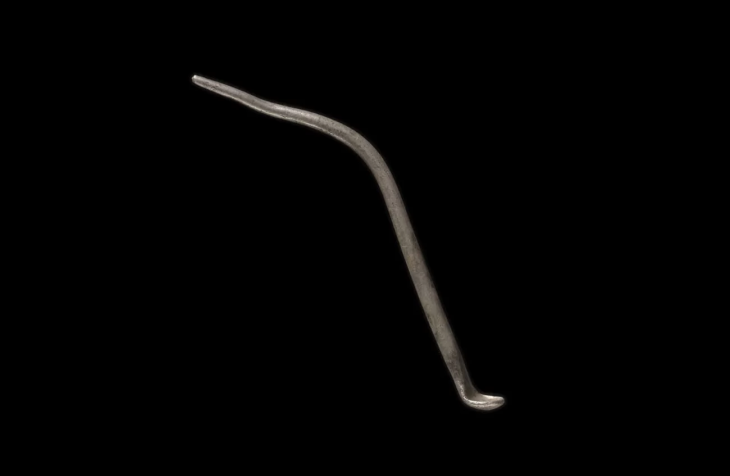
Archaeologists have discovered a rare 2,000-year-old oil lamp in David, Jerusalem.
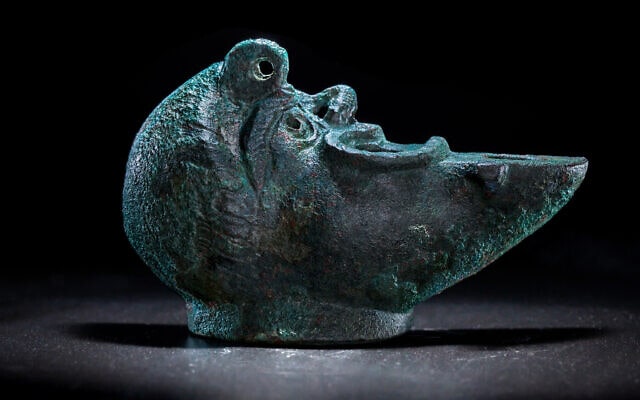
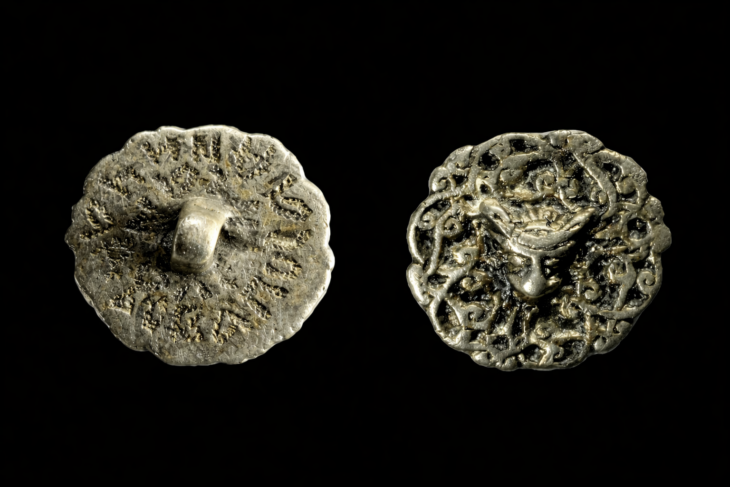
Archaeologists have discovered a rare oil lamp, shaped like a grotesque face cut in half, at the foundation of a building erected in Jerusalem’s City of David.
It is the first discovery of its kind in Israel and such works are very rare worldwide.
Israel Antiquities Authority researchers said in a statement Wednesday that they believe the bronze lamp was used as a foundation deposit — a ritual burial of an offering — to bring good fortune to the Roman Period building’s residents. It is estimated to be from the late 1st century or the early 2nd century CE.
The discovery, made on the Pilgrimage Road in the City of David, also contained the lamp’s wick, which was remarkably well-preserved.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Pilgrimage Road was used by Jewish pilgrims 2,000 years ago as they traveled to the Temple Mount, Judaism’s holiest spot.
“The offering of this lamp may attest to the importance of the building, which may have been linked to the protection of the Siloam Pool, the city’s primary water source,” said Dr. Yuval Baruch and Ari Levy, according to the IAA statement.

“This lamp is a very unique find, and as far as we know, the first of its kind discovered in Israel,” they were quoted as saying. “The uniqueness of the current object is that it is only half a face.”
The statement stated that the reason for this may have been practical — the lamp could have been fixed to a flat object or wall and used as a wall lamp — but the clarification stressed that the object’s primary use was ceremonial.
“Foundation deposits (offerings) were prevalent in the ancient world, and were intended for luck, and to ensure the continued existence of the building and its occupants, and they were usually buried under the floors of buildings or foundations,” the archaeologists said.
The lamp, according to the statement, was poured into a sculpted mold shaped like half of a bearded man’s face with a grotesque appearance. The lamp’s head is in the form of a crescent moon, and the handle is in the shape of an acanthus herb. The lamp’s decoration is reminiscent of a traditional Roman artistic motif, identical to a theatrical mask.
Researchers discovered the lamp’s wick, which was remarkably well-preserved after it was sent to an IAA laboratory. Dr. Naama Sukenik, curator of organic materials at the IAA, examined the wick, which is an extremely unusual discovery. She discovered that the wick was made of flax after microscopic analysis. Future analysis will look for some oil residue on the wick, which will help ascertain whether the lamp was used and, if so, what oil was used to light it.
“The building where the lamp was discovered was built directly on top of the Pilgrimage Road at the end of the Second Temple period,” said Ari Levy, director of the IAA excavations. “The construction of such a massive structure in the period after the destruction of Jewish Jerusalem demonstrates the importance of the area even after the destruction of the Second Temple.
Source: The Times Of Israel