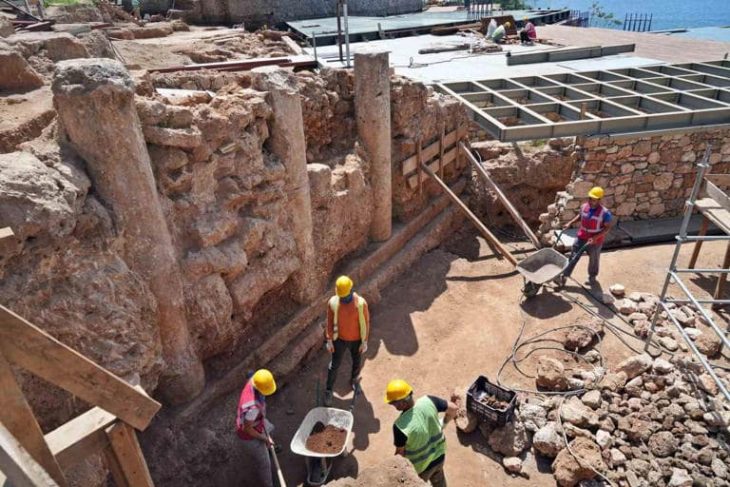
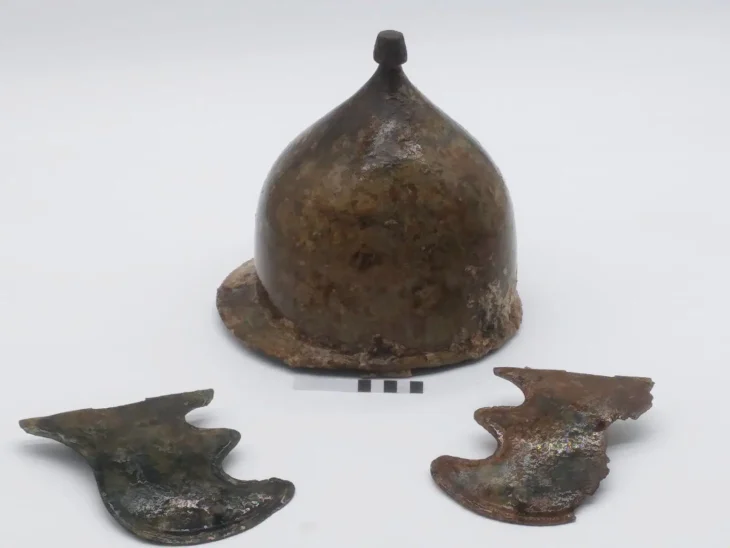
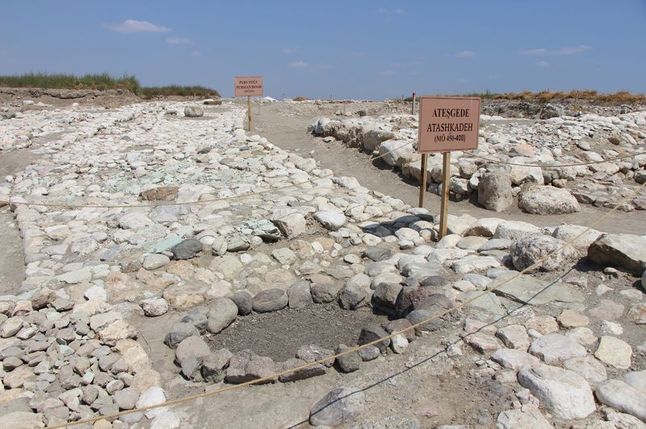
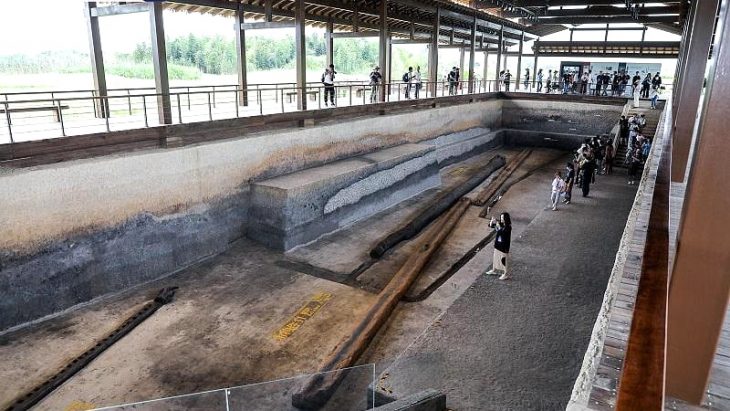
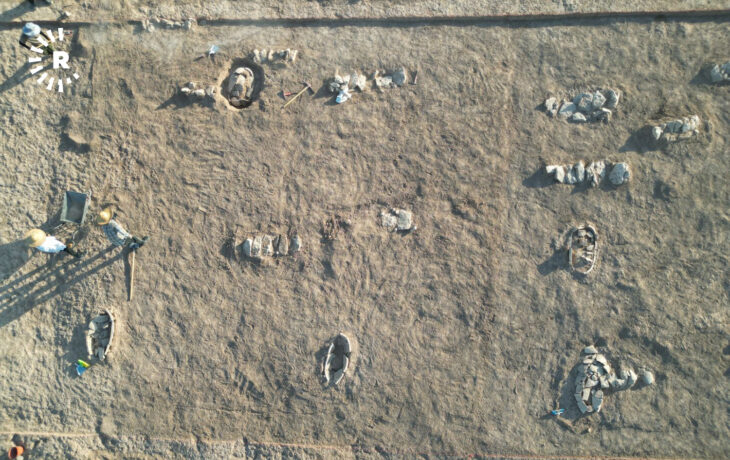
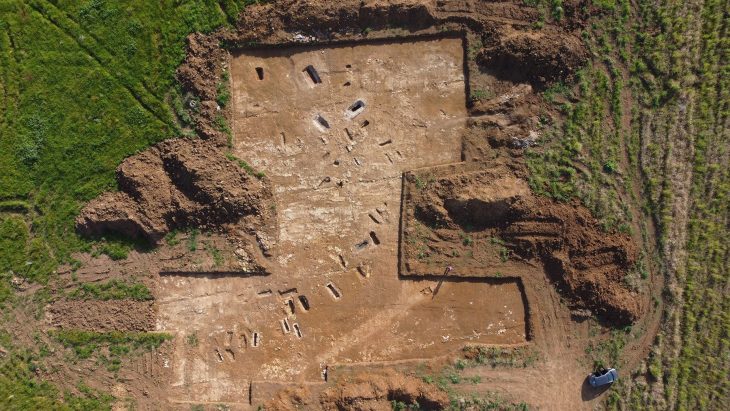
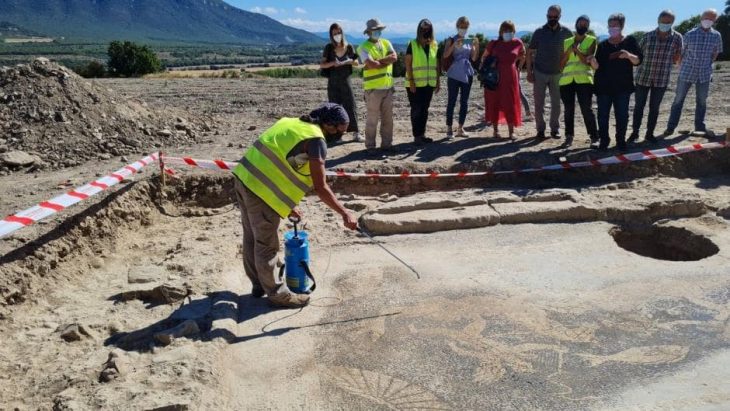
After two years of excavation, Chinese archaeologists recently exposed Zhongdu, the capital city of the Jin Dynasty (1115-1234) next to the Ritz financial and commercial district in Beijing.
Although only three sections of the ancient city walls, namely the Gaoloucun section to the west and the Wanquansi and Fenghuangzui sections to the south, have been preserved, a total of 2,500 square meters of the bygone capital were discovered during excavations by the Beijing Cultural Relics Institute. Besides, part of the ancient city was found during the construction of the Beijing metro in the Fengtai district.
Beijing was previously considered an important city for border defense or temporary capital. However, Ding Lina, a researcher in charge of the archaeological project, said that from the Jin Dynasty, it became the second choice for the capital in the following dynasties. “This discovery marks a historical turning point in the selection and construction of China‘s capital cities.”

Zhongdu served as the capital of Jin for over six decades during the heyday of the dynasty during about 120 years of rule and was later abandoned at the end of the Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368).
“The overlap between the ancient capital and the modern city has made the excavation hard as the southern part of the city wall was almost destroyed during road and landfill construction,” Ding said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
During the excavation, archaeologists also discovered protruding walls, which were used as defensive facilities. Researchers say that each protruding city wall has three faces, which can greatly broaden the guard’s vision and enhance the overall defense capabilities.
The excavation team adopted various high-tech measures to better detect and record cultural relics. They collected soil samples for further analysis of plant pollen to understand the agricultural conditions at that time. Some unearthed animal specimens were also analyzed to study the living environment and eating patterns in the past.
Archaeologists believe that Zhongdu was rebuilt on the basis of Youzhou City in the Tang Dynasty (618-907) and Nanjing (907-1125) in the Liao Dynasty, but few cultural relics can prove this. Ding said that tombs dating back to the Tang and Liao period were found under the moderate city wall, providing direct evidence for this claim.
The project also initiated detailed measurement and mapping and 3D laser scanning, laying a solid foundation for future restoration and display of cultural relics.
Source of news: http://www.china.org.cn