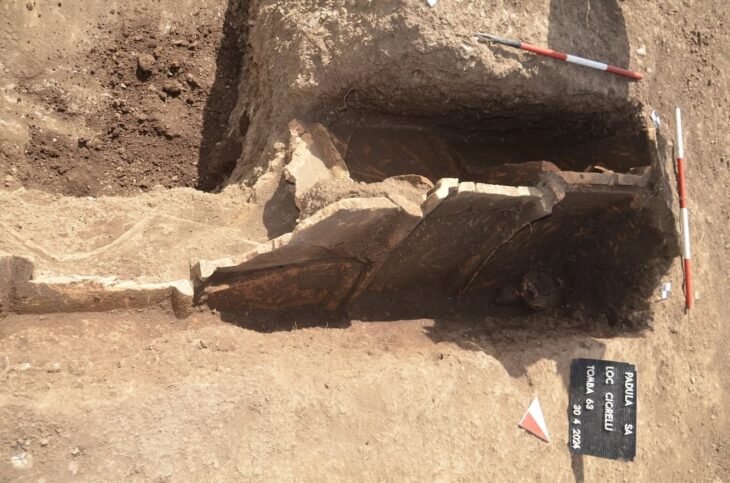
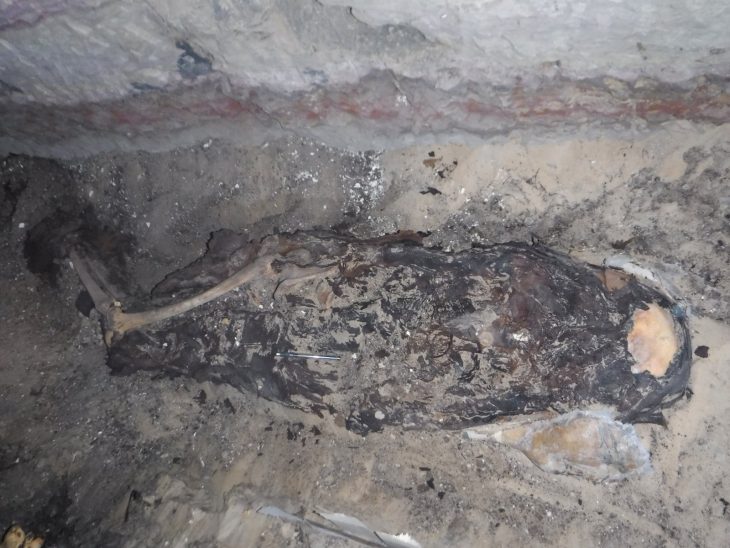
Researchers identified an ilium (one of the three bones that make up the human pelvis) belonging to a newborn (AR-63) whose morphology required a thorough analysis to compare it to that of 2 Neanderthals and 32 recent individuals deceased during the perinatal period (the period around the time of birth) to explore their morphological variation.
The bone, determined to be from a newborn baby, was found to be neither Neanderthal nor entirely anatomically modern human. By comparing it with other Neanderthal and modern baby bones, researchers noted that its shape differed from both species. This suggests that the bone represents a distinct lineage of Homo sapiens with slight differences from AMHs.
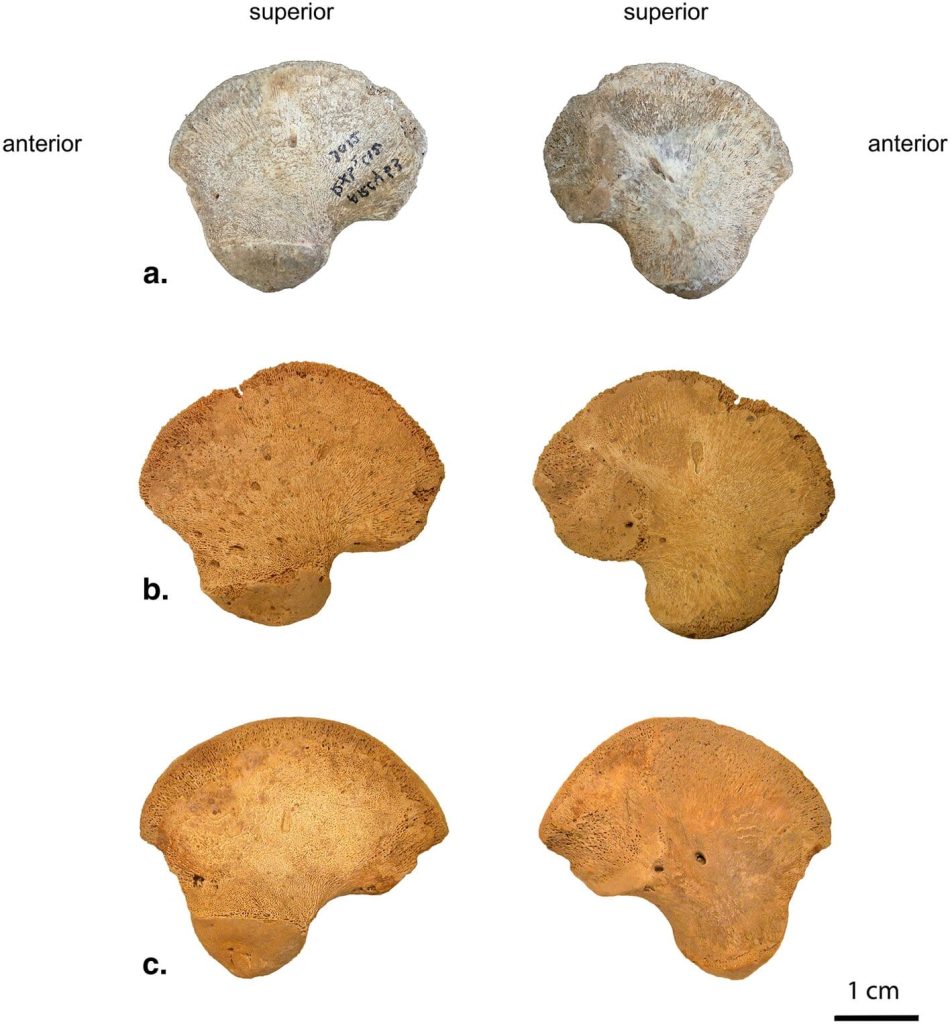

“Our results indicate a morphological distinction between the ilia of Neanderthals and anatomically modern neonates. Although AR-63 is slightly outside recent variability, it clearly differs from the Neanderthals. We propose that this is due to its belonging to an early modern human lineage whose morphology differs slightly from present-day humans,” the researchers state in their paper.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Additionally, the research team proposes that the stone tools found in the Châtelperronian techno-cultural complex layer of the cave may have been the result of diffusion. Under this theory, AMHs would have developed the tools, and Neanderthals would have adopted and potentially modified them to suit their unique needs. This hybridization could have occurred during the time when Neanderthals and AMHs coexisted in various parts of Europe.
The research, published in the journal Scientific Reports, contributes to our understanding of human evolution and the complex interactions between different hominid species. Further research in the Grotte du Renne cave and other archaeological sites may provide additional insights into the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens.
Note: The article has been revised for clarity and brevity.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-39767-2
Cover Photo: Grotte du Renne cave