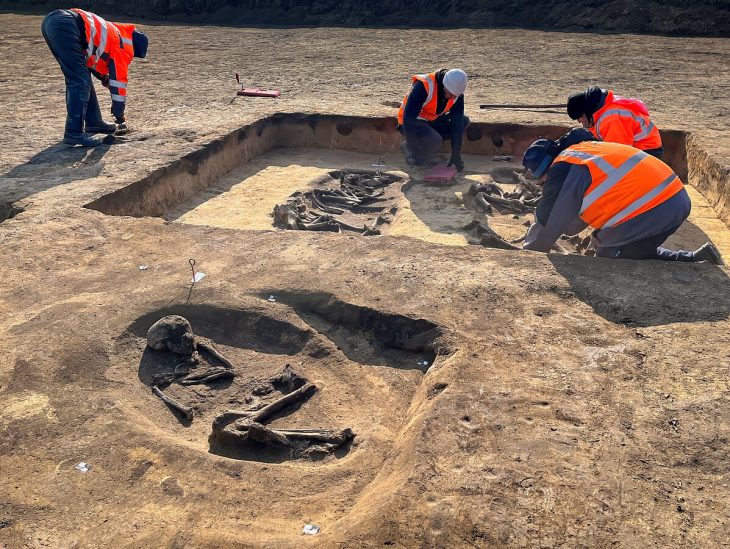
A modest Iron Age agricultural settlement excavated at Blainville-sur-Orne in Normandy, northwest France, led to the unexpected discovery of a vast Iron Age necropolis that had been in use for almost 300 years (from 540 to 250 BC).
Although inhumation was the most common mode of burial in the Necropolis, however, the discovery of several secondary cremation burials dating to the 4th century confirmed the coexistence of both types of burial.
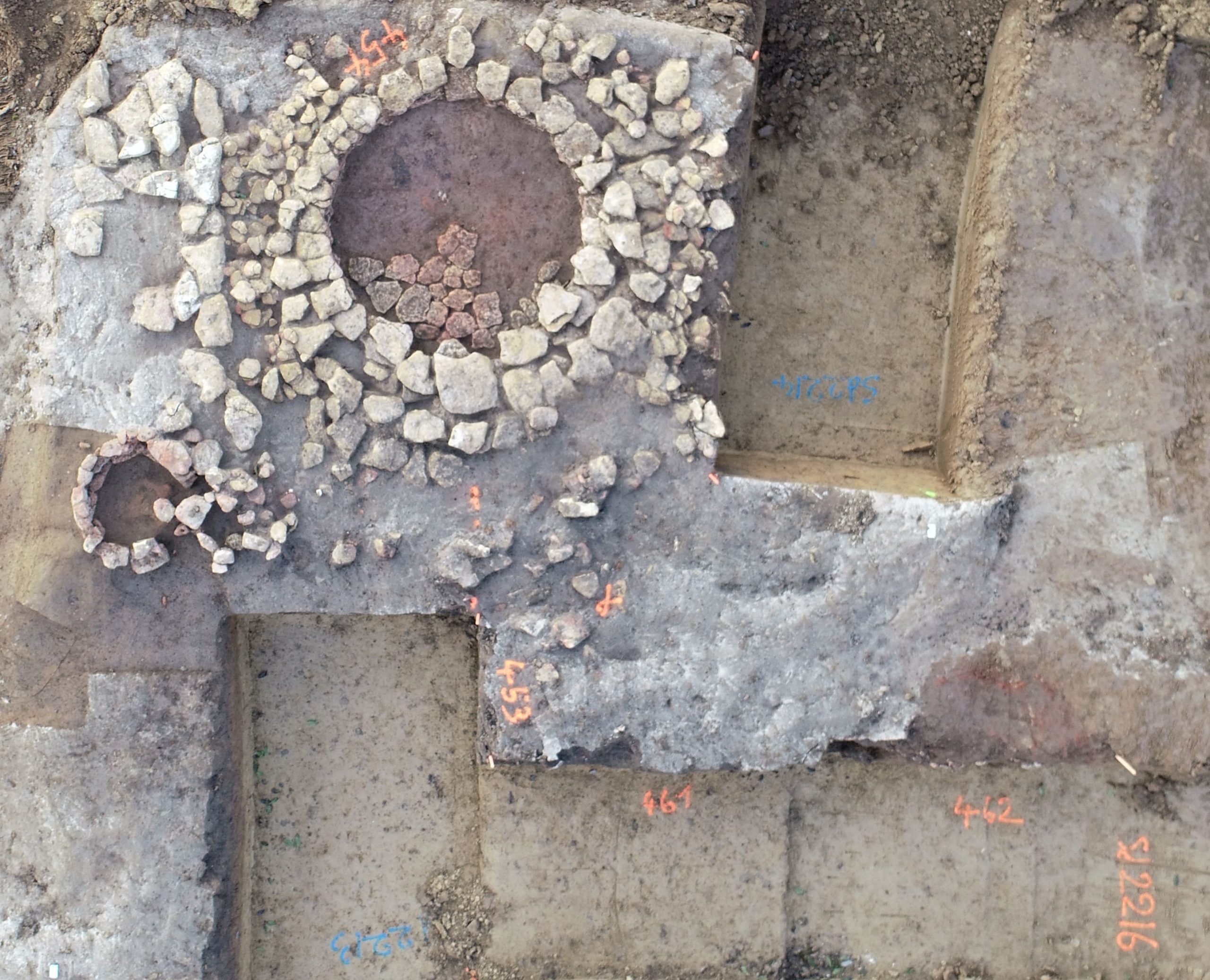
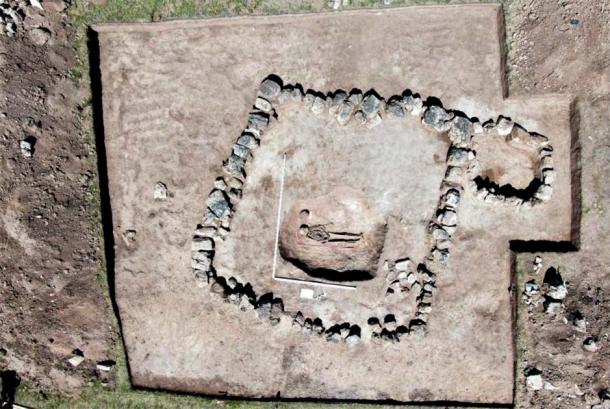
The necropolis consists of 121 inhumation graves, six cremation graves, and also found were two funerary enclosures, one square (10 m side) and the other rectangular (10 m x 13 m) with human remains in and around them.
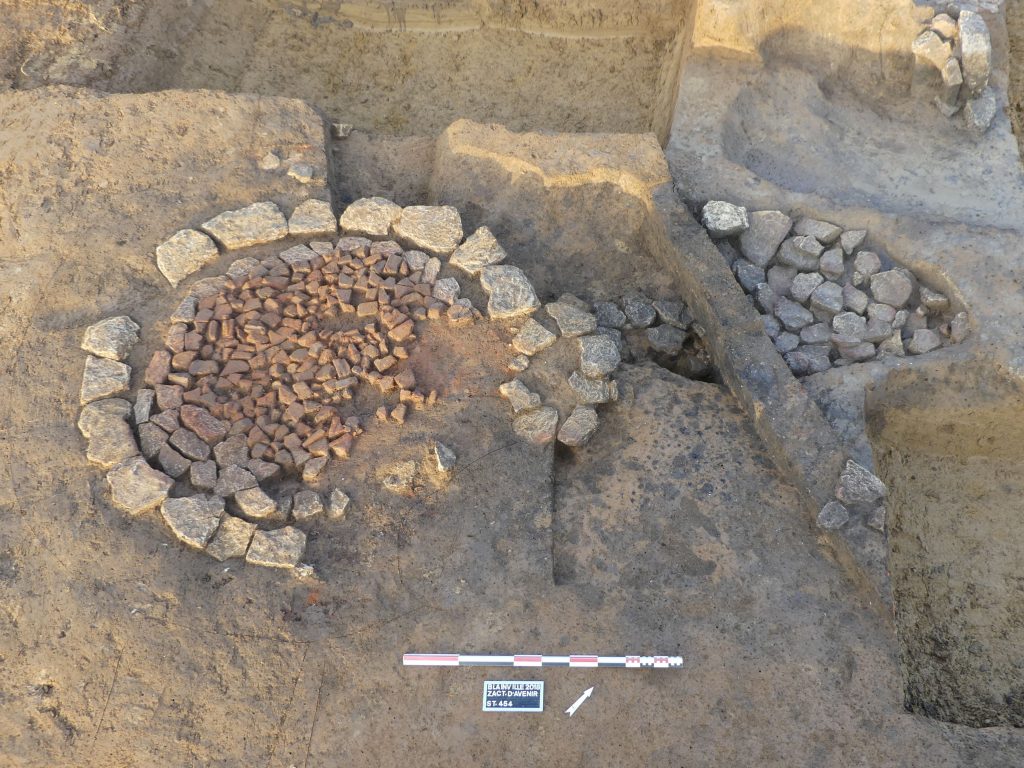

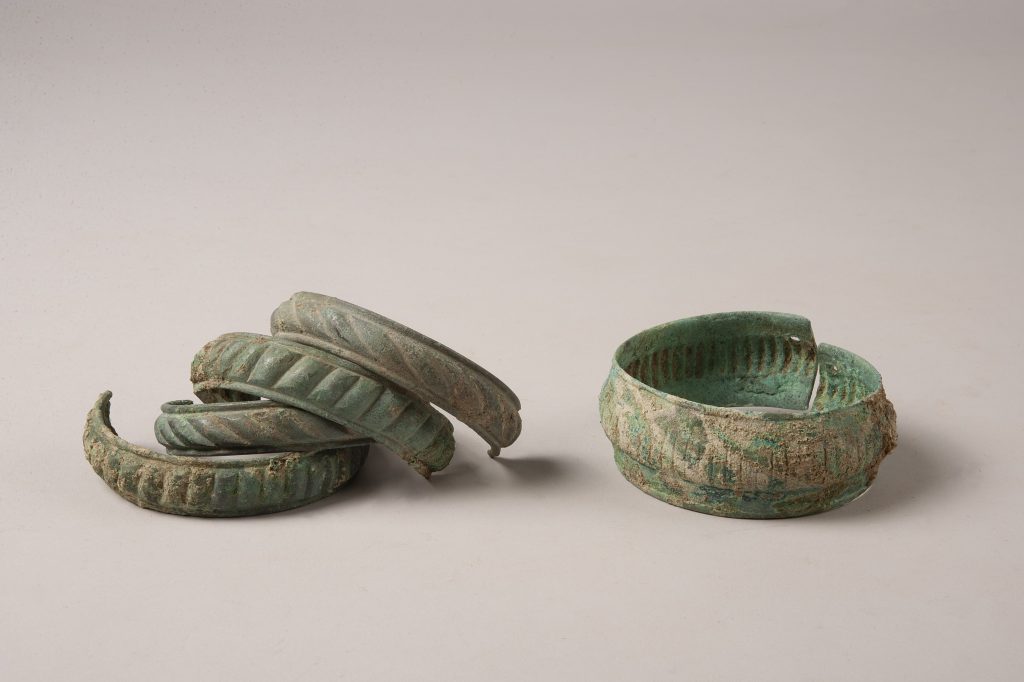
The inhumed individuals were for the most part buried in coffins or formwork built in a pit and were buried with copious metal jewelry (torques, bracelets, brooches, rings).
The Blainville-sur-Orne necropolis is similar in size to the important necropolises of the Caen Plain, such as Eterville (“Le clos des Lilas”) or Ifs (“Object’Ifs Sud”). Studies complement previous data on the practice of cremation, which was particularly poorly documented during the Gallic period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The agricultural use of this site increased later in the Iron Age, so until the 3rd century BC. the place was fenced off and dotted with storage pits for large crops. Analysis of plant debris in storage pits identified barley, millet, wheat, emmer, peas, and beans. The remains of cattle, goats, pigs, and sheep found in the fencing ditches testify to the diversity of cattle in the settlement. They were not the only sources of food. The shells of 33 species of marine invertebrates – clams, cockles, and oysters – point to settlers who relied on crustaceans for their staple food.

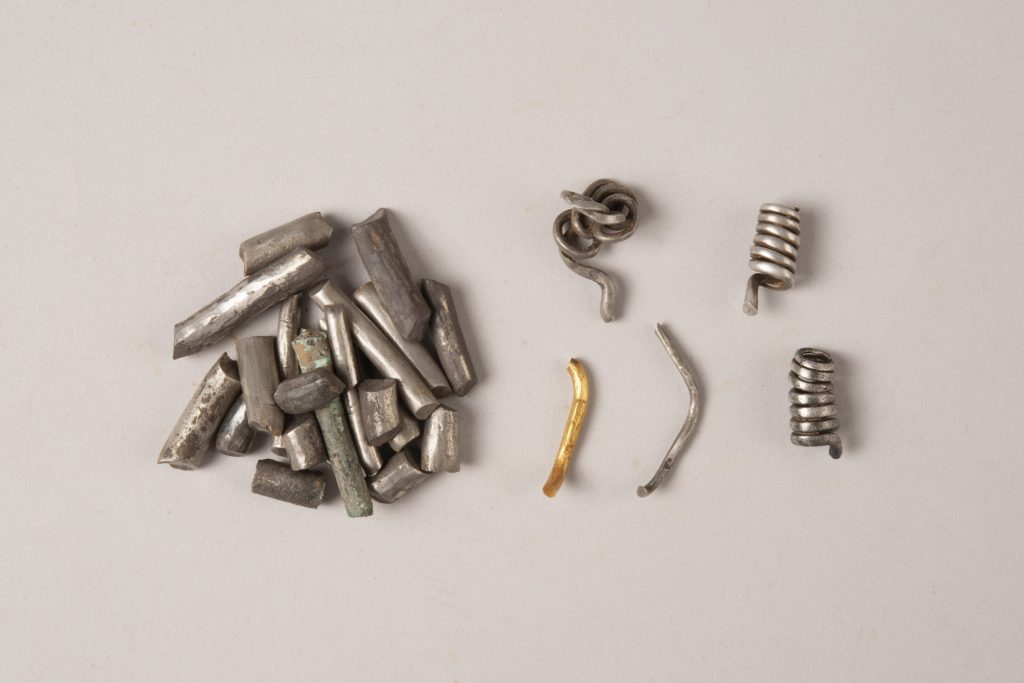
Finally, excavations have revealed evidence of metallurgical activities targeting both the settlement’s agricultural purposes (production and maintenance of tools such as plowshares) and artisanal activities (jewelry production). An extremely rare cache with 29 silver, gold, and copper alloy bars dating from 50-30 BC was found in one surrounding ditch. They were probably not intended for goldsmithing, but rather as a form of currency.

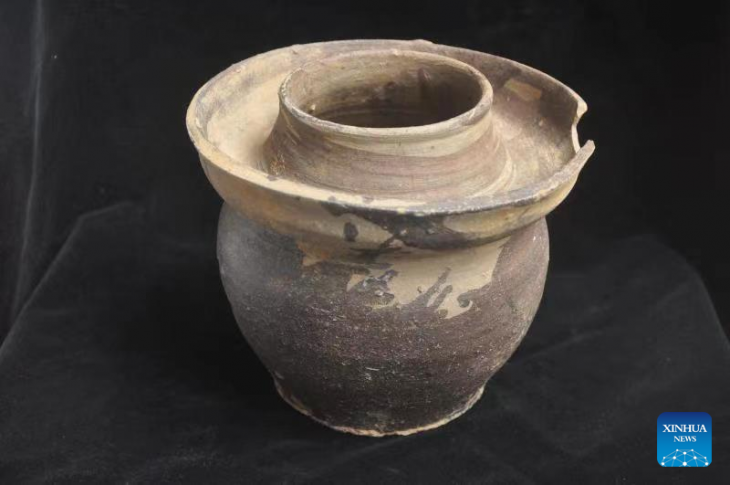
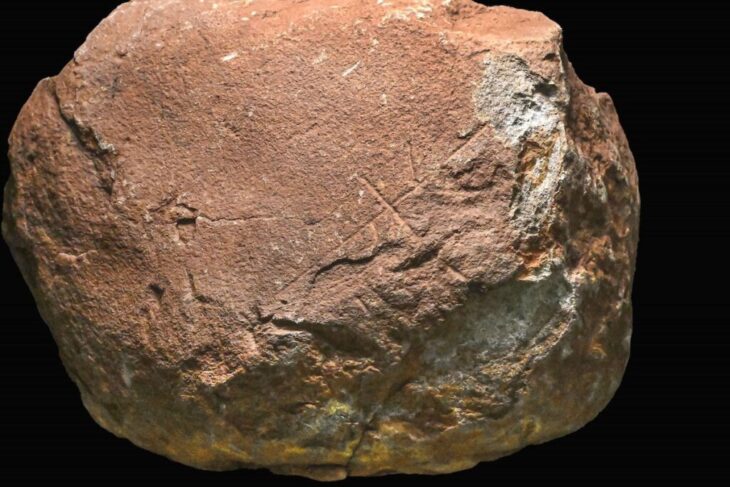
It is noteworthy that most of the items found in the necropolis are metal. Of the 167 objects unearthed, 101 are copper alloy jewelry. Ankle bracelets were widely used in the community. One individual was buried wearing a neck torc and ankle bracelets, all copper alloy. Thicker and more ornate specimens were found in other skeletons. One individual had an ankle bracelet made of lignite.
Cover Photo: Olivier Morin, Inrap