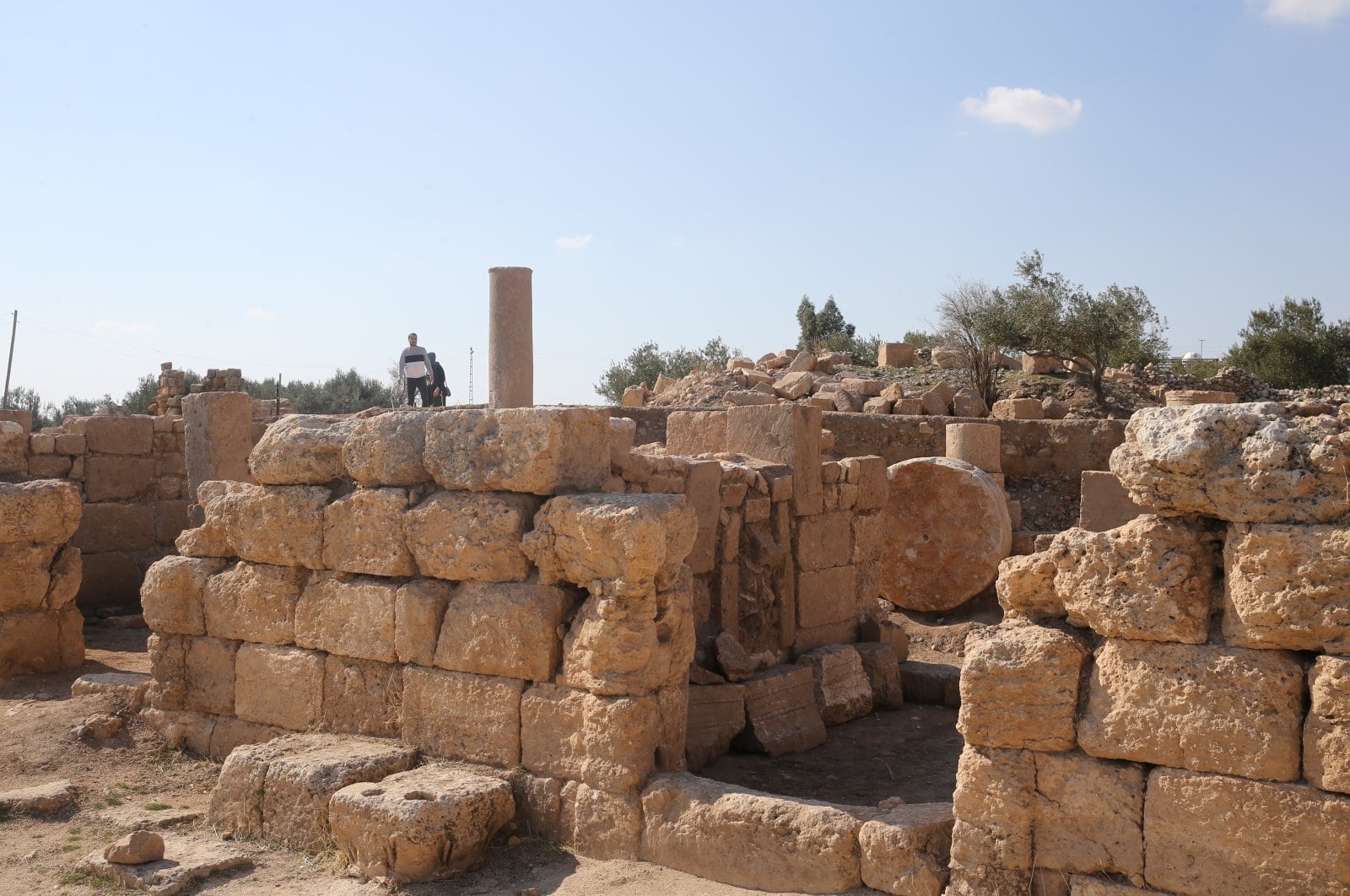
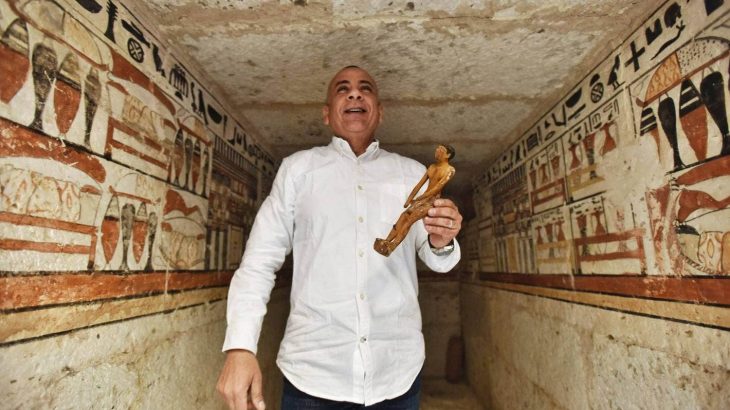
An olive workshop dating back to the 6th century was unearthed in the ancient city of Dara, one of the most important trade centers of ancient Mesopotamia in southeastern Turkey.
This new finding revealed that the historical site was an important olive production and trade center.
Excavations and research have been carried out for 34 years in Dara, in Oguz, Mardin, some 30 kilometers (19 miles) from the provincial center.
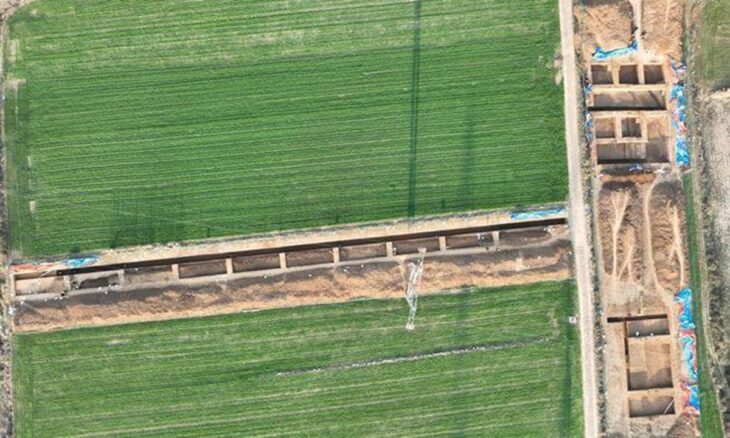
Excavations continue in the 5,000-year-old ancient city, with the support of the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, the Turkish Historical Society, Dicle Development Agency, Mardin Governorship, and Mardin Metropolitan Municipality under the direction of associate professor Hüseyin Metin of Kafkas University’s archeology department. During the recent digs, archaeologists found an olive workshop used in the city in ancient times.
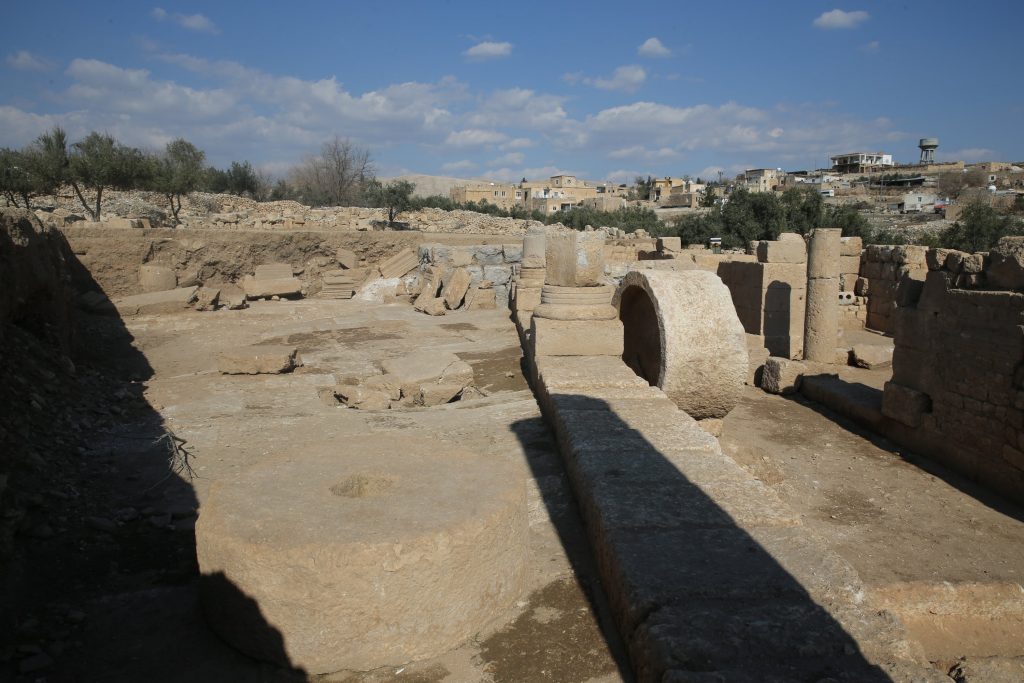

Associate professor Hüseyin Metin, the head of the excavations, said that they have revealed very important findings regarding the civil architectural structures in Dara with the studies they have conducted to date. One of these architectural structures is the olive oil workshop. “The olive oil workshop is one of the industries that had a very important place in ancient times,” Metin added.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Emphasizing that olive and olive oil were produced more in ancient times, Metin continued: “We think that the workshop was built because there were more wetlands here at these times and olives and olive oil had a great commercial return in that period. Oil was food and was also used as a lighting tool in ancient times. From here, we can deduce that olives in this workshop did not only meet the needs of the city but were also used commercially. Therefore, Dara was a place of olive production and trade. I believe that we will provide more detailed information about the extent of this trade with the excavations we carry out in the coming period.”

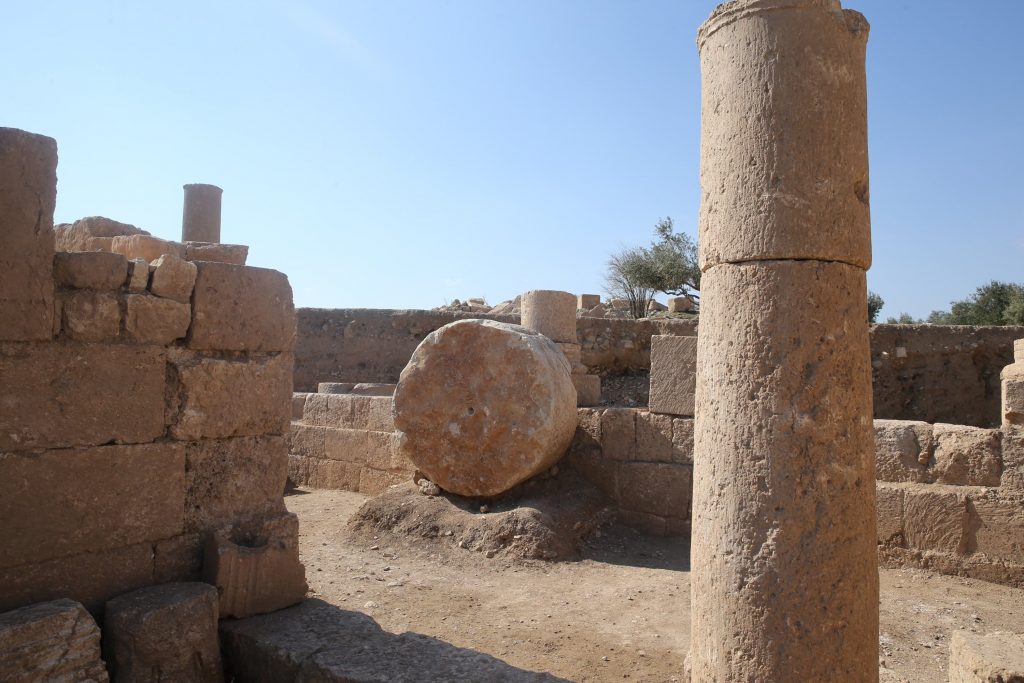
According to Metin, the only object unearthed in the workshop is a cylindrical olive crushing stone. “This is the first find for us in terms of olive oil production in Dara but we will probably reveal more traces.”
He informed that olives used to be brought here and then transferred in sacks to the crushing section where they were crushed with the big stone that they have unearthed. This process is similar to today’s mass production, according to Metin.
Noting that there are cracks in some parts of the stone, Metin continued: “After repairing them, we will now have one more material providing information about daily life in Dara. We will present them to visitors with promotional signs the next year.”

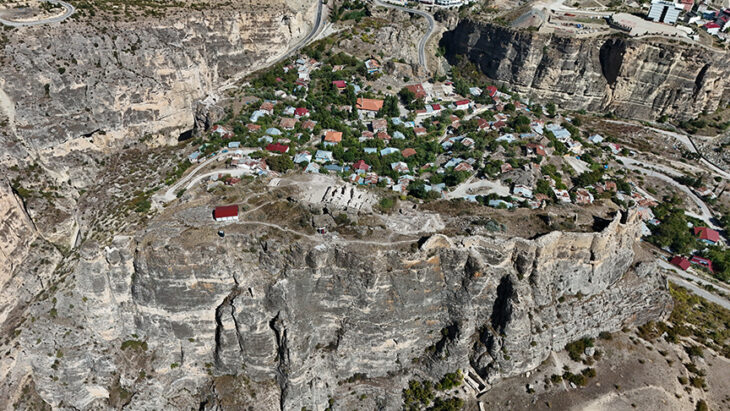
The ruins of the ancient city of Dara, featuring ancient rock tombs dating back to the fifth century A.D., are hailed as the “Ephesus of Mesopotamia.” Dara was an important settlement along the famed Silk Road. The Roman-era ancient city also boasts a popular necropolis where religious ceremonies were held and hundreds of people were laid to rest.
The ancient city, founded by the Eastern Roman Empire in order to protect their border against the Sasanian or Neo-Persian Empire, archaeological excavations began in 1986, but only some 10% of the area of an ancient village has been unearthed so far.
Over a period of 25 years, archaeological digs slowly revealed a monumental mass graveyard or necropolis.