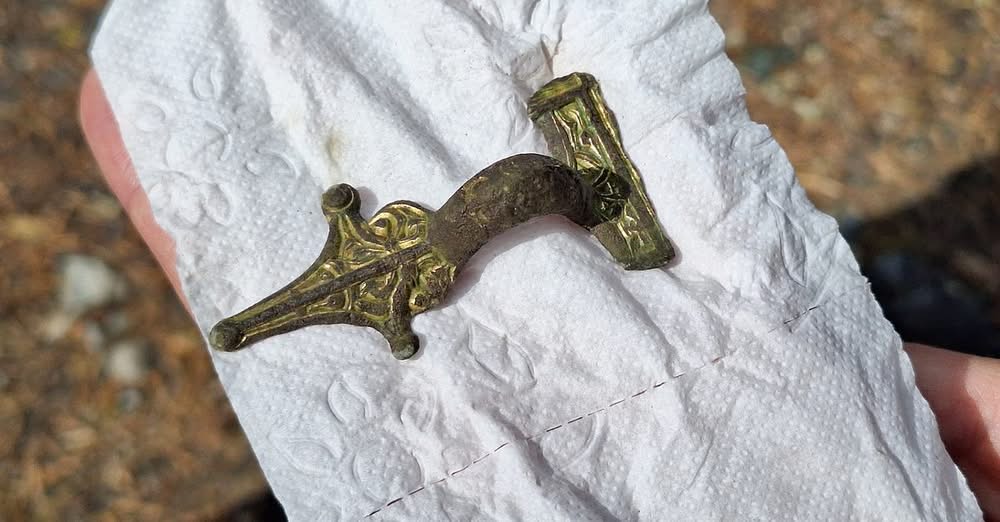
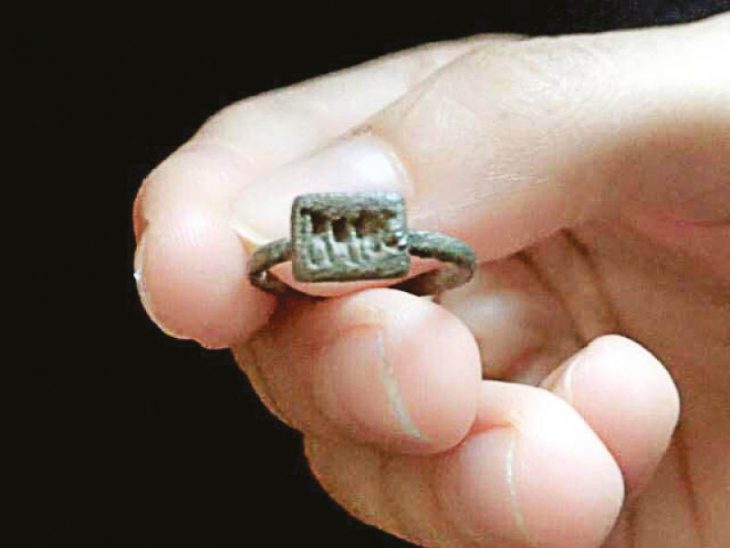
A remarkable archaeological discovery in the Finnish town of Kemi is offering fresh insights into the lives of elite women during the Iron Age. While casually using her metal detector, a local woman stumbled upon an intricately decorated brooch – a rare and culturally significant item now on display at the Tornedalen Museum.
The brooch, dating back to the later part of the Migration Period (approximately 475–550 AD), was used by high-status women to fasten their garments at the chest. More than a functional object, it served as a powerful symbol of wealth and social standing.
A Singular Find in Northern Finland
This brooch is no ordinary find. According to Finnish heritage officials, it represents only the second known artifact of its kind in Finland. The only comparable brooch with similar relief-style ornamentation was previously discovered in Rovaniemi, located further north.
What makes this discovery even more significant is the geographical context. Until now, no such finds have been documented in northern Sweden, and comparable artifacts have primarily been uncovered in central Sweden—particularly Hälsingland—and southern Norway. This suggests that the cultural influences and trade networks during the Migration Period extended much further north than previously believed.
“This find opens up entirely new perspectives on the Iron Age in Lapland and the Tornedalen region,” says Sami Raninen, an archaeologist and curator at the Finnish Heritage Agency.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Migration Period: A Time of Cultural Transformation
The Migration Period, spanning roughly from 375 to 568 AD, was marked by widespread movement of peoples across Europe—particularly Germanic tribes—following the decline of the Western Roman Empire. While it falls within the broader Iron Age, which was characterized by the use of iron tools and weapons, the Migration Period stands out as a distinct phase of intense cultural transformation, political upheaval, and shifting power structures.
These migrations significantly reshaped the political, cultural, and social landscapes of the continent, laying the groundwork for the early medieval era.

In northern Europe, this era saw the formation of complex societies and long-distance trade networks. Artifacts like the Kemi brooch not only reflect advanced craftsmanship but also hint at connections between distant communities, possibly through marriage alliances, trade, or elite networks.
The presence of such a high-status item in Finnish Lapland suggests that this northern region was not isolated but actively participating in broader Iron Age dynamics.
Responsible Discovery Matters
Authorities remind amateur metal detectorists that in Finland and Sweden, discovering ancient artifacts carries legal and ethical responsibilities. If you find an item that could be of historical value, it’s important to stop digging, avoid cleaning the object, and report the find to the appropriate authorities.
In Sweden, metal detecting is only allowed with a permit from the County Administrative Board (Länsstyrelsen), even on private land.
A Window into the Past
The brooch now housed at the Tornedalen Museum serves not only as a beautiful artifact but also as a critical piece of the puzzle in understanding the role of women in Iron Age society. These brooches, typically worn by women, offer archaeologists valuable clues about dress, identity, and societal structures of the time.
As more discoveries like this one come to light, researchers can continue to build a richer, more inclusive picture of life in northern Europe during the Migration Period—an era that helped shape the foundations of modern European cultures.
Cover Image Credit: Tornedalens Museum