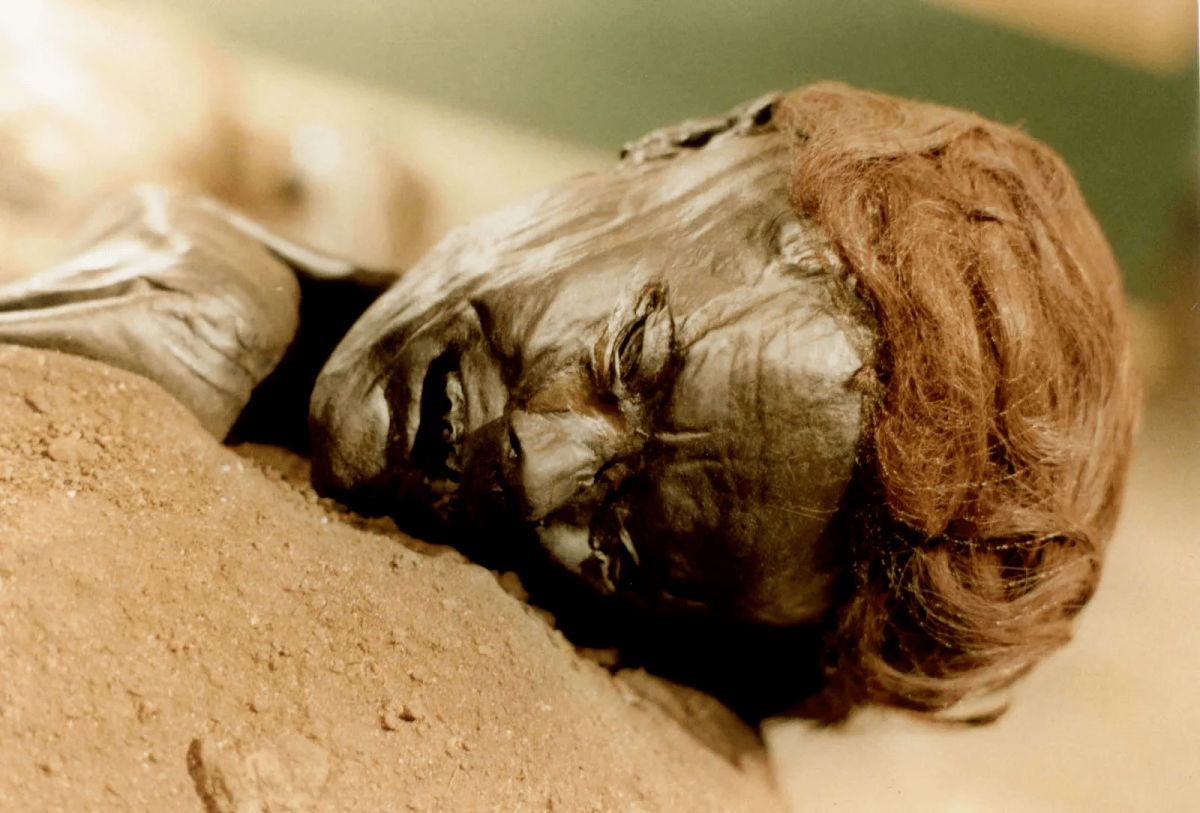
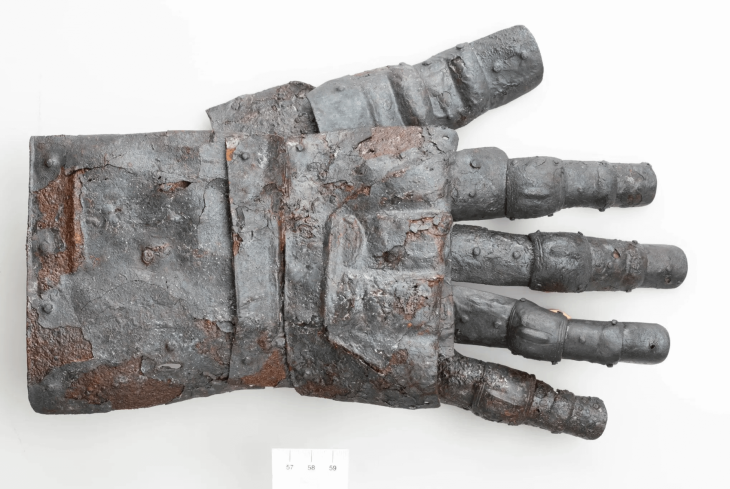
Archaeologists have studied hundreds of ancient “Bog Bodies” discovered in Europe’s wetlands, revealing that they were part of a millennia-old tradition. Besides new analysis shows the majority of these individuals met a ‘gruesome’ end before being intentionally discarded into the wet, spongy bogland.
Bog contains very little oxygen. This means that organic materials like wood, leather, textiles, and even, in some cases, human flesh do not rot.
The Koelbjerg Man from Denmark, who has been dated to 8000 BC during the Mesolithic period, is the oldest known bog body. People were buried in bogs as early as the prehistoric period. Many bog bodies are renowned for being remarkably well-preserved, including Yde Girl from the Netherlands, Tollund Man from Denmark, and Lindow Man from the United Kingdom.
In this study, the researchers examined the marsh skeleton and partial remains of bone, skin, soft tissue, and hair. Bog bodies, because of their high level of preservation, allow researchers to reconstruct aspects of an individual’s life in the distant past, such as their last meal from traces preserved in the stomach, or even the cause of death.
Archaeologists believe that many bog bodies were killed and dumped in the bogs as part of a widespread cultural tradition of human sacrifice, primarily during the Iron Age, because they share a number of characteristics, such as violent deaths and a lack of clothing.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr Roy van Beek, from Wageningen University in the Netherlands, said: ‘Literally thousands of people have met their end in bogs, only to be found again ages later during peat cutting.
‘The well-preserved examples only tell a small part of this far larger story.’
Examining all types of bog bodies reveals that they are part of a millennia-long, deep-rooted tradition, the researchers said.
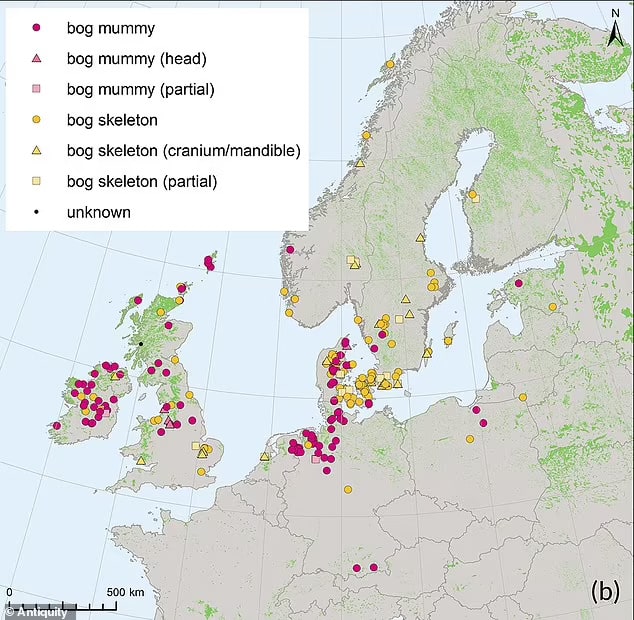
The research revealed that the bog body practice is part of a millennia-old, deeply rooted tradition. The phenomenon begins in southern Scandinavia around 5000 BC during the Neolithic period and gradually spreads across Northern Europe. The most recent discoveries, from Ireland, the United Kingdom, and Germany, show that the tradition persisted into the Middle Ages and early modern times.
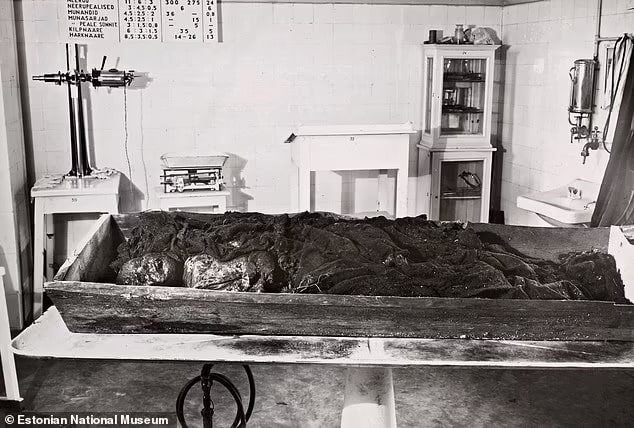

The majority of those whose causes of death could be determined appear to have met a horrifying end and were probably left in bogs on purpose. This violence is frequently perceived as victims of violence, criminals who have been executed, or ritual sacrifices. However, in the last few centuries, written sources indicate there were a significant number of accidental deaths in bogs, as well as suicides.
Writing in the journal Antiquity, Doctor van Beek said: ‘Setting aside accidental deaths, the significant evidence for violent deaths and a large number of repeatedly used sites make it safe to assume that most finds of human remains…reflect intentional depositions.’
The study also discovered that bog body hotspots can be identified in wetlands where the remains of multiple people have been discovered. In some cases, these discoveries are the result of a single act, such as the mass burial of battle dead. Other bogs were used on multiple occasions, and the human remains were accompanied by a variety of other objects interpreted as ritual offerings, ranging from animal bones to bronze weapons or ornaments.
“All in all, the fascinating new picture that emerges is one of an age-old, diverse and complex phenomenon, that tells multiple stories about major human themes like violence, religion and tragic losses,” said Doctor van Beek.
This study published in the journal Antiquity by an international team of Dutch, Swedish, and Estonian researchers examined over 1000 remains from 266 sites across Europe.
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2022.163
Cover Photo: Grauballe Man. Sven Rosborn