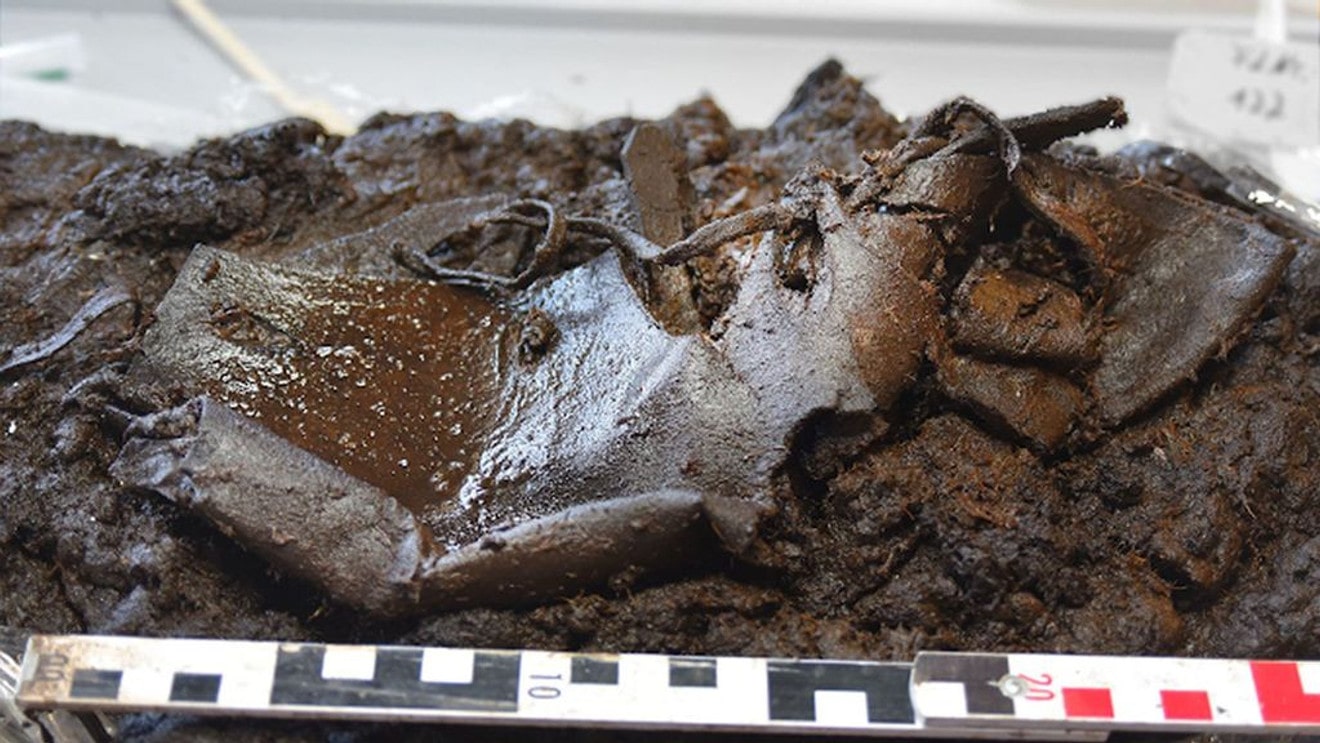
Archaeologists discovered a leather shoe that had been lost in a bog for 2,000 years and believe it may have fallen off the owner’s foot when they walked in the sticky muck by mistake.
The shoe was discovered alongside a wooden road estimated to be over two millennia old by researchers from the State Office for Monument Preservation in Lower Austria and the excavation company denkmal3D of Vechta, Germany.
The road is simply a collection of worn wooden planks that were originally placed over the wetlands to allow people to pass securely.
The wooden planks were put down to assist people to negotiate the marshes. In addition to the shoe, a broken axle was found, leading archeologists to believe that while changing it for a new one, the owner lost a shoe in the boggy ground.
Researchers who participated in the excavations think that the acidic conditions of the bog where the shoe was discovered allow for the preservation of materials such as skin, hair, nails, wool, and leather, all of which include the protein keratin.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The State Office for Monument Preservation reported that the shoe is a type of sandal, with a closed toe and a leather strap.
“Lower Saxony’s moorlands hold the testimonies of several thousands years of history,” said Lower Saxony Minister of Science and Culture Bjorn Thumle. “They are a unique archive, as they have not only preserved processed pieces and metal objects, but organic finds, too.”
‘The axle of a wooden cart, probably pulled by cattle, broke in two and the cart had an accident on the bumpy road,’ excavation company denkmal3D of Vechta, Germany, shared in a translated statement.
‘While doing this or trying to recover the car parts, the owner of the shoe fell or stepped beside the path and the shoe got stuck in the sticky mud.’
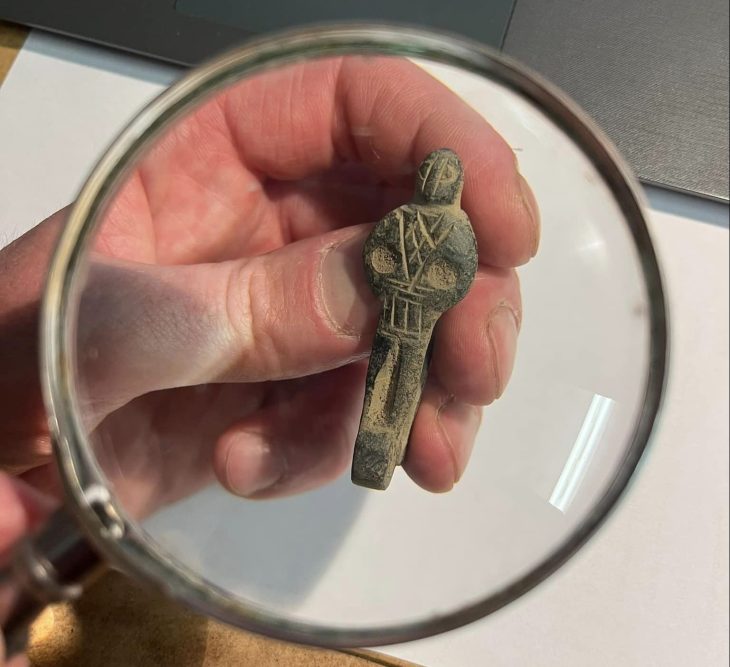
Lower Saxony’s Minister for Science and Culture, Björn Thümler said in the statement: ‘The best known are the bog corpses, but also wooden idols, long wooden paths and numerous other remnants of life at that time are part of it.’
‘A shoe that is lost and found again after 2,000 years, the oldest shoe from Lower Saxony to date, is an immensely personal testimony to a previous life.
The lone shoe resembles a sandal, with a closed toe and a leather strap connecting one side to the other.
As for the road itself, the archaic route between Lohne and Diepholz was built of wooden boards set next to each other for a distance of 2.5 miles (4 kilometers). The route, which is thought to date back to the Late Bronze Age, was unearthed in Lower Saxonian moorland in June 2019.
Cover Photo: (Niedersachsisches Landesamt fur Denkmalpflege (NLD):Zenger News)