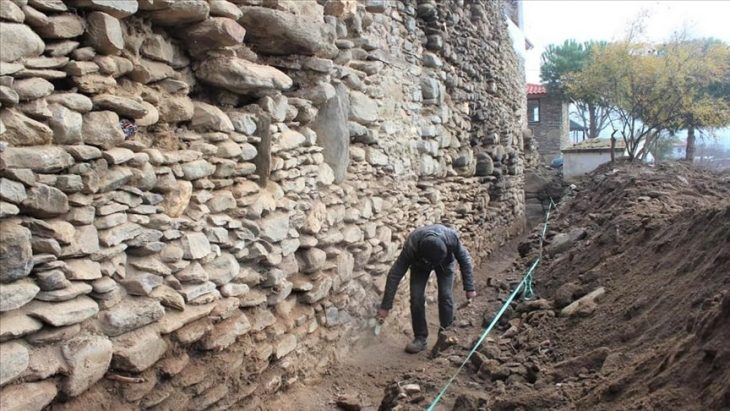
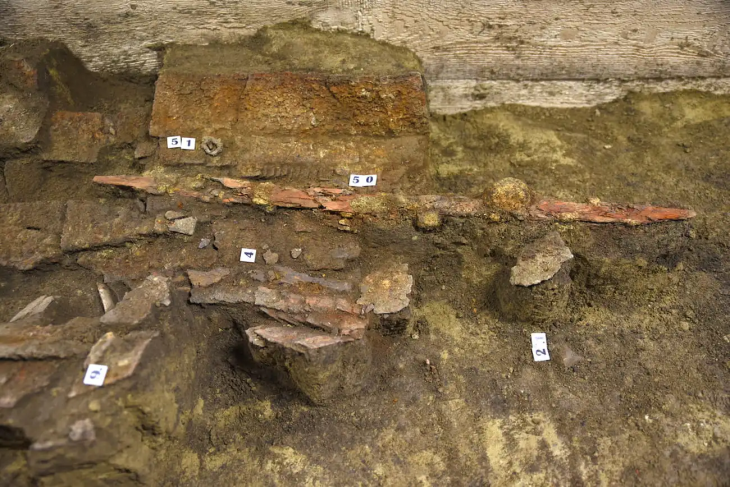
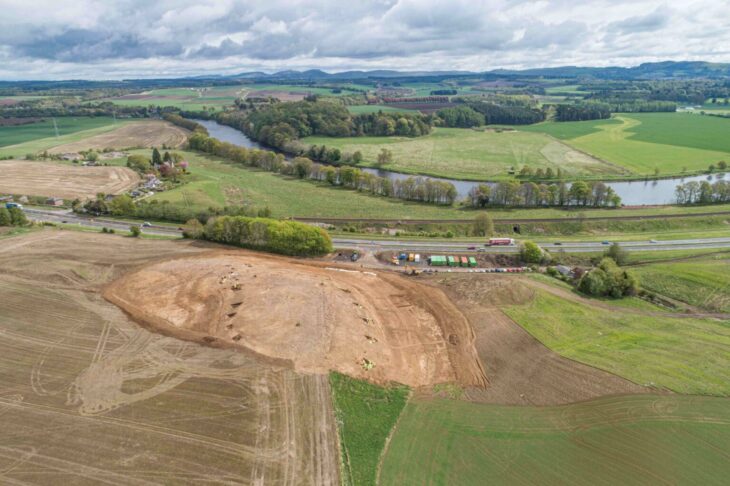
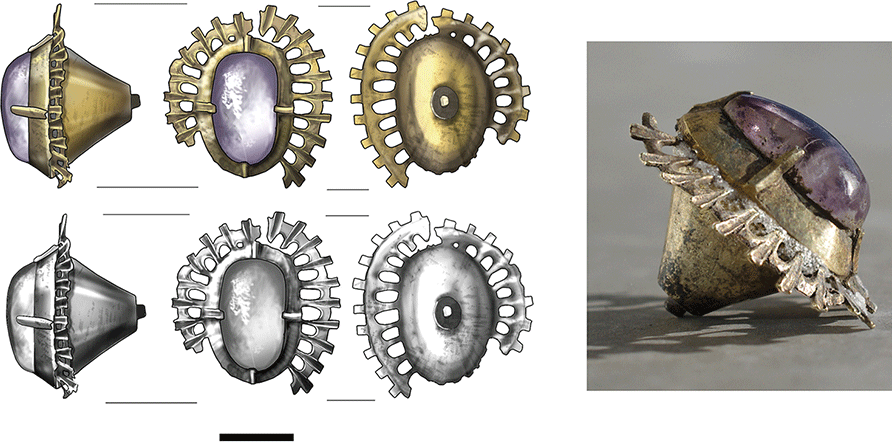
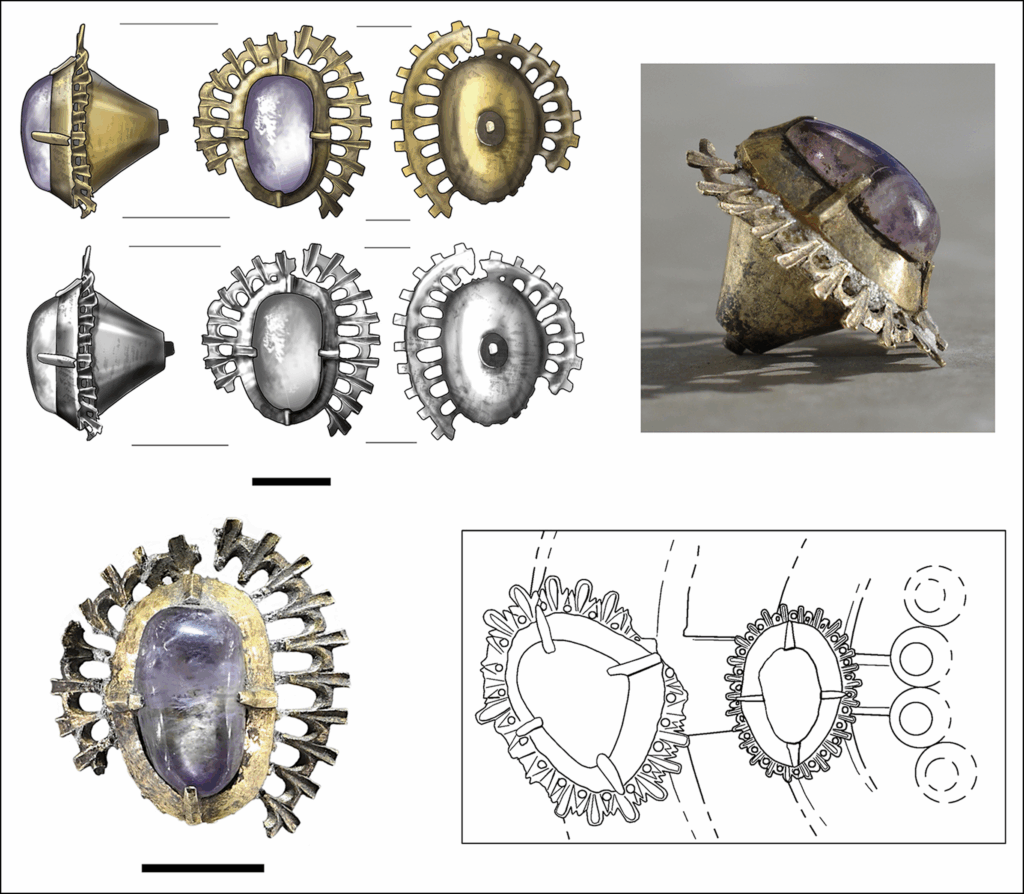
A remarkable archaeological discovery from the moat of Castle Kolno in Poland is offering fresh insight into medieval aristocratic culture and luxury consumption. Researchers from the University of Wrocław have uncovered an ornate silver-gilt amethyst jewel that once formed part of a larger brooch—an extremely rare find in a settlement context and a rare glimpse into the lifestyle of Europe’s medieval elite.
The jewel, found during systematic excavations at the historic ducal stronghold, stands out not only for its craftsmanship but also for the unique circumstances of its loss. While precious metal jewellery is typically recovered from hoards or elite burials, discovering such an artefact in everyday-use layers is unusual. This particular piece was recovered from sediments accumulated between timber bridge posts at the northern crossing of the castle moat. Its location suggests it may have been lost by someone traveling to or from the fortress during the early 14th to mid-15th century.
A Jewel Fit for a Duke
Castle Kolno originally functioned as a ducal customs point on the medieval border between the duchies of Opole and Brzeg. Its first documented owner, Duke Bolesław III of Brzeg, and subsequent noble residents would have hosted high-ranking visitors. The jewel’s quality reflects this elite environment: an amethyst cabochon set in a conical silver claw mount, surrounded by an intricate halo of openwork rays or palmette petals—decorative elements associated with international luxury fashion of the 13th century.
The craftsmanship is consistent with the period’s aristocratic jewellery, comparable to high-status objects such as the coronets of Wawel Castle in Kraków, the brooch from the famed treasure of Środa Śląska, and the luxurious medieval adornments held in the Cathedral Treasury of Split.
High-Tech Scientific Analysis Reveals More
To determine its composition and manufacturing technique, the research team conducted advanced non-destructive analyses, including X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and scanning electron microscopy paired with energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS). These tests confirmed that the artifact was produced from silver and enhanced with fire-gilding—a sophisticated process where gold is applied using mercury. Elevated mercury signatures detected in the spectra support this conclusion.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Microscopic examination also revealed traces of lead solder and a silver pin on the back, evidence that the jewel was originally attached to a larger ornamental structure, likely a luxurious brooch worn by an aristocrat.
Luxury, Symbolism, and Status in Medieval Society
While today jewellery is primarily decorative, in the medieval world it carried layers of meaning—economic, social, and symbolic. Scholars emphasize that analysing luxury artifacts helps reconstruct patterns of social identity and consumption. In this context, the jewel from Castle Kolno serves as a tangible indicator of aristocratic presence and the display of wealth.
The medieval nobility often expressed status through objects that were economically unnecessary but symbolically powerful. Theories of “conspicuous consumption,” first articulated by economist Thorstein Veblen, help explain why such items proliferated among elites. Precious jewellery, even when not strictly functional, communicated lineage, power, and allegiance.
But medieval gemstones also held spiritual significance. The amethyst, in particular, was believed to protect its wearer from intoxication, venom, bad dreams, betrayal, and enchantment. Literature from the period often references magical jewels, including Arthurian romances where gemstones offer protection in battle. Such beliefs suggest that the jewel’s value extended far beyond its aesthetic appeal.
A Unique Glimpse Into Medieval Life
The jewel’s presence at Castle Kolno highlights the blend of practicality, prestige, and belief systems governing medieval society. Its accidental loss—rather than deliberate deposition—makes it even more valuable archaeologically, offering an unfiltered snapshot of daily life among high-status individuals frequenting the castle.
Although the fortress was ultimately destroyed in 1443, its moat preserved this exceptional artifact for centuries. Today, the jewel serves as a miniature time capsule, illuminating the luxurious tastes, cultural symbolism, and social dynamics of medieval Poland.
As research continues, the find underscores how even a single misplaced object can reshape our understanding of the past. For archaeologists, Castle Kolno’s jewel is not just a decorative piece—it is a rare, glittering key to the world of medieval aristocracy.
Marek, L., & Miazga, B. (2025). A jewel worthy of a duke from the moat of Castle Kolno. Antiquity, 99(407), e45. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.10097
Cover Image Credit: Marek & Miazga (2025), Antiquity